Abstract
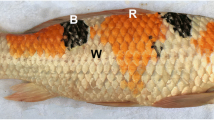
Botia superciliaris, an endemic cobitid fish in China, is widely accepted by Chinese consumers because its edibility. Recently, the black and yellow stripes of B. superciliaris skin have made this species increasingly popular as a novel ornamental fish. However, the genetic basis of the stripe patterns in B. superciliaris skin has not been extensively studied. In this study, Illumina sequencing was employed to identify the mRNAs and miRNAs involved in stripe pattern formation in B. superciliaris skin. A total of 147.25 and 155.15 million (M) high-quality transcriptome reads were generated from three black and yellow skin libraries respectively, which resulted in 159,327 unigenes that were used as reference sequences. A total of 3169 genes exhibited significantly differential expression patterns (fold-change ≥ 2 or ≤ 0.5 and q ≤ 0.05), including 1891 upregulated genes (59.67%) and 1278 downregulated genes (40.33%) in black vs yellow skin. These genes were enriched in 50 GO terms and 10 KEGG pathways (q ≤ 0.05), including melanogenesis, with 21 upregulated genes and 5 downregulated genes in black vs yellow skin. Based on the zebrafish genome, miRNA-seq identified a total of 355 miRNAs, which included 38 novel miRNAs. Furthermore, 87 differentially expressed miRNAs including 50 upregulated and 37 downregulated miRNAs were identified in different color skin (fold-change ≥ 2 or ≤ 0.5 and q ≤ 0.05). Then, target prediction revealed a variety of putative target genes; differentially expressed mRNAs and miRNAs patterns of high-throughput sequencing were validated in 5 mRNAs and miR-217-5p by qRT-PCR. In vivo tests and dual-luciferase reporter assay revealed that overexpression of miR-217-5p can inhibit pheomelanin formation by targeting Zgc. In this study, a comparative analysis was conducted to profile the transcriptome of black and yellow skin for B. superciliaris, and we detected key genes and important miRNAs involved in the B. superciliaris skin pigmentation process. These results will enhance understanding of molecular mechanisms underlying skin pigmentation and facilitate molecular-assisted selection of highly valued skin colors.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DE genes:
-
differentially expressed genes
- DE miRNA:
-
differentially expressed miRNA
- Nr:
-
non-redundant protein database
- COG:
-
Cluster of Orthologous Groups of proteins
- GO:
-
Gene Ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- qPCR:
-
quantitative polymerase chain reaction
References
Altschmied J, Delfgaauw J, Wilde B, Duschl J, Bouneau L, Volff JN, Schartl M (2002) Subfunctionalization of duplicate mitf genes associated with differential degeneration of alternative exons in fish. Genetics 161:259–267
Berson JF, Harper DC, Tenza D, Raposo G, Marks MS (2001) Pmel17 initiates premelanosome morphogenesis within multivesicular bodies. Mol Biol Cell 12:3451–3464
Bin HE, Chen XJ, Wen T, Long ZH, Meng-Jun LI (2014) Embryonic development of Botia superciliaris Southwest China. J Agric Sci 27:1332–1336
Braasch I, Liedtke D, Volff JN, Schartl M (2009) Pigmentary function and evolution of tyrp1 gene duplicates in fish. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 22:839–850
Braasch I, Schartl M, Volff JN (2007) Evolution of pigment synthesis pathways by gene and genome duplication in fish. BMC Evol Biol 7:74
Budi EH (2011) The role of ErbB3 in adult pigment cell development dissertations & theses - gradworks
Chun-Tao LI, Zhu CK, Wang ZJ (2011) The primary studies on the structure of digestive duct in Botia superciliaris. J Southwest China Normal Univ 36:144–149
Chung SY, Seo YK, Park JM, Seo MJ, Park JK, Kim JW, Park CS (2009) Fermented rice bran downregulates MITF expression and leads to inhibition of alpha-MSH-induced melanogenesis in B16F1 melanoma. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:1704–1710
Citri A, Skaria KB, Yarden Y (2003) The deaf and the dumb: the biology of ErbB-2 and ErbB-3. Exp Cell Res 284:54–65
Ginger R et al (2008) SLC24A5 encodes a trans-Golgi network protein with potassium-dependent sodium-calcium exchange activity that regulates human epidermal melanogenesis. J Biol Chem 283:5486–5495
Guarneri F, Asmundo A, Sapienza D, Cannavò SP (2011) Glutathione S-transferase M1/T1 gene polymorphisms and vitiligo in a Mediterranean population. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 24:731–733
Guo J, Zhang JF, Wang WM, Cheung FWK, Lu YF, Ng CF, Kung HF, Liu WK (2014) MicroRNA-218 inhibits melanogenesis by directly suppressing microphthalmia-associated transcription factor expression. RNA Biol 11:732–741
Henning F, Jones JC, Franchini P, Meyer A (2013) Transcriptomics of morphological color change in polychromatic Midas cichlids. BMC Genomics 14:171–171
Hubbard JK, Uy JA, Hauber ME, Hoekstra HE, Safran RJ (2010) Vertebrate pigmentation: from underlying genes to adaptive function. Trends Genet 26:231–239
Jiang Y, Zhang S, Xu J, Feng J, Mahboob S, al-Ghanim KA, Sun X, Xu P (2014) Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals the genetic basis of skin color variation in common carp. PLoS One 9:e108200
Kedam TR, Chittoor P, Kurumala D (2017) Glutathione- S -Transferases
Kelsh RN et al (1996) Zebrafish pigmentation mutations and the processes of neural crest development. Development 123:369
Kelsh RN, Inoue C, Momoi A, Kondoh H, Furutani-Seiki M, Ozato K, Wakamatsu Y (2004) The Tomita collection of medaka pigmentation mutants as a resource for understanding neural crest cell development. Mech Dev 121:841–859
Kennell JA, Cadigan KM, Shakhmantsir I, Waldron EJ (2012) The microRNA miR-8 is a positive regulator of pigmentation and eclosion in Drosophila. Dev Dyn 241:161–168
Kondo S, Iwashita M, Yamaguchi M (2009) How animals get their skin patterns: fish pigment pattern as a live Turing wave. Int J Dev Biol 53:851–856
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL (2009) Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10:R25
Li S, Wang C, Yu W, Zhao S, Gong Y (2012) Identification of genes related to White and black plumage formation by RNA-Seq from white and black feather bulbs in ducks. PLoS One 7:e36592
Lu L, Wu W, Tu Y, Yang Z, He L, Guo M (2014) Association of glutathione S-transferase M1/T1 polymorphisms with susceptibility to vitiligo. Gene 535:12–16
Ng’Oma E, Groth M, Ripa R, Platzer M, Cellerino A (2014) Transcriptome profiling of natural dichromatism in the annual fishes Nothobranchius furzeri and Nothobranchius kadleci. BMC Genomics 15:754
Noguchi S, Kumazaki M, Yasui Y, Mori T, Yamada N, Akao Y (2014) MicroRNA-203 regulates melanosome transport and Tyrosinase expression in melanoma cells by targeting kinesin superfamily protein 5b. J Investig Dermatol 134:461–469
Pabst MJ, Habig WH, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferase a. a novel kinetic mechanism in which the major reaction pathway depends on substrate concentration. J Biol Chem 249:7140
Parichy DM (2006) Evolution of danio pigment pattern development. Heredity 97:200–210
Pasello M, Manara MC, Michelacci F, Fanelli M, Hattinger CM, Nicoletti G, Landuzzi L, Lollini PL, Caccuri A, Picci P, Scotlandi K, Serra M (2011) Targeting glutathione-S transferase enzymes in musculoskeletal sarcomas: a promising therapeutic strategy. Anal Cell Pathol 34:131–145
Protas ME, Patel NH (2008) Evolution of coloration patterns. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 24:425–446
Qiang LI, Yao MY, Zhou B, Chen XJ, Long ZH, Zhou CJ, Meng-Jun LI (2011) Technique of artificial reproduction of Botia superciliaris Günther freshwater fisheries.
Robinson MD, Mccarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2009) edgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26:139
Rodgers GM, Kelley JL, Morrell LJ (2010) Colour change and assortment in the western rainbowfish. Anim Behav 79:1025–1030
Senjo M, Ishibashi T (2017) Specific localization of glutathione S-transferases in astrocytes and ependymal cells of rat brain: immunocytochemical demonstration. Biomed Res 6:433–436
Suzuki I, Tada A, Ollmann MM, Barsh GS, Im S, Lynn Lamoreux M, Hearing VJ, Nordlund JJ, Abdel-Malek ZA (1997) Agouti signaling protein inhibits melanogenesis and the response of human melanocytes to alpha-melanotropin. J Investig Dermatol 108:838–842
Vlachos IS et al (2015) DIANA-miRPath v3.0: deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res 43:460–466
Yan B, Liu B, Zhu CD, Li KL, Yue LJ, Zhao JL, Gong XL, Wang CH (2013) microRNA regulation of skin pigmentation in fish. J Cell Sci 126:3401–3408
Yang ZY, Liang HW, Li Z, Wang XY, Zou GW (2013) Mitochondrial genome sequence of the Botia superciliaris (Teleostei, Cypriniformes). Mitochondrial DNA 24:347–349
Yuwen L, Jie Z, White KP (2014) RNA-seq differential expression studies: more sequence or more replication? Bioinformatics 30:301
Zamore PD, Tuschl T, Sharp PA, Bartel DP (2000) RNAi: double-stranded RNA directs the ATP-dependent cleavage of mRNA at 21 to 23 nucleotide intervals. Cell 101:25–33
Zhu W, Wang L, Dong Z, Chen X, Song F, Liu N, Yang H, Fu J (2016) Comparative transcriptome analysis identifies candidate genes related to skin color differentiation in red tilapia. Sci Rep 6:31347
Zhu Z, He J, Jia X, Jiang J, Bai R, Yu X, Lv L, Fan R, He X, Geng J, You R, Dong Y, Qiao D, Lee KB, Smith GW, Dong C (2010) MicroRNA-25 functions in regulation of pigmentation by targeting the transcription factor MITF in alpaca (Lama pacos) skin melanocytes. Domest Anim Endocrinol 38:200–209
Funding
This work was financially supported by Breeding Technology and Large- scale Farming Technology for Research and Demonstration of Botia superciliaris (2016ZYPZ027). This research was also supported by the “Double Support Project” fund of Sichuan Agricultural University (SICAU, No. 03573018; No. 03572013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jian Zhou, Jideng Ma, Han Zhao, and Song Yang designed the experiment and wrote the manuscript. Lu Zhang, Can Liu, Siyuan Feng, and Yingkai Liu carried out the experiments data organization and statistical analyses. Qiang Li, Hongyu Ke, Xinyu Wang, and Lingyan Liu provided the experimental samples. Chao Liu and Xutao Su participated in the study design and discussed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(XLS 423 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Zhao, H., Zhang, L. et al. Integrated analysis of RNA-seq and microRNA-seq depicts miRNA–mRNA networks involved in stripe patterns of Botia superciliaris skin. Funct Integr Genomics 19, 827–838 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-019-00683-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-019-00683-2