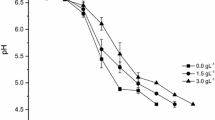
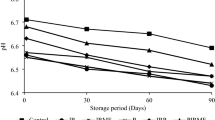
Abstract
Sour cream is a popular fermented dairy product and galactomannans are widely used in the food industry to improve texture and stability. In this study, it was investigated the effects of different galactomannans (guar gum (GG), locust bean gum (LBG), and GG/LBG) on the rheological, physicochemical, and microbial properties of sour creams. All the sour cream samples had similar pHs (4.55–4.57), acidity (0.83–0.86%), and lactic acid bacteria viable counts (8.08–8.15 log CFU/g) after fermentation. The rheological parameters (ηa,50, K, G′, G″, and tan δ) of the sour creams increased after the addition of galactomannans. The sour cream with GG showed higher ηa,50, K, G′, and G″ values than the sour cream with LBG. Furthermore, the combination of galactomannans (GG/LBG) did not have any synergistic effect on the sour cream. The water-holding capacity of sour creams was enhanced by the addition of galactomannans, resulting in reduced syneresis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almusallam IA, Ahmed IAM, Babiker EE, Al-Juhaimi FY, Saleh A, Qasem AA, Maiman SA, Osman MA, Ghafoor K, Hajji HA, Al-Shawaker AS. Effect of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) spikelets extract on the physicochemical and microbial properties of set-type yogurt during cold storage. LWT-Food Science and Technology. 148: 111762 (2021)
AOAC. Official Method of Analysis of AOAC Intl. 15th ed. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington DC, USA (2005)
Barak S, Mudgil D. Locust bean gum: Processing, properties and food applications-A review. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 66: 74-80 (2014)
Benmeziane F, Raigar RK, Ayat NE, Aoufi D, Djermoune-Arkoub L, Chala A. Lentil (Lens culinaris) flour addition to yogurt: Impact on physicochemical, microbiological and sensory attributes during refrigeration storage and microstructure changes. LWT-Food Science and Technology. 140: 110793 (2021)
Bourriot S, Garnier C, Doublier JL. Phase separation, rheology and structure of micellar casein-galactomannan mixtures. International Dairy Journal. 9: 353-357 (1999)
Cândido de Souza WF, Souza do Amaral CR, Lima da Silva Bernardino PD. The addition of skim milk powder and dairy cream influences the physicochemical properties and the sensory acceptance of concentrated Greek-style yogurt. International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science. 24: 100349 (2021)
Gibson, M. Mik and Dairy. pp. 133–168. In: Food science and the culinary arts. Academic Press, Cambridge, MA, USA (2018)
Hui YH, Evranuz Ö. Sour cream and crème fraîche, pp. 235–246. In: Handbook of animal-based fermented food and beverage technology. Goddik LM (ed). CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, FL, USA (2012)
Hussain M, Bakalis S, Gouseti O, Akhtar S, Hameed A, Ismail A. Microstructural and dynamic oscillatory aspects of yogurt as influenced by hydrolysed guar gum. International Journal of Food Science and Technology. 52(10): 2210-2216 (2017)
Kim Y, Yoon S, Shin H, Jo M, Lee S, Kim S. Isolation of Lactococcus lactis ssp. cremoris LRCC5306 and optimization of diacetyl production conditions for manufacturing sour cream. Food Science of Animal Resources. 41(3): 373-385 (2021)
Lee Y, Chang YH. Influence of guar gum addition on physicochemical, microbial, rheological and sensory properties of stirred yoghurt. International Journal of Dairy Technology. 69(3): 356-363 (2016)
Li H, Liu T, Zou X, Yang C, Li H, Cui W, Yu J. Utilization of thermal-denatured whey protein isolate-milk fat emulsion gel microparticles as stabilizers and fat replacers in low-fat yogurt. LWT-Food Science and Technology. 150: 112045 (2021)
Narvhus JA, Østby N, Abrahamsen RK. Science and technology of cultured cream products: A review. International Dairy Journal. 93: 57-71 (2019)
Pachekrepapol U, Kokhuenkhan Y, Ongsawat J. Formulation of yogurt-like product from coconut milk and evaluation of physicochemical, rheological, and sensory properties. International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science. 25: 100393 (2021)
Prajapati VD, Jani GK, Moradiya NG, Randeria NP, Nagar BJ, Naikwadi NN, Variya BC. Galactomannan: A versatile biodegradable seed polysaccharide. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 60: 83-92 (2013)
Samil Kök M. Characterization of galactomannan stabilised yogurt drink using dynamic rheology. International Journal of Food Properties. 13: 209-220 (2010)
Seo CW, Kang SH, Shin YK, Yoo B. Effect of homogenization pressure and supplementation with sucrose fatty acid ester on the physical properties of dairy cream-based emulsions. Korean Journal for Food Science of Animal Resources. 38(3): 476-486 (2018)
Shepard L, Miracle RE, Leksrisompong P, Drake MA. Relating sensory and chemical properties of sour cream to consumer acceptance. Journal of Dairy Science. 96: 5435-5454 (2013)
Shori AB, Aljohani GS, Al-zahrani AJ, Al-sulbi OS, Baba AS. Viability of probiotics and antioxidant activity of cashew milk-based yogurt fermented with selected strains of probiotic Lactobacillus spp. LWT-Food Science and Technology. 153: 112482 (2022)
Sittikijyothin W, Torres D, Gonc¸alves MP. Modelling the rheological behaviour of galactomannan aqueous solutions. Carbohydrate Polymers. 59: 339-350 (2005)
Tavares C, Lopes da Silva JA. Rheology of galactomannan–whey protein mixed systems. International Dairy Journal. 13: 699-706 (2003)
Wu Y, Cui W, Eskin NAM, Goff HD. An investigation of four commercial galactomannans on their emulsion and rheological properties. Food Research International. 42: 1141-1146 (2009)
Yu J, Mo L, Pan L, Yao C, Ren D, An X, Tsogtgerel T, Zhang H, Liu W. Bacterial microbiota and metabolic character of traditional sour cream and butter in Buryatia, Russia. Frontiers in Microbiology. 9: 2496 (2018)
Acknowledgements
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, C.W. Effect of galactomannan addition on rheological, physicochemical, and microbial properties of cultured sour cream. Food Sci Biotechnol 31, 571–577 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-022-01066-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-022-01066-3