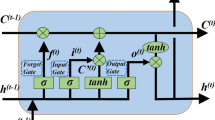
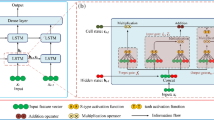
Abstract
Displacement prediction is critical for the early detection of landslides, and the empirical, statistical, and machine learning models have been commonly used. In the Three Gorges reservoir area (TGRA), many landslides experience step-like deformations due to the periodic change of influencing factors. In this study, a novel and dynamic model is proposed to predict the displacements of step-like landslides. Two typical landslides in the TGRA are taken as case studies. Variational mode decomposition (VMD) is used to decompose the cumulative displacements into stochastic, periodic, and trend components. The influencing factors are decomposed into low-frequency and high-frequency components. Two principles, including the physical connotation and minimum sample entropy, are employed to optimize the VMD parameters. The trend displacement is fitted and predicted by a polynomial expression with an optimized order, and the periodic and stochastic displacements are dynamically modeled by the bidirectional long short-term memory (LSTM) model. The cumulative displacement prediction is the addition of the three displacement components. The proposed model has been shown to exhibit superior performance in the displacement prediction of step-like landslides. To achieve acceptable prediction, a size ratio between the training and testing datasets greater than or equal to five is recommended. The min–max and zero-mean normalizations are applicable to the data preprocessing of this work.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aditian A, Kubota T, Shinohara Y (2018) Comparison of GIS-based landslide susceptibility models using frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network in a tertiary region of Ambon, Indonesia. Geomorphology 318:101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.06.006
Atef S, Eltawil AB (2020) Assessment of stacked unidirectional and bidirectional long short-term memory networks for electricity load forecasting. Electr Pow Syst Res 187:106489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2020.106489
Azarafza M, Ghazifard A, Akgun H, Asghari-Kaljahi E (2018) Landslide susceptibility assessment of South Pars Special Zone, southwest Iran. Environ Earth Sci 77(24):805. https://doi.org/10.1016/10.1007/s12665-018-7978-1
Bayona V (2019) Comparison of moving least squares and RBF plus poly for interpolation and derivative approximation. J Sci Comput 81(1):486–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-019-01028-8
Bogaard T, Greco R (2018) Invited perspectives: hydrological perspectives on precipitation intensity-duration thresholds for landslide initiation: proposing hydrometeorological thresholds. Nat Hazard Earth Sys 18(1):31–39. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-18-31-2018
Bui DT, Tsangaratos P, Nguyen VT, Liem NV, Trinh PT (2020) Comparing the prediction performance of a Deep Learning Neural Network model with conventional machine learning models in landslide susceptibility assessment. CATENA 188:104426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104426
Cai ZL, Xu WY, Meng YD, Shi C, Wang RB (2016) Prediction of landslide displacement based on GA-LSSVM with multiple factors. Bull Eng Geol Environ 75(2):637–646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-015-0804-z
Chen JJ, Zeng ZG, Jiang P, Tang HM (2015) Deformation prediction of landslide based on functional network. Neurocomputing 149:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2013.10.044
Chung CF, Fabbri A, Van Westen CJ (1995) Multivariate regression analysis for landslide hazard zonation. In: Carrara A, Guzzetti F (eds) Geographical information systems in assessing natural hazards. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Dragomiretskiy K, Zosso D (2014) Variational mode decomposition. IEEE T Singal Proces 62(3):531–544. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675
Du H, Song DQ, Chen Z, Shu HP, Guo ZZ (2020) Prediction model oriented for landslide displacement with step-like curve by applying ensemble empirical mode decomposition and the PSO-ELM method. J Clean Prod 270:122248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122248
Du J, Yin KL, Lacasse S (2013) Displacement prediction in colluvial landslides, Three Gorges Reservoir. China Landslides 10(2):203–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-012-0326-8
Fang ZC, Wang Y, Peng L, Hong HY (2020) Integration of convolutional neural network and conventional machine learning classifiers for landslide susceptibility mapping. Comput Geosci 139:104470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2020.104470
Fang ZC, Wang Y, Peng L, Hong HY (2021) A comparative study of heterogeneous ensemble-learning techniques for landslide susceptibility mapping. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 35(2):321–347. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2020.1808897
Fathani TF, Karnawati D, Wilopo W (2016) An integrated methodology to develop a standard for landslide early warning systems. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 16:2123–2135. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-16-2123-2016
Gao W, Dai S, Chen X (2019) Landslide prediction based on a combination intelligent method using the GM and ENN: two cases of landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir. China Landslides 19(1):111–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01273-w
Graves A, Jaitly N (2014) Towards end-to-end speech recognition with recurrent neural networks. 31st International Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing, China: W&CP, 1764–1772
Guo ZZ, Chen LX, Gui L, Du J, Yin KL, Do MH (2019) Landslide displacement prediction based on variational mode decomposition and WA-GWO-BP model. Landslides 16(7):567–583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01314-4
Hanson J, Yang YD, Paliwal K, Zhou YQ (2017) Improving protein disorder prediction by deep bidirectional long short-term memory recurrent neural networks. Bioinformatics 33(5):685–692. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw678
Hochreite S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 9(8):1735–1780. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Hu XL, Wu SS, Zhang GC, Zheng WB, Liu C, He CC, Liu ZX, Guo XY, Zhang H (2021) Landslide displacement prediction using kinematics-based random forests method: A case study in Jinping Reservoir Area, China. Eng Geol 283:105975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105975
Huang FM, Huang J, Jiang S, Zhou C (2017) Landslide displacement prediction based on multivariate chaotic model and extreme learning machine. Eng Geol 218:173–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.01.016
Huang FM, Yin KL, Zhang GR, Gui L, Yang BB, Liu L (2016) Landslide displacement prediction using discrete wavelet transform and extreme learning machine based on chaos theory. Environ Earth Sci 75(20):1376–1393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6133-0
Li CD, Criss RE, Fu ZY, Long JJ, Tan QW (2021) Evolution characteristics and displacement forecasting model of landslides with stair-step sliding surface along the Xiangxi River, three Gorges Reservoir region. China Eng Geol 283:105961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105961
Li HJ, Xu Q, He YS, Deng JH (2018) Prediction of landslide displacement with an ensemble-based extreme learning machine and copula models. Landslides 15:2047–2059. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1020-2
Li HJ, Xu Q, He YS, Fan XM, Li SM (2020a) Modeling and predicting reservoir landslide displacement with deep belief network and EWMA control charts: a case study in Three Gorges Reservoir. Landslides 3:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01312-6
Li SC, Yang SY, Liang JH (2020b) Recognition of ships based on vector sensor and bidirectional long short-term memory networks. Appl Acoust 164:107248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2020.107248
Li SH, Wu LZ, Chen JJ, Huang RQ (2020c) Multiple data-driven approach for predicting landslide deformation. Landslides 17(3):709–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01320-6
Lian C, Zeng ZG, Yao W, Tang HM (2013) Displacement prediction model of landslide based on a modified ensemble empirical mode decomposition and extreme learning machine. Nat Hazards 66(2):759–771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0517-6
Lian C, Zeng ZG, Yao W, Tang HM (2014) Ensemble of extreme learning machine for landslide displacement prediction based on time series analysis. Neural Comput Applic 24(1):99–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-013-1446-3
Lian C, Zeng ZG, Yao W, Tang HM (2015) Multiple neural networks switched prediction for landslide displacement. Eng Geol 186:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.11.014
Liao K, Wu YP, Miao FS, Li LW, Xue Y (2019) Using a kernel extreme learning machine with grey wolf optimization to predict the displacement of step-like landslide. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(2):673–685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01598-9
Liu Q, Lu GY, Dong J (2021) Prediction of landslide displacement with step-like curve using variational mode decomposition and periodic neural network. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80(5):3783–3799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02136-2
Liu Y, Xu C, Huang B, Ren XW, Liu CQ, Hu BD, Chen Z (2020a) Landslide displacement prediction based on multi-source data fusion and sensitivity states. Eng Geol 271:105608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105608
Liu ZQ, Guo D, Lacasse S, Li JH, Yang BB, Choi JC (2020b) Algorithms for intelligent prediction of landslide displacements. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci A (appl Phys & Eng) 21(6):412–429. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A2000005
Luo SL, Huang D (2020) Deformation characteristics and reactivation mechanisms of the Outang ancient landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. China Bull Eng Geol Environ 79(8):3943–3958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01838-3
Miao FS, Wu YP, Xie YH, Li YN (2018) Prediction of landslide displacement with step-like behavior based on multialgorithm optimization and a support vector regression model. Landslides 15(3):475–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0883-y
Nanehkaran YA, Mao YM, Azarafza M, Kockar MK, Zhu HH (2021) Fuzzy-based multiple decision method for landslide susceptibility and hazard assessment: A case study of Tabriz, Iran. Geomech Eng 24(5):407–418. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2021.24.5.407
Pincus SM (2001) Assessing serial irregularity and its implications for health. Ann Ny Acad Sci 954:245–267
Ren F, Wu XL, Zhang KX, Niu RQ (2015) Application of wavelet analysis and a particle swarm optimized support vector machine to predict the displacement of the Shuping landslide in the Three Gorges. China Environ Earth Sci 73(8):4791–4804. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3764-x
Segalini A, Valletta A, Carri A (2018) Landslide time-of-failure forecast and alert threshold assessment: a generalized criterion. Eng Geol 245:72–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.08.003
Shang HK, Lo KL, Li F (2017) Partial discharge feature extraction based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition and sample entropy. Entropy 19:439. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19090439
Shihabudheen KV, Peethambaran B (2017) Landslide displacement prediction technique using improved neuro-fuzzy system. Arab J Geosci 10(22):502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3278-4
Shihabudheen KV, Pillai GN, Peethambaran B (2017) Prediction of landslide displacement with controlling factors using extreme learning adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ELANFIS). Appl Soft Comput 61:892–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.09.001
Wang WD, Li JY, Qu X, Han Z, Liu P (2019a) Prediction on landslide displacement using a new combination model: a case study of Qinglong landslide in China. Nat Hazards 96:1121–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03595-3
Wang ZJ, He GF, Du WH, Zhou J, Han XF, Wang JT, He HH, Guo XM, Wang JY, Kou YF (2019b) Application of parameter optimized variational mode decomposition method in fault diagnosis of gearbox. IEEE Access 7:44871–44882. 0.1109/ACCESS.2019.2909300
Xing Y, Yue JP, Chen C (2020a) Interval estimation of landslide displacement prediction based on time series decomposition and long short-term memory network. IEEE Access 8:3187–3196. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2961295
Xing Y, Yue JP, Chen C, Cong KL, Zhu SL, Bian YK (2019) Dynamic displacement forecasting of dashuitian landslide in China using variational mode decomposition and stack long short-term memory network. Appl Sci-Basel 9(15):2951. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9152951
Xing Y, Yue JP, Chen C, Qin YL, Hu J (2020b) A hybrid prediction model of landslide displacement with risk-averse adaptation. Comput Geosci 141:104527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2020.104527
Xu B, Zhou FX, Li HP, Yan BK, Liu Y (2019) Early fault feature extraction of bearings based on Teager energy operator and optimal VMD. Isa T 86:249–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2018.11.010
Xu SL, Niu RQ (2018) Displacement prediction of Baijiabao landslide based on empirical mode decomposition and long short-term memory neural network in Three Gorges area, China. Comput Geosci 111:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2017.10.013
Yang BB, Yin KL, Lacasse S, Liu ZQ (2019a) Time series analysis and long short-term memory neural network to predict landslide displacement. Landslides 16:677–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-01127-x
Yang K, Wang GF, Dong Y, Zhang QB, Sang LL (2019b) Early chatter identification based on an optimized variational mode decomposition. Mech Syst Signal Pr 115:238–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.05.052
Yu SH, Yu XH, Man ZH (2004) A fuzzy neural network approximator with fast terminal sliding mode and its applications. Fuzzy Set Syst 148(3):469–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2003.12.004
Yu Y, Hu CH, Si XS, Zheng JF, Zhang JX (2020) Averaged Bi-LSTM networks for RUL prognostics with non-life-cycle labeled dataset. Neurocomputing 402:134–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.03.041
Zhao Q, Han T, Jiang DX, Yin K (2019) Application of Variational Mode Decomposition to Feature Isolation and Diagnosis in a Wind Turbine. J Vib Eng Technol 7(6):639–646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42417-019-00156-7
Zhou C, Yin KL, Cao Y, Ahmed B (2016) Application of time series analysis and PSO-SVM model in predicting the Bazimen landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Eng Geol 204:108–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.02.009
Zhou C, Yin KL, Cao Y, Intrieri E, Ahmed B, Catani F (2018) Displacement prediction of step-like landslide by applying a novel kernel extreme learning machine method. Landslides 15(11):2211–2225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1022-0
Zhu X, Xu Q, Tang MG (2017) Comparison of two optimized machine learning models for predicting displacement of rainfall-induced landslide: a case study in Sichuan Province, China. Eng Geol 218:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.01.022
Zou ZX, Yang YM, Fan ZQ, Tang HM, Zou M, Hu XL, Xiong CR, Ma JW (2020) Suitability of data preprocessing methods for landslide displacement forecasting. Stoch Env Res Risk A 34(8):1105–1119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01824-x
Acknowledgements
We want to express our gratitude to the National Cryosphere Desert Data Center/National Service Center for Specialty Environmental Observation Stations formaking available valuable research data on historical landslides. Special thanks are given to the anonymous reviewers who have helped to improve the paper.
Funding
This study was supported by the China National Natural Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 11902128, 41762021) and the Applied Basic Research Foundation of Yunnan Province, China (Grant Nos. 2019FI012, 2018FB093).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Zhang, K., Cai, C. et al. Displacement prediction of step-like landslides based on feature optimization and VMD-Bi-LSTM: a case study of the Bazimen and Baishuihe landslides in the Three Gorges, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80, 8481–8502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02454-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02454-5