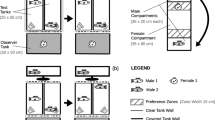
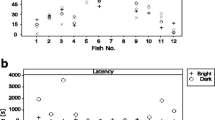
Abstract
Recent studies on consistent individual differences in behavioural tendencies (animal personality) raised the question of whether individual differences in cognitive abilities can be linked to certain personality types. We tested female Atlantic mollies (Poecilia mexicana) in two different classical conditioning experiments. For the first time, we provide evidence for highly consistent individual differences in associative learning speed in fish. We characterized the same individuals for boldness in two experimental situations (latency to emerge from shelter and freezing time after a simulated predator attack) and found high behavioural repeatability. When we tested for a potential correlation between associative learning speed and boldness, however, there was no evidence for a link between them. Our study design included several steps to avoid typical pitfalls of disadvantaging shy individuals during learning tests. We caution that other experimental studies may have suffered from erroneous interpretations due to a more cautious coping style of shy individuals in the respective setup used to assess learning.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amy M, van Oers K, Naguib M (2012) Worms under cover: relationships between performance in learning tasks and personality in great tits (Parus major). Anim Cogn 15:763–770
Bebus SE, Small TW, Jones BC, Elderbrock EK, Schoech SJ (2016) Associative learning is inversely related to reversal learning and varies with nestling corticosterone exposure. Anim Behav 111:251–260
Bell AM, Hankison SJ, Laskowski KL (2009) The repeatability of behaviour: a meta-analysis. Anim Behav 77:771–783
Bensky MK, Paitz R, Pereira L, Bell AM (2017) Testing the predictions of coping styles theory in threespined sticklebacks. Behav Process 136:1–10
Benus RF, Koolhaas JM, van Oortmerssen GA (1987) Individual differences in behavioural reaction to a changing environment in mice and rats. Behaviour 100:105–121
Bierbach D, Sommer-Trembo C, Hanisch J, Wolf M, Plath M (2015) Personality affects mate choice: bolder males show stronger audience effects under high competition. Behav Ecol 26:1314–1325
Bierbach D, Arias-Rodriguez L, Plath M (2018) Intrasexual competition enhances reproductive isolation between locally adapted populations. Curr Zool 64:125–133
Biro PA, Beckmann C, Stamps JA (2010) Small within-day increases in temperature affects boldness and alters personality in coral reef fish. Proc R Soc Lond B 277:71–77
Boogert NJ, Reader SM, Laland KN (2006) The relation between social rank, neophobia and individual learning in starlings. Anim Behav 72:1229–1239
Bousquet CAH, Petit O, Arrivé M, Robin J-P, Sueur C (2015) Personality tests predict responses to a spatial-learning task in mallards, Anas platyrhynchos. Anim Behav 110:145–154
Brown C, Braithwaite VA (2004) Size matters: a test of boldness in eight populations of the poeciliid Brachyraphis episcopi. Anim Behav 68:1325–1329
Brown GE, Godin J-GJ (1997) Anti-predator responses to conspecific and heterospecific skin extracts by threespine sticklebacks: alarm pheromones revisited. Behaviour 134:1123–1134
Brown GE, Smith RJF (1998) Acquired predator recognition in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): conditioning hatchery-reared fish to recognize chemical cues of a predator. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 55:611–617
Brown C, Jones F, Braithwaite V (2005) In situ examination of boldness-shyness traits in the tropical poeciliid, Brachyraphis episcopi. Anim Behav 70:1003–1009
Brown GE, Ferrari MCO, Malka PH, Fregeau L, Kayello L, Chivers DP (2013a) Retention of acquired predator recognition among shy versus bold juvenile rainbow trout. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 67:43–51
Brown GE, Ferrari MCO, Elvidge CK, Ramnarine I, Chivers DP (2013b) Phenotypically plastic neophobia: a response to variable predation risk. Proc Royal Soc B Biol Sci 280(1756):20122712
Brust V, Guenther A (2017) Stability of the guinea pigs personality-cognition-linkage over time. Behav Pocess 134:4–11
Brydges NM, Holmes AM, Braithwaite VA (2008) How do different populations of three-spined sticklebacks Gasterosteus aculeatus combine spatial information? J Fish Biol 73:2580–2586
Budaev SV, Zhuikov AY (1998) Avoidance learning and “personality” in the guppy (Poecilia reticulata). J Comp Psychol 112:92–94
Carazo P, Noble DWA, Chandrasoma D, Whiting MJ (2014) Sex and boldness explain individual differences in spatial learning in a lizard. Proc R Soc Lond B 281:20133275
Carere C, Locurto C (2011) Interaction between animal personality and animal cognition. Curr Zool 57:491–498
Carter AJ, Feeney WE, Marshall HH, Cowlishaw G, Heinsohn R (2013) Animal personality: what are behavioural ecologists measuring? Biol Rev 88:465–475
Coleman K, Tully LA, McMillan JL (2005) Temperament correlates with training success in adult rhesus macaques. Am J Primatol 65:63–71
Cote J, Fogarty S, Weinersmith K, Brodin T, Sih A (2010) Personality traits and dispersal tendency in the invasive mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). Proc R Soc Lond B 277:1571–1579
DePasquale C, Wagner T, Archard GA, Ferguson B, Braithwaite VA (2014) Learning rate and temperament in a high predation risk environment. Oecologia 176:661–667
Dugatkin LA, Alfieri MS (2003) Boldness, behavioral inhibition and learning. Ethol Ecol Evol 15:43–49
Dugatkin LA, Godin J-GJ (1993) Female mate copying in the guppy (Poecilia reticulata): age-dependent effects. Behav Ecol 4:289–292
Dukas R (1999) Ecological relevance of associative learning in fruit fly larvae. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 45:195–200
Evans JP, Pilastro A, Schlupp I (eds) (2010) Ecology and evolution of poeciliid fishes. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Exnerová A, Svádová KH, Fučíková E, Drent P, Štys P (2010) Personality matters: individual variation in reactions of naive bird predators to aposematic prey. Proc R Soc Lond B 277:723–728
Ferrari MCO, Trowell JJ, Brown GE, Chivers DP (2005) The role of learning in the development of threat-sensitive predator avoidance by fathead minnows. Anim Behav 70:777–784
Gaikwad S, Steward A, Hart P, Wong K, Piet V, Cachat J, Kalueff AV (2011) Acute stress disrupts performance of zebrafish in the cued and spatial memory tests: the utility of fish models to study stress-memory interplay. Behav Process 87:224–230
Galsworthy MJ, Paya-Cano JL, Monleón S, Plomin R (2002) Evidence for general cognitive ability (g) in heterogeneous stock mice and an analysis of potential confounds. Genes Brain Behav 1:88–95
Gomes-Silva G, Liu K, Chen B, Plath M, Sommer-Trembo C (2017) Does individual variation in male mate choice copying reflect differences in social responsiveness? Ann Biol Sci 5:25–36
Gray JA (1964) Strength of the nervous system and levels of arousal: a reinterpretation. In: Gray JA, Eyesenck HJ (eds) Pavlov’s typology: recent theoretical and experimental developments from the laboratory of B.M. Teplov. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Griffin AS, Guillette LM, Healy SD (2015) Cognition and personality: an analysis of an emerging field. Trends Ecol Evol 30:207–214
Guenther A, Brust V, Dersen M, Trillmich F (2014) Learning and personality types are related in cavies (Cavia aperea). J Comp Psychol 128:74–81
Guillette LM, Reddon AR, Hurd PL, Sturdy CB (2009) Exploration of a novel space is associated with individual differences in learning speed in black-capped chickadees, Poecile atricapillus. Behav Process 82:265–270
Guillette LM, Reddon AR, Hoeschele M, Sturdy CB (2011) Sometimes slower is better: slow-exploring birds are more sensitive to changes in a vocal discrimination task. Proc Royal Soc B Biol Sci 278(1706):767–773
Guillette LM, Hahn AH, Hoeschele M, Przyslupski A-M, Sturdy CB (2015) Individual differences in learning speed, performance accuracy and exploratory behaviour in black-capped chickadees. Anim Cogn 18:165–178
Guillette LM, Baron DM, Sturdy CB, Spetch ML (2017a) Fast- and slow-exploring pigeons differ in how they use previously learned rules. Behav Process 134:54–62
Guillette LM, Naguib M, Griffin AS (2017b) Individual differences in cognition and personality. Behav Process 134:1–3
Holmes TH, McCormick MI (2010) Smell, learn and live: the role of chemical alarm cues in predator learning during early life history in a marine fish. Behav Process 83:299–305
Ibi D, Takuma K, Koike H, Mizoguchi H, Tsuritani K, Kuwahara Y, Kamei H, Nagai T, Yoneda Y, Nabeshima T, Yamada K (2008) Social isolation rearing-induced impairment of the hippocampal neurogenesis is associated with deficits in spatial memory and emotion-related behaviors in juvenile mice. J Neurochem 105:921–932
Johnsson JI, Sernland E, Blixt M (2001) Sex-specific aggression and antipredator behaviour in young brown trout. Ethology 107:587–599
Kazlauckas V, Schuh J, Dall’Igna OP, Pereira GS, Bonan CD, Lara DR (2005) Behavioral and cognitive profile of mice with high and low exploratory phenotypes. Behav Brain Res 162:272–278
Kelley JL, Magurran AE (2003) Learned predator recognition and antipredator responses in fishes. Fish Fish 4:216–226
Kelley JL, Passow CN, Plath M, Arias Rodriguez L, Yee M-C, Tobler M (2012) Genomic resources for a model in adaptation and speciation research: characterization of the Poecilia mexicana transcriptome. BMC Genom 13:652
Körner KE, Schlupp I, Plath M, Loew ER (2006) Spectral sensitivity of mollies: comparing surface- and cave-dwelling Atlantic mollies, Poecilia mexicana. J Fish Biol 69:54–65
Light KR, Kolata S, Hale G, Grossman H, Matzel LD (2008) Up-regulation of exploratory tendencies does not enhance general learning abilities in juvenile or young-adult outbred mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90:317–329
Locurto C (2007) Individual differences and animal personality. Comp Cogn Behav Rev 2:67–78
Lonsdorf EV, Eberly LE, Pusey AE (2004) Sex differences in learning in chimpanzees. Nature 428:715
Lucchetta P, Bernstein C, Théry M, Lazzari C, Desouhant E (2008) Foraging and associative learning of visual signals in a parasitic wasp. Anim Cogn 11:525–533
Lucon-Xiccato T, Bisazza A (2014) Discrimination reversal learning reveals greater female behavioural flexibility in guppies. Biol Lett 10:20140206
Lucon-Xiccato T, Bisazza A (2017) Individual differences in cognition among teleost fishes. Behav Process 141:184–195
Lucon-Xiccato T, Dadda M (2017) Personality and cognition: sociability negatively predicts shoal size discrimination performance in guppies. Front Psychol 8:1118
Martins CIM, Silva PIM, Conceição LEC, Costas B, Höglund E, Øverli Ø, Schrama JW (2011) Linking fearfulness and coping styles in fish. PLoS One 6(11):e28084
Mathis A, Smith JF (1993) Fathead minnows, Pimephales promelas, learn to recognize northern pike, Esox lucius, as predators on the basis of chemical stimuli from minnows in the pike’s diet. Anim Behav 46:645–656
Matzel LD, Han YR, Grossman H, Karnik MS, Patel D, Scott N, Specht SM, Gandhi CC (2003) Individual differences in the expression of a “general” learning ability in mice. J Neurosci 23:6423–6433
Matzel LD, Kolata S, Light K, Sauce B (2017) The tendency for social submission predicts superior cognitive performance in previously isolated male mice. Behav Process 134:12–21
Mendl M (1999) Performing under pressure: stress and cognitive function. Appl Anim Behav Sci 65:221–244
Mesquita FO, Borcato FL, Huntingford FA (2015) Cue-based and algorithmic learning in common carp: a possible link to stress coping style. Behav Process 115:25–29
Mitchell MD, McCormick MI, Ferrari MCO, Chivers DP (2011) Coral reef fish rapidly learn to identify multiple unknown predators upon recruitment to the reef. PLoS One 6:e15764
Nakagawa S, Schielzeth H (2010) Repeatability for Gaussian and non-Gaussian data: a practical guide for biologists. Biol Rev 85:935–956
Nawroth C, Prentice PM, McElligott AG (2017) Individual personality differences in goats predict their performance in visual learning and non-associative cognitive tasks. Behav Process 134:43–53
Odling-Smee L, Braithwaite VA (2003) The role of learning in fish orientation. Fish Fish 4:235–246
Petrazzini MEM, Agrillo C (2016) Turning to the larger shoal: are there individual differences in small-and large-quantity discrimination of guppies? Ethol Ecol Evol 28:211–220
Piyapong C, Krause J, Chapman BB, Ramnarine IW, Louca V, Croft DP (2010) Sex matters: a social context to boldness in guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Behav Ecol 21:3–8
Plath M, Hauswaldt JS, Moll K, Tobler M, García de León FJ, Schlupp I, Tiedemann R (2007) Local adaptation and pronounced genetic differentiation in an extremophile fish, Poecilia mexicana, inhabiting a Mexican cave with toxic hydrogen sulphide. Mol Ecol 16:967–976
Plath M, Pfenninger M, Lerp H, Riesch R, Eschenbrenner C, Slattery PA, Bierbach D, Herrmann N, Schulte M, Arias-Rodriguez L, Rimber Indy J, Passow C, Tobler M (2013) Genetic differentiation and selection against migrants in evolutionarily replicated extreme environments. Evolution 67:2647–2661
Réale D, Reader SM, Sol D, McDougall PT, Dingemanse NJ (2007) Integrating animal temperament within ecology and evolution. Biol Rev 82:291–318
Rowe C, Healy SD (2014) Measuring variation in cognition. Behav Ecol 25:1287–1292
Schulz-Mirbach T, Ladich F, Riesch R, Plath M (2010) Otolith morphology and hearing abilities in cave- and surface-dwelling ecotypes of the Atlantic molly, Poecilia mexicana (Teleostei: Poeciliidae). Hear Res 267:137–148
Sih A, Del Giudice M (2012) Linking behavioural syndromes and cognition: a behavioural ecology perspective. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 367:2762–2772
Sih A, Mathot KJ, Moirón M, Montiglio P-O, Wolf M, Dingemanse NJ (2015) Animal personality and state-behaviour feedbacks: a review and guide for empiricists. Trends Ecol Evol 30:50–60
Sneddon LU (2003) The bold and the shy: individual differences in rainbow trout. J Fish Biol 62:971–975
Sommer-Trembo C, Bierbach D, Arias-Rodriguez L, Verel Y, Jourdan J, Zimmer C, Riesch R, Streit B, Plath M (2016) Does personality affect premating isolation between locally-adapted populations? BMC Evol Biol 16:138
Teskey GC, Ossenkopp K-P, Kavalierst M, Innis NK, Boon FH (1998) Individual differences in radial maze performance and locomotor activity in the meadow vole, Microtus pennsylvanicus. Physiol Behav 65:555–561
Titulaer M, van Oers K, Naguib M (2012) Personality affects learning performance in difficult tasks in a sex-dependent way. Anim Behav 83:723–730
Tobler M, Kelley JL, Plath M, Riesch R (2018) Extreme environments and the origins of biodiversity: adaptation and speciation in sulphide spring fishes. Mol Ecol 27:843–859
Toms CN, Echevarria DJ, Jouandot DJ (2010) A methodological review of personality-related studies in fish: focus on the shy-bold axis of behavior. Int J Comp Psychol 23:1–25
Trompf L, Brown C (2014) Personality affects learning and trade-offs between private and social information in guppies, Poecilia reticulata. Anim Behav 88:99–106
van Horik JO, Langley EJG, Whiteside MA, Madden JR (2017) Differential participation in cognitive tests is driven by personality, sex, body condition and experience. Behav Process 134:22–30
Warburton K (1990) The use of local landmarks by foraging goldfish. Anim Behav 40:500–505
White SL, Wagner T, Gowan C, Braithwaite VA (2017) Can personality predict individual differences in brook trout spatial learning ability? Behav Pocess 141:220–228
Winocur G, Greenwood CE (1999) The effects of high fat diets and environmental influences on cognitive performance in rats. Behav Brain Res 101:153–161
Wong RY, So P, Cummings ME (2011) How female size and male displays influence mate preference in a swordtail. Anim Behav 82:691–697
Woody DR, Mathis A (1998) Acquired recognition of chemical stimuli from an unfamiliar predator: associative learning by adult newts, Notophthalmus viridescens. Copeia 4:1027–1031
Yamaguchi A (2001) Sex differences in vocal learning in birds. Nature 411:257
Acknowledgements
We thank Holger Geupel and Eva Maria Wörner for help with animal care.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CST designed the study, collected data and conducted the statistical analyses. Both authors wrote the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable national and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All experiments comply with current German law and were approved by Regierungspräsidium Darmstadt (V-54-19c-20/15-F104/Anz.18). Both authors declare that they have no conflict of interest and agree upon the content of the article.
Data accessibility
The dataset supporting this article will be uploaded as an additional spread sheet in the electronic supplemental material upon acceptance.
Conflict of interest
Carolin Sommer-Trembo declares that she has no conflict of interest. Martin Plath declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 26784 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sommer-Trembo, C., Plath, M. Consistent individual differences in associative learning speed are not linked to boldness in female Atlantic mollies. Anim Cogn 21, 661–670 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-018-1201-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-018-1201-3