Abstract
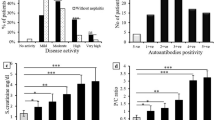
A variety of autoantibodies has been involved in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), some of which are well known and applied as disease biomarkers. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of a novel autoantibody, anti-tubulin-α-1C, in patients with SLE and investigate its clinical significance. Anti-tubulin-α-1C autoantibody levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in 128 SLE patients, 38 primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) patients, and 106 healthy controls (HCs).White blood cell (WBC) count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), IgM, IgG, C3, C4, RF, ANA, dsDNA, Sm, AnuA, aCL, anti-SSA, and anti-SSB were measured by standard laboratory techniques. SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) was evaluated accordingly. Anti-tubulin-α-1C antibody levels were significantly increased in SLE patients. Elevated anti-tubulin-α-1C were correlated with higher levels of SLEDAI, increased titers of anti-Sm antibody, and decreased titers of anti-dsDNA antibody and significantly associated with cutaneous and mucosal vasculitis and milder renal involvement. Anti-tubulin-α-1C may become a novel biomarker indicative of active vasculitis in SLE and could be applied in future clinical practice.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Z, Davidson A (2012) Taming lupus—a new understanding of pathogenesis is leading to clinical advances. Nat Med 18(6):871–882. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2752
Sherer Y, Gorstein A, Fritzler MJ, Shoenfeld Y (2004) Autoantibody explosion in systemic lupus erythematosus: more than 100 different antibodies found in SLE patients. Semin Arthritis Rheum 34(2):501–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2004.07.002
Migliorini P, Baldini C, Rocchi V, Bombardieri S (2005) Anti-Sm and anti-RNP antibodies. Autoimmunity 38(1):47–54. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916930400022715
ter Borg EJ, Horst G, Hummel EJ, Limburg PC, Kallenberg CG (1990) Measurement of increases in anti-double-stranded DNA antibody levels as a predictor of disease exacerbation in systemic lupus erythematosus. A long-term, prospective study. Arthritis Rheum 33(5):634–643. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780330505
Popovic K, Brauner S, Ek M, Wahren-Herlenius M, Nyberg F (2007) Fine specificity of the Ro/SSA autoantibody response in relation to serological and clinical findings in 96 patients with self-reported cutaneous symptoms induced by the sun. Lupus 16:10–17
Ibrahim A. Al-Homood(2012) Thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: a review article. ISRNRheumatol 2012: 428269
Doyle M (2006) Vasculitis associated with connective tissue disorders. Curr Rheumatol Rep 8:312–316
Pyrpasopoulou A, Chatzimichailidou S, Aslanadis S (2012) Vascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmune Dis 2012:876456
Janke C1 (2014) The tubulin code: molecular components, readout mechanisms, and functions. J Cell Biol 206:461–472
Fagerberg L, Hallström BM, Oksvold P, Kampf C, Djureinovic D et al (2014) Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 13(2):397–406
Trudie A. Goers, Sabarinathan Ramachandran, Aviva Aloush, et al. (2008 )De novo production of K-α1 tubulin specific antibodies: role in chronic lung allograft rejection. J Immunol 180: 4487–4494
Hachema RR, Tiriveedhib V, Pattersonc G et al (2012) Antibodies to K-a 1 tubulin and collagen V are associated with chronic rejection after lung transplantation. Am J Transplant 12(8):2164–2171. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04079.x
Cong Y, Eric Gershwin M, Chang C (2014) Diagnostic criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus: a critical review. J Autoimmun 48–49:10–13
Yung S, Chan TM (2015) Mechanisms of kidney injury in lupus nephritis—the role ofanti-dsDNA antibodies. Front Immunol 6:475
Avrameas S, Guilbert B, Dighiero G (1981) Natural antibodies against tubulin, actin myoglobin, thyroglobulin, fetuin, albumin and transferrin are present in normal human sera and monoclonal immunoglobulins from multiple myeloma and Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia may express similar antibody specificities. AnnImmunol (Paris) 132C:231–236
Dighiero G, Guilbert B, Avrameas S (1982) Naturally occurring antibodies against nine common antigens in humans sera. II. High incidence of monoclonal Ig exhibiting antibody activity against actin and tubulin and sharing antibody specificities with natural antibodies. J Immunol 128:2788–2792
Karsenti E, Guilbert B, Bornens M, Avrameas S (1977) Anti-actin and anti-tubulin antibodies in the serum of non-immunized animals. AnnImmunol (Paris) 128:195–200
Kurki P, Virtanen I (1984) The detection of human antibodies against cytoskeletal components. J Immunol Methods 67:209–223
Mead GM, Cowin P, Whitehouse JM (1980) Antitubulin antibody in healthy adults and patients with infectious mononucleosis and its relationship to smooth muscle antibody (SMA). ClinExpImmunol 39:328–336
Newcombe J, Gahan S, Cuzner ML (1985) Serum antibodies against central nervous system proteins in human demyelinating disease. Clin Exp Immunol 59:383–390
Rousset B, Bernier-Valentin F, Poncet C, Orgiazzi J, Madec AM, Monier JC, Mornex R (1983) Anti-tubulin antibodies in autoimmune thyroid disorders. Clin Exp Immuno l52:325–332
Newcombe J, Gahan S, Cuzner ML (1985) Serum antibodies against central nervous system proteins in human demyelinating disease. Clin Exp Immunol 59:383–390
Drenkard C, Villa AR, Reyes E, Abello M, Alarcón-Segovia D (1997) Vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 6(3):235–242. https://doi.org/10.1177/096120339700600304
Ramos-Casals M, Nardi N, Lagrutta M et al (2006) Vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus: prevalence and clinical characteristics in 670 patients. Medicine 85:95–104
D'Cruz D (1998) Vasculitis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 7:270–274
Bacon PA, Carruthers DM (1995) Vasculitis associated with connective tissue disorders. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 21:1077–1096
Praprotnik S, Blank M, Meroni PL et al (2001) Classification of antiendothelial cell antibodies into antibodies against microvascular and macrovascular endothelial cells. Arthritis Rheum 44:1484–1494
Funding
This work was supported by funding from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81471601 and 81671602), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7152150), and Beijing Nova Program (Z171100001117025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Peking University People’s Hospital according to the declaration of Helsinki with the following reference number: 2015PHB219-01. All patients had been informed and signed the consent for the participation in this study.
Disclosures
None.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 187 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Cheng, Y., Gan, Y. et al. Anti-tubulin-α-1C autoantibody in systemic lupus erythematosus: a novel indicator of disease activity and vasculitis manifestations. Clin Rheumatol 37, 1229–1237 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4024-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4024-3