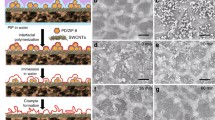
Abstract
Nanofiltration has been attracting great attention in alleviating the global water crisis because of its high efficiency, mild operation, and strong adaptability. Over decades, it remains a challenge to break the upper limit of performance and establish the formation-structure-property relationship for nanofiltration membranes. This feature article summarizes our recent progress in the preparation of high-performance thin-film composite (TFC) nanofiltration membranes, focusing on the mussel-inspired deposition method and the optimized interfacial polymerization (IP). By accelerating the oxidation of polydopamine and equilibrating the rate of aggregation and deposition processes, the mussel-inspired deposition method realizes the rapid and uniform formation of selective coatings or nanofilms. Diverse deposition systems endow the selective layer with rich chemical structures and easy post-functionalization, highlighting its potential in water treatment. As for optimizing the conventional IP, the rapid polycondensation of amine and acid chloride groups is slowed down to enable the controllability of IP at the water-organic interface. The homogeneity and integrity of the TFC membranes are improved by constructing a uniform reaction platform and introducing a viscous medium to control the amine diffusion, which facilitates the water permeability and promotes the separation efficiency. We have proposed a series of practical strategies for improving TFC membranes and might provide more inspiration for other nanofiltration techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lim, Y. J.; Goh, K.; Kurihara, M.; Wang, R. Seawater desalination by reverse osmosis: current development and future challenges in membrane fabrication—a review. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 629, 119292.
Liang, H. Q.; Hung, W. S.; Yu, H. H.; Hu, C. C.; Lee, K. R.; Lai, J. Y.; Xu, Z.-K. Forward osmosis membranes with unprecedented water flux. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 47–54.
Chowdhury, M. R.; Steffes, J.; Huey, B. D.; McCutcheon, J. R. 3D printed polyamide membranes for desalination. Science 2018, 361, 682–686.
Shannon, M. A.; Bohn, P. W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J. G.; Mariñas, B. J.; Mayes, A. M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310.
Qiu, Z. L.; Fang, L. F.; Shen, Y. J.; Yu, W. H.; Zhu, B. K.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Zhang, W. Ionic dendrimer based polyamide membranes for ion separation. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7522–7535.
Marchetti, P.; Jimenez Solomon, M. F.; Szekely, G.; Livingston, A. G. Molecular separation with organic solvent nanofiltration: a critical review. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10735–10806.
Ding, Y.; Weng, L. T.; Yang, M.; Yang, Z.; Lu, X.; Huang, N.; Leng, Y. Insights into the aggregation/deposition and structure of a polydopamine film. Langmuir 2014, 30, 12258–12269.
Mohammad, A. W.; Teow, Y. H.; Ang, W. L.; Chung, Y. T.; Oatley-Radcliffe, D. L.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration membranes review: recent advances and future prospects. Desalination 2015, 356, 226–254.
Warsinger, D. M.; Chakraborty, S.; Tow, E. W.; Plumlee, M. H.; Bellona, C.; Loutatidou, S.; Karimi, L.; Mikelonis, A. M.; Achilli, A.; Ghassemi, A.; Padhye, L. P.; Snyder, S. A.; Curcio, S.; Vecitis, C. D.; Arafat, H. A.; Lienhard, J. H. A review of polymeric membranes and processes for potable water reuse. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 81, 209–237.
Ji, C.; Zhai, Z.; Jiang, C.; Hu, P.; Zhao, S.; Xue, S.; Yang, Z.; He, T.; Niu, Q. J. Recent advances in high-performance TFC membranes: a review of the functional interlayers. Desalination 2021, 500, 114869.
Ramon, G. Z.; Wong, M. C. Y.; Hoek, E. M. V. Transport through composite membrane, part 1: Is there an optimal support membrane?. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415, 298–305.
Gorgojo, P.; Karan, S.; Wong, H. C.; Jimenez-Solomon, M. F.; Cabral, J. T.; Livingston, A. G. Ultrathin polymer films with intrinsic microporosity: anomalous solvent permeation and high flux membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4729–4737.
You, X.; Wu, H.; Su, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, R.; Yu, Q.; Wu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, X. Precise nanopore tuning for a high-throughput desalination membrane via co-deposition of dopamine and multifunctional POSS. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 13191–13202.
Yang, Z.; Guo, H.; Tang, C. Y. The upper bound of thin-film composite (TFC) polyamide membranes for desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 590, 117297.
Ilyas, S.; Joseph, N.; Szymczyk, A.; Volodin, A.; Nijmeijer, K.; de Vos, W. M.; Vankelecom, I. F. J. Weak polyelectrolyte multilayers as tunable membranes for solvent resistant nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 322–331.
Lau, W. J.; Ismail, A. F.; Misdan, N.; Kassim, M. A. A recent progress in thin film composite membrane: a review. Desalination 2012, 287, 190–199.
Tanardi, C. R.; Pinheiro, A. F. M.; Nijmeijer, A.; Winnubst, L. PDMS grafting of mesoporous γ-alumina membranes for nanofiltration of organic solvents. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 471–477.
Raaijmakers, M. J. T.; Benes, N. E. Current trends in interfacial polymerization chemistry. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 63, 86–142.
Park, H. B.; Kamcev, J.; Robeson, L. M.; Elimelech, M.; Freeman, B. D. Maximizing the right stuff: the trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science 2017, 356, 1138–1148.
Yang, H. C.; Waldman, R. Z.; Wu, M. B.; Hou, J.; Chen, L.; Darling, S. B.; Xu, Z.-K. Dopamine: just the right medicine for membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705327.
Seah, M. Q.; Lau, W. J.; Goh, P. S.; Tseng, H. H.; Wahab, R. A.; Ismail, A. F. Progress of interfacial polymerization techniques for polyamide thin film (nano)composite membrane fabrication: a comprehensive review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2817.
Lee, H.; Dellatore, S. M.; Miller, W. M.; Messersmith, P. B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430.
Fang, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Cao, X. A facile approach to construct hierarchical dense membranes via polydopamine for enhanced propylene/nitrogen separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 290–300.
Zhang, C.; Yang, H. C.; Wan, L. S.; Liang, H. Q.; Li, H.; Xu, Z.-K. Polydopamine-coated porous substrates as a platform for mineralized β-FeOOH nanorods with photocatalysis under sunlight. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11567–11574.
Ryou, M. H.; Lee, Y. M.; Park, J. K.; Choi, J. W. Mussel-inspired polydopamine-treated polyethylene separators for high-power Li-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3066–3070.
Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115.
Ku, S. H.; Ryu, J.; Hong, S. K.; Lee, H.; Park, C. B. General functionalization route for cell adhesion on non-wetting surfaces. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2535–2541.
Li, X. L.; Zhu, L. P.; Jiang, J. H.; Yi, Z.; Zhu, B. K.; Xu, Y. Y. Hydrophilic nanofiltration membranes with self-polymerized and strongly-adhered polydopamine as separating layer. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2012, 30, 152–163.
Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Ma, J.; Shao, L. Highly regenerable alkali-resistant magnetic nanoparticles inspired by mussels for rapid selective dye removal offer high-efficiency environmental remediation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19960–19968.
Yang, H. C.; Liao, K. J.; Huang, H.; Wu, Q. Y.; Wan, L. S.; Xu, Z.-K. Mussel-inspired modification of a polymer membrane for ultrahigh water permeability and oil-in-water emulsion separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 10225–10230.
Bozzi, Y.; Borrelli, E. Dopamine in neurotoxicity and neuroprotection: what do D2 receptors have to do with it. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 167–174.
Xi, Z. Y.; Xu, Y. Y.; Zhu, L. P.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B. K. A facile method of surface modification for hydrophobic polymer membranes based on the adhesive behavior of poly(DOPA) and poly(dopamine). J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 244–253.
Zhang, R.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, Z. A novel positively charged composite nanofiltration membrane prepared by bio-inspired adhesion of polydopamine and surface grafting of poly(ethylene imine). J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 9–17.
Lv, Y.; Yang, H. C.; Liang, H. Q.; Wan, L. S.; Xu, Z.-K. Novel nanofiltration membrane with ultrathin zirconia film as selective layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 500, 265–271.
Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; He, M.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Elimelech, M.; Jiang, Z. Antifouling membranes for sustainable water purification: Strategies and mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5888–5924.
Zhang, C.; Ou, Y.; Lei, W. X.; Wan, L. S.; Ji, J.; Xu, Z.-K. CuSO4/H2O2-induced rapid deposition of polydopamine coatings with high uniformity and enhanced stability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3054–3057.
Zhang, C.; Lv, Y.; Qiu, W. Z.; He, A.; Xu, Z.-K. Polydopamine coatings with nanopores for versatile molecular separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14437–14444.
Wang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Cheng, X.; Lau, C. H.; Shao, L. Mussel-inspired hybrid coatings that transform membrane hydrophobicity into high hydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity for oil-in-water emulsion separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9534–9545.
Wang, Z. X.; Lau, C. H.; Zhang, N. Q.; Bai, Y. P.; Shao, L. Mussel-inspired tailoring of membrane wettability for harsh water treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 2650–2657.
Ren, P. F.; Yang, H. C.; Jin, Y. N.; Liang, H. Q.; Wan, L. S.; Xu, Z.-K. Underwater superoleophobic meshes fabricated by poly(sulfobetaine)/polydopamine co-deposition. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 47592–47598.
Zhou, R.; Ren, P. F.; Yang, H. C.; Xu, Z.-K. Fabrication of antifouling membrane surface by poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate)/polydopamine co-deposition. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 18–25.
Lv, Y.; Yang, H. C.; Liang, H. Q.; Wan, L. S.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanofiltration membranes via co-deposition of polydopamine/polyethylenimine followed by cross-linking. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 50–58.
Gin, D. L.; Noble, R. D. Designing the next generation of chemical separation membranes. Science 2011, 332, 674–676.
Bowen, W. R.; Welfoot, J. S. Modelling the performance of membrane nanofiltration-critical assessment and model development. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 1121–1137.
da Silva Burgal, J.; Peeva, L. G.; Kumbharkar, S.; Livingston, A. Organic solvent resistant poly(ether-ether-ketone) nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 479, 105–116.
Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. Crosslinked layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte nanofiltration hollow fiber membrane for low-pressure water softening with the presence of SO42− in feed water. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 486, 169–176.
Guo, S.; Wan, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, J. Loose nanofiltration membrane custom-tailored for resource recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 127376.
Lau, W. J.; Gray, S.; Matsuura, T.; Emadzadeh, D.; Paul Chen, J.; Ismail, A. F. A review on polyamide thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes: history, applications, challenges and approaches. Water Res. 2015, 80, 306–324.
Du, Y.; Lv, Y.; Qiu, W. Z.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanofiltration membranes with narrowed pore size distribution via pore wall modification. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8589–8592.
Du, Y.; Yang, H. C.; Xu, X. L.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Polydopamine as a catalyst for thiol coupling. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 3822–3825.
Du, Y.; Qiu, W. Z.; Lv, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanofiltration membranes with narrow pore size distribution via contra-diffusion-induced mussel-inspired chemistry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29696–29704.
Wei, Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Zhao, C. Oxidant-induced dopamine polymerization for multifunctional coatings. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 1430.
Yang, H. C.; Xu, W.; Du, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Composite freestanding films of polydopamine/polyethyleneimine grown at the air/water interface. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45415–45418.
Yang, H. C.; Wu, M. B.; Hou, J.; Darling, S. B.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanofilms directly formed on macro-porous substrates for molecular and ionic sieving. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 2908–2913.
Wu, M. B.; Fan, X. L.; Yang, H. C.; Yang, J.; Zhu, M. M.; Ren, K. F.; Ji, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Ultrafast formation of pyrogallol/polyethyleneimine nanofilms for aqueous and organic nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570, 270–277.
Sileika, T. S.; Barrett, D. G.; Zhang, R.; Lau, K. H. A.; Messersmith, P. B. Colorless multifunctional coatings inspired by polyphenols found in tea, chocolate, and wine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 125, 10966–10970.
Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Cai, C.; Guo, J.; Fan, H.; Zhu, C.; Dong, H.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Mussel inspired modification of polypropylene separators by catechol/polyamine for Li-Ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5602–5608.
Qiu, W. Z.; Yang, H. C.; Wan, L. S.; Xu, Z.-K. Co-deposition of catechol/polyethyleneimine on porous membranes for efficient decolorization of dye water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14438–14444.
Qiu, W. Z.; Wu, G. P.; Xu, Z.-K. Robust coatings via catechol-amine codeposition: mechanism, kinetics, and application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5902–5908.
Qiu, W. Z.; Lv, Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, H. C.; Xu, Z.-K. Composite nanofiltration membranes via the co-deposition and cross-linking of catechol/polyethylenimine. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 34096–34102.
Qiu, W. Z.; Du, Y.; Lv, Y.; Yang, H. C.; Xu, Z.-K. Codeposition of catechol-polyethyleneimine followed by interfacial polymerization for nanofiltration membranes with enhanced stability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45422.
Qiu, W. Z.; Zhong, Q. Z.; Du, Y.; Lv, Y.; Xu, Z.-K. Enzyme-triggered coatings of tea catechins/chitosan for nanofiltration membranes with high performance. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 6205–6208.
Li, Y.; He, G.; Wang, S.; Yu, S.; Pan, F.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Recent advances in the fabrication of advanced composite membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 10058.
Van der Bruggen, B.; Mänttäri, M.; Nyström, M. Drawbacks of applying nanofiltration and how to avoid them: a review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 63, 251–263.
Lai, G. S.; Lau, W. J.; Gray, S. R.; Matsuura, T.; Gohari, R. J.; Subramanian, M. N.; Lai, S. O.; Ong, C. S.; Ismail, A. F.; Emazadah, D.; Ghanbari, M. A practical approach to synthesize polyamide thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes with improved separation properties for water/wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 4134–4144.
Yin, J.; Deng, B. Polymer-matrix nanocomposite membranes for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 479, 256–275.
Lv, Y.; Du, Y.; Qiu, W. Z.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanocomposite membranes via the codeposition of polydopamine/polyethylenimine with silica nanoparticles for enhanced mechanical strength and high water permeability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2966–2972.
Lv, Y.; Du, Y.; Chen, Z. X.; Qiu, W. Z.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanocomposite membranes of polydopamine/electropositive nanoparticles/polyethyleneimine for nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 99–106.
You, F.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, L. Bio-inspired Ni2+-polyphenol hydrophilic network to achieve unconventional high-flux nanofiltration membranes for environmental remediation. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 6128–6131.
Lv, Y.; Zhang, C.; He, A.; Yang, S. J.; Wu, G. P.; Darling, S. B.; Xu, Z.-K. Photocatalytic nanofiltration membranes with self-cleaning property for wastewater treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700251.
Cadotte, J. E.; King, R. S.; Majerle, R. J.; Petersen, R. J. Interfacial synthesis in the preparation of reverse osmosis membranes. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A — Chem. 1981, 15, 727–755.
Zhang, F.; Fan, J.; Wang, S. Interfacial polymerization: from chemistry to functional materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 21840–21856.
Freger, V. Kinetics of film formation by interfacial polycondensation. Langmuir 2005, 21, 1884–1894.
Nowbahar, A.; Mansard, V.; Mecca, J. M.; Paul, M.; Arrowood, T.; Squires, T. M. Measuring interfacial polymerization kinetics using microfluidic interferometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3173–3176.
McGilvery, C. M.; Abellan, P.; Kłosowski, M. M.; Livingston, A. G.; Cabral, J. T.; Ramasse, Q. M.; Porter, A. E. Nanoscale chemical heterogeneity in aromatic polyamide membranes for reverse osmosis applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19890–19902.
Park, S. J.; Lee, J. H. Fabrication of high-performance reverse osmosis membranes via dual-layer slot coating with tailoring interfacial adhesion. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118449.
Zhao, Q.; Zhao, D. L.; Chung, T. S. Thin-film nanocomposite membranes incorporated with defective ZIF-8 nanoparticles for brackish water and seawater desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 625, 119158.
Li, Y.; You, X.; Li, Y.; Yuan, J.; Shen, J.; Zhang, R.; Wu, H.; Su, Y.; Jiang, Z. Graphene quantum dot engineered ultrathin loose polyamide nanofilms for high-performance nanofiltration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 23930–23938.
Zhang, X.; Lv, Y.; Yang, H. C.; Du, Y.; Xu, Z.-K. Polyphenol coating as an interlayer for thin-film composite membranes with enhanced nanofiltration performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32512–32519.
Yang, X.; Du, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, A.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanofiltration membrane with a mussel-inspired interlayer for improved permeation performance. Langmuir 2017, 33, 2318–2324.
Pan, K.; Fang, P.; Cao, B. Novel composite membranes prepared by interfacial polymerization on polypropylene fiber supports pretreated by ozone-induced polymerization. Desalination 2012, 294, 36–43.
Kwon, S. J.; Park, K.; Kim, D. Y.; Zhan, M.; Hong, S.; Lee, J. H. Highperformance and durable pressure retarded osmosis membranes fabricated using hydrophilized polyethylene separators. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 619, 118796.
Huang, L.; Arena, J. T.; McCutcheon, J. R. Surface modified PVDF nanofiber supported thin film composite membranes for forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 352–360.
Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Zhu, C. Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanofiltration membranes with hydrophobic microfiltration substrates for robust structure stability and high water permeation flux. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 593, 117444.
Wang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Xie, C.; Zhao, S.; Ng, D.; Xie, Z. Dopamine incorporated forward osmosis membranes with high structural stability and chlorine resistance. Processes 2018, 6, 151.
Heidari, A. A.; Mahdavi, H.; Khodaei kahriz, P. Thin film composite solvent resistant nanofiltration membrane via interfacial polymerization on an engineered polyethylene membrane support coated with polydopamine. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 634, 119406.
Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, S.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y. A robust dually charged membrane prepared via catechol-amine chemistry for highly efficient dye/salt separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 629, 119287.
Dai, R.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. Constructing interlayer to tailor structure and performance of thin-film composite polyamide membranes: a review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 282, 102204.
Wu, M. B.; Lv, Y.; Yang, H. C.; Liu, L. F.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.-K. Thin film composite membranes combining carbon nanotube intermediate layer and microfiltration support for high nanofiltration performances. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 515, 238–244.
Wang, J. J.; Yang, H. C.; Wu, M. B.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanofiltration membranes with cellulose nanocrystals as an interlayer for unprecedented performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16289–16295.
Zhu, C. Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.-K. Polyamide-based membranes consisting of nanocomposite interlayers for high performance nanofiltration. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 49940.
Xu, D.; Zhu, X.; Luo, X.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Tang, X.; Li, G.; Liang, H. MXene nanosheet templated nanofiltration membranes toward ultrahigh water transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1270–1278.
Kim, J. H.; Park, G. S.; Kim, Y. J.; Choi, E.; Kang, J.; Kwon, O.; Kim, S. J.; Cho, J. H.; Kim, D. W. Large-area Ti3C2Tx-MXene coating: toward industrial-scale fabrication and molecular separation. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 8860–8869.
Kang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Wen, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, X. Spin-assisted interfacial polymerization strategy for graphene oxidepolyamide composite nanofiltration membrane with high performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 508, 145198.
Kong, B. S.; Geng, J.; Jung, H. T. Layer-by-layer assembly of graphene and gold nanoparticles by vacuum filtration and spontaneous reduction of gold ions. Chem. Commun. 2009, 16, 2174.
Zhu, C. Y.; Li, H. N.; Yang, J.; Li, J. J.; Ye, J. R.; Xu, Z.-K. Vacuum-assisted diamine monomer distribution for synthesizing polyamide composite membranes by interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 616, 118557.
Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y.; Darling, S. B. Sharpening nanofiltration: strategies for enhanced membrane selectivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 39948–39966.
Nadler, R.; Srebnik, S. Molecular simulation of polyamide synthesis by interfacial polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 315, 100–105.
Zhu, C. Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Guo, B. B.; Li, H. N.; Xu, Z.-K. Polyamide nanofilms with linearly-tunable thickness for high performance nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 627, 119142.
Wu, M.; Peng, Q. Y.; Han, L. B.; Zeng, H. B. Self-healing hydrogels and underlying reversible intermolecular interactions. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 39, 1246–1261.
Ma, Z. Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Dong, S. N.; Yang, J.; Wu, G. P.; Xu, Z.-K. Polyamide nanofilms synthesized: via controlled interfacial polymerization on a “jelly” surface. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 7249–7252.
Ma, Z. Y.; Xue, Y. R.; Xu, Z.-K. Alginate hydrogel assisted controllable interfacial polymerization for high-performance nanofiltration membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 435.
Hartanto, Y.; Corvilain, M.; Mariën, H.; Janssen, J.; Vankelecom, I. F. J. Interfacial polymerization of thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes using ionic liquids as organic reagent phase. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 601, 117869.
Ong, C.; Falca, G.; Huang, T.; Liu, J.; Manchanda, P.; Chisca, S.; Nunes, S. P. Green synthesis of thin-film composite membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 11541–11548.
Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Guo, B. B.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Xu, Z.-K. Interfacial polymerization at the alkane/ionic liquid interface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 14636–14643.
Liu, C.; An, Y. P.; Yang, J.; Guo, B. B.; Yu, H. H.; Xu, Z.-K. Osmotic pressure as driving force for recovering ionic liquids from aqueous solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 599, 117835.
Guo, B. B.; Liu, C.; Xin, J. H.; Zhu, C. Y.; Xu, Z.-K. Visualizing and monitoring interfacial polymerization by aggregation-induced emission. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 4332–4336.
Liao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Van der Bruggen, B. Regulating composition and structure of nanofillers in thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes for enhanced separation performance: a critical review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 266, 118567.
Ma, M. Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, C. Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanocomposite membranes embedded with functionalized MoS2 nanosheets for enhanced interfacial compatibility and nanofiltration performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117316.
Yu, J. C.; Ma, M. Q.; Zhu, C. Y.; Hu, D. F.; Ji, J.; Xu, Z.-K. MoS2 membranes with photothermal conversion property for nanofiltration and antibacterial activity. Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese) 2021, 52, 505–513.
Huang, S.; Wu, M. B.; Zhu, C. Y.; Ma, M. Q.; Yang, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Polyamide nanofiltration membranes incorporated with cellulose nanocrystals for enhanced water flux and chlorine resistance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 9b01651.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22135006). We also thank the contributions from Dr. Hao-Cheng Yang, Dr. Yan Lv, Dr. Yong Du, Dr. Wen-Ze Qiu, Dr. Ming-Bang Wu and Mr. Chang Liu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Biography
Zhi-Kang Xu is a Qiushi Distinguished Professor at Zhejiang University and the director of the Key Laboratory of Adsorption and Separation in Zhejiang Province. He received his PhD degree in polymer chemistry and physics from the Chemistry Department of Zhejiang University in 1991. His current research focuses on the surface and interface engineering of polymer membranes.
Notes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, BB., Zhu, CY. & Xu, ZK. Surface and Interface Engineering for Advanced Nanofiltration Membranes. Chin J Polym Sci 40, 124–137 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-022-2654-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-022-2654-z