Abstract
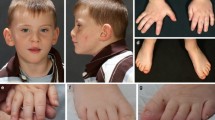
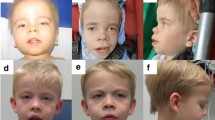
The etiology of intellectual disabilities (ID) remains unknown for the majority of patients. Due to reduced reproductive fitness in many individuals with ID, de novo mutations account for a significant portion of severe ID. The ATP-dependent SWI/SNF chromatin modifier has been linked with neurodevelopmental disorders including ID and autism. ARID2 is an intrinsic component of polybromo-associated BAF (PBAF), the SWI/SNF subcomplex. In this study, we used clinical whole exome sequencing (WES) in proband-parent-trios to identify the etiology of ID. We identified four independent, novel, loss of function variants in ARID2 gene in four patients, three of which were confirmed to be de novo. The patients all have ID and share other clinical characteristics including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, short stature, dysmorphic facial features, and Wormian bones. All four novel variants are predicted to lead to a premature termination with the loss of the two conservative zinc finger motifs. This is the first report of mutations in ARID2 associated with developmental delay and ID.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Bokhoven H (2011) Genetic and epigenetic networks in intellectual disabilities. Annu Rev Genet 45:81–104. doi:10.1146/annurev-genet-110410-132512
Srivastava AK, Schwartz CE (2014) Intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorders: causal genes and molecular mechanisms. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 46P2:161–174. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.02.015
Vissers LE, de Ligt J, Gilissen C, Janssen I, Steehouwer M, de Vries P, van Lier B, Arts P, Wieskamp N, del Rosario M, van Bon BW, Hoischen A, de Vries BB, Brunner HG, Veltman JA (2010) A de novo paradigm for mental retardation. Nat Genet 42(12):1109–1112. doi:10.1038/ng.712
Ku CS, Polychronakos C, Tan EK, Naidoo N, Pawitan Y, Roukos DH, Mort M, Cooper DN (2013) A new paradigm emerges from the study of de novo mutations in the context of neurodevelopmental disease. Mol Psychiatry 18(2):141–153. doi:10.1038/mp.2012.58
Yang Y, Muzny DM, Xia F, Niu Z, Person R, Ding Y, Ward P, Braxton A, Wang M, Buhay C, Veeraraghavan N, Hawes A, Chiang T, Leduc M, Beuten J, Zhang J, He W, Scull J, Willis A, Landsverk M, Craigen WJ, Bekheirnia MR, Stray-Pedersen A, Liu P, Wen S, Alcaraz W, Cui H, Walkiewicz M, Reid J, Bainbridge M, Patel A, Boerwinkle E, Beaudet AL, Lupski JR, Plon SE, Gibbs RA, Eng CM (2014) Molecular findings among patients referred for clinical whole-exome sequencing. JAMA 312(18):1870–1879. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.14601
Vignali M, Hassan AH, Neely KE, Workman JL (2000) ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes. Mol Cell Biol 20(6):1899–1910
Levine M, Tjian R (2003) Transcription regulation and animal diversity. Nature 424(6945):147–151. doi:10.1038/nature01763
Mohrmann L, Langenberg K, Krijgsveld J, Kal AJ, Heck AJ, Verrijzer CP (2004) Differential targeting of two distinct SWI/SNF-related Drosophila chromatin-remodeling complexes. Mol Cell Biol 24(8):3077–3088
Nie Z, Xue Y, Yang D, Zhou S, Deroo BJ, Archer TK, Wang W (2000) A specificity and targeting subunit of a human SWI/SNF family-related chromatin-remodeling complex. Mol Cell Biol 20(23):8879–8888
Wang X, Nagl NG, Wilsker D, Van Scoy M, Pacchione S, Yaciuk P, Dallas PB, Moran E (2004) Two related ARID family proteins are alternative subunits of human SWI/SNF complexes. Biochem J 383(Pt 2):319–325. doi:10.1042/BJ20040524
Yan Z, Cui K, Murray DM, Ling C, Xue Y, Gerstein A, Parsons R, Zhao K, Wang W (2005) PBAF chromatin-remodeling complex requires a novel specificity subunit, BAF200, to regulate expression of selective interferon-responsive genes. Genes Dev 19(14):1662–1667. doi:10.1101/gad.1323805
Backx L, Seuntjens E, Devriendt K, Vermeesch J, Van Esch H (2011) A balanced translocation t(6;14)(q25.3;q13.2) leading to reciprocal fusion transcripts in a patient with intellectual disability and agenesis of corpus callosum. Cytogenet Genome Res 132(3):135–143. doi:10.1159/000321577
Hoyer J, Ekici AB, Endele S, Popp B, Zweier C, Wiesener A, Wohlleber E, Dufke A, Rossier E, Petsch C, Zweier M, Gohring I, Zink AM, Rappold G, Schrock E, Wieczorek D, Riess O, Engels H, Rauch A, Reis A (2012) Haploinsufficiency of ARID1B, a member of the SWI/SNF-a chromatin-remodeling complex, is a frequent cause of intellectual disability. Am J Hum Genet 90(3):565–572. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.02.007
Halgren C, Kjaergaard S, Bak M, Hansen C, El-Schich Z, Anderson CM, Henriksen KF, Hjalgrim H, Kirchhoff M, Bijlsma EK, Nielsen M, den Hollander NS, Ruivenkamp CA, Isidor B, Le Caignec C, Zannolli R, Mucciolo M, Renieri A, Mari F, Anderlid BM, Andrieux J, Dieux A, Tommerup N, Bache I (2012) Corpus callosum abnormalities, intellectual disability, speech impairment, and autism in patients with haploinsufficiency of ARID1B. Clin Genet 82(3):248–255. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.2011.01755.x
O’Roak BJ, Vives L, Girirajan S, Karakoc E, Krumm N, Coe BP, Levy R, Ko A, Lee C, Smith JD, Turner EH, Stanaway IB, Vernot B, Malig M, Baker C, Reilly B, Akey JM, Borenstein E, Rieder MJ, Nickerson DA, Bernier R, Shendure J, Eichler EE (2012) Sporadic autism exomes reveal a highly interconnected protein network of de novo mutations. Nature 485(7397):246–250. doi:10.1038/nature10989
Santen GW, Aten E, Sun Y, Almomani R, Gilissen C, Nielsen M, Kant SG, Snoeck IN, Peeters EA, Hilhorst-Hofstee Y, Wessels MW, den Hollander NS, Ruivenkamp CA, van Ommen GJ, Breuning MH, den Dunnen JT, van Haeringen A, Kriek M (2012) Mutations in SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex gene ARID1B cause Coffin-Siris syndrome. Nat Genet 44(4):379–380. doi:10.1038/ng.2217
Tsurusaki Y, Okamoto N, Ohashi H, Kosho T, Imai Y, Hibi-Ko Y, Kaname T, Naritomi K, Kawame H, Wakui K, Fukushima Y, Homma T, Kato M, Hiraki Y, Yamagata T, Yano S, Mizuno S, Sakazume S, Ishii T, Nagai T, Shiina M, Ogata K, Ohta T, Niikawa N, Miyatake S, Okada I, Mizuguchi T, Doi H, Saitsu H, Miyake N, Matsumoto N (2012) Mutations affecting components of the SWI/SNF complex cause Coffin-Siris syndrome. Nat Genet 44(4):376–378. doi:10.1038/ng.2219
Van Houdt JK, Nowakowska BA, Sousa SB, van Schaik BD, Seuntjens E, Avonce N, Sifrim A, Abdul-Rahman OA, van den Boogaard MJ, Bottani A, Castori M, Cormier-Daire V, Deardorff MA, Filges I, Fryer A, Fryns JP, Gana S, Garavelli L, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Hall BD, Horn D, Huylebroeck D, Klapecki J, Krajewska-Walasek M, Kuechler A, Lines MA, Maas S, Macdermot KD, McKee S, Magee A, de Man SA, Moreau Y, Morice-Picard F, Obersztyn E, Pilch J, Rosser E, Shannon N, Stolte-Dijkstra I, Van Dijck P, Vilain C, Vogels A, Wakeling E, Wieczorek D, Wilson L, Zuffardi O, van Kampen AH, Devriendt K, Hennekam R, Vermeesch JR (2012) Heterozygous missense mutations in SMARCA2 cause Nicolaides-Baraitser syndrome. Nat Genet 44(4):445–449. doi:10.1038/ng.1105, S441
Kosho T, Okamoto N, Coffin-Siris Syndrome International C (2014) Genotype-phenotype correlation of Coffin-Siris syndrome caused by mutations in SMARCB1, SMARCA4, SMARCE1, and ARID1A. Am J Med Genet C: Semin Med Genet 166C(3):262–275. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31407
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25(14):1754–1760. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C, Philippakis AA, del Angel G, Rivas MA, Hanna M, McKenna A, Fennell TJ, Kernytsky AM, Sivachenko AY, Cibulskis K, Gabriel SB, Altshuler D, Daly MJ (2011) A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet 43(5):491–498. doi:10.1038/ng.806
Genomes Project C, Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, Handsaker RE, Kang HM, Marth GT, McVean GA (2012) An integrated map of genetic variation from 1092 human genomes. Nature 491(7422):56–65. doi:10.1038/nature11632
Serve EV, NHLBI GO (2015) NHLBI GO exome sequencing project (ESP). Seattle, WA
OMIM Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. In: McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine JHM, National Human Genome Research Institute, editor. An online catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. Baltimore, MA
Landrum MJ, Lee JM, Riley GR, Jang W, Rubinstein WS, Church DM, Maglott DR (2014) ClinVar: public archive of relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):D980–D985. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1113
Bartholdi D, Roelfsema JH, Papadia F, Breuning MH, Niedrist D, Hennekam RC, Schinzel A, Peters DJ (2007) Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: delineation of the phenotype of the first patients carrying mutations in EP300. J Med Genet 44(5):327–333. doi:10.1136/jmg.2006.046698
Zhang X, Azhar G, Zhong Y, Wei JY (2006) Zipzap/p200 is a novel zinc finger protein contributing to cardiac gene regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346(3):794–801. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.05.211
Patsialou A, Wilsker D, Moran E (2005) DNA-binding properties of ARID family proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 33(1):66–80. doi:10.1093/nar/gki145
Wilsker D, Patsialou A, Dallas PB, Moran E (2002) ARID proteins: a diverse family of DNA binding proteins implicated in the control of cell growth, differentiation, and development. Cell Growth Differ 13(3):95–106
Kortschak RD, Tucker PW, Saint R (2000) ARID proteins come in from the desert. Trends Biochem Sci 25(6):294–299
Lessard J, Wu JI, Ranish JA, Wan M, Winslow MM, Staahl BT, Wu H, Aebersold R, Graef IA, Crabtree GR (2007) An essential switch in subunit composition of a chromatin remodeling complex during neural development. Neuron 55(2):201–215. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2007.06.019
He L, Tian X, Zhang H, Hu T, Huang X, Zhang L, Wang Z, Zhou B (2014) BAF200 is required for heart morphogenesis and coronary artery development. PLoS One 9(10), e109493. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109493
Xue Y, Canman JC, Lee CS, Nie Z, Yang D, Moreno GT, Young MK, Salmon ED, Wang W (2000) The human SWI/SNF-B chromatin-remodeling complex is related to yeast rsc and localizes at kinetochores of mitotic chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(24):13015–13020. doi:10.1073/pnas.240208597
Yoo AS, Crabtree GR (2009) ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling in neural development. Curr Opin Neurobiol 19(2):120–126. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2009.04.006
Loe-Mie Y, Lepagnol-Bestel AM, Maussion G, Doron-Faigenboim A, Imbeaud S, Delacroix H, Aggerbeck L, Pupko T, Gorwood P, Simonneau M, Moalic JM (2010) SMARCA2 and other genome-wide supported schizophrenia-associated genes: regulation by REST/NRSF, network organization and primate-specific evolution. Hum Mol Genet 19(14):2841–2857. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq184
Son EY, Crabtree GR (2014) The role of BAF (mSWI/SNF) complexes in mammalian neural development. Am J Med Genet C: Semin Med Genet 166C(3):333–349. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.31416
Kruger AV, Jelier R, Dzyubachyk O, Zimmerman T, Meijering E, Lehner B (2014) Comprehensive single cell-resolution analysis of the role of chromatin regulators in early C. elegans embryogenesis. Dev Biol. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.10.014
Xu F, Flowers S, Moran E (2012) Essential role of ARID2 protein-containing SWI/SNF complex in tissue-specific gene expression. J Biol Chem 287(7):5033–5041. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.279968
Schratt G, Philippar U, Hockemeyer D, Schwarz H, Alberti S, Nordheim A (2004) SRF regulates Bcl-2 expression and promotes cell survival during murine embryonic development. EMBO J 23(8):1834–1844. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600188
Poser S, Impey S, Trinh K, Xia Z, Storm DR (2000) SRF-dependent gene expression is required for PI3-kinase-regulated cell proliferation. EMBO J 19(18):4955–4966. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.18.4955
Wang Z, Wang DZ, Hockemeyer D, McAnally J, Nordheim A, Olson EN (2004) Myocardin and ternary complex factors compete for SRF to control smooth muscle gene expression. Nature 428(6979):185–189. doi:10.1038/nature02382
Bajpai R, Chen DA, Rada-Iglesias A, Zhang J, Xiong Y, Helms J, Chang CP, Zhao Y, Swigut T, Wysocka J (2010) CHD7 cooperates with PBAF to control multipotent neural crest formation. Nature 463(7283):958–962. doi:10.1038/nature08733
Vissers LE, van Ravenswaaij CM, Admiraal R, Hurst JA, de Vries BB, Janssen IM, van der Vliet WA, Huys EH, de Jong PJ, Hamel BC, Schoenmakers EF, Brunner HG, Veltman JA, van Kessel AG (2004) Mutations in a new member of the chromodomain gene family cause CHARGE syndrome. Nat Genet 36(9):955–957. doi:10.1038/ng1407
Sanlaville D, Verloes A (2007) CHARGE syndrome: an update. Eur J Hum Genet 15(4):389–399. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201778
Watanabe R, Ui A, Kanno S, Ogiwara H, Nagase T, Kohno T, Yasui A (2014) SWI/SNF factors required for cellular resistance to DNA damage include ARID1A and ARID1B and show interdependent protein stability. Cancer Res 74(9):2465–2475. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3608
Tolstorukov MY, Sansam CG, Lu P, Koellhoffer EC, Helming KC, Alver BH, Tillman EJ, Evans JA, Wilson BG, Park PJ, Roberts CW (2013) Swi/Snf chromatin remodeling/tumor suppressor complex establishes nucleosome occupancy at target promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(25):10165–10170. doi:10.1073/pnas.1302209110
Helming KC, Wang X, Roberts CW (2014) Vulnerabilities of mutant SWI/SNF complexes in cancer. Cancer Cell 26(3):309–317. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2014.07.018
Kakarougkas A, Ismail A, Chambers AL, Riballo E, Herbert AD, Kunzel J, Lobrich M, Jeggo PA, Downs JA (2014) Requirement for PBAF in transcriptional repression and repair at DNA breaks in actively transcribed regions of chromatin. Mol Cell 55(5):723–732. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.06.028
Shiraishi Y, Fujimoto A, Furuta M, Tanaka H, Chiba K, Boroevich KA, Abe T, Kawakami Y, Ueno M, Gotoh K, Ariizumi S, Shibuya T, Nakano K, Sasaki A, Maejima K, Kitada R, Hayami S, Shigekawa Y, Marubashi S, Yamada T, Kubo M, Ishikawa O, Aikata H, Arihiro K, Ohdan H, Yamamoto M, Yamaue H, Chayama K, Tsunoda T, Miyano S, Nakagawa H (2014) Integrated analysis of whole genome and transcriptome sequencing reveals diverse transcriptomic aberrations driven by somatic genomic changes in liver cancers. PLoS One 9(12), e114263. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0114263
Guichard C, Amaddeo G, Imbeaud S, Ladeiro Y, Pelletier L, Maad IB, Calderaro J, Bioulac-Sage P, Letexier M, Degos F, Clement B, Balabaud C, Chevet E, Laurent A, Couchy G, Letouze E, Calvo F, Zucman-Rossi J (2012) Integrated analysis of somatic mutations and focal copy-number changes identifies key genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet 44(6):694–698. doi:10.1038/ng.2256
Hodis E, Watson IR, Kryukov GV, Arold ST, Imielinski M, Theurillat JP, Nickerson E, Auclair D, Li L, Place C, Dicara D, Ramos AH, Lawrence MS, Cibulskis K, Sivachenko A, Voet D, Saksena G, Stransky N, Onofrio RC, Winckler W, Ardlie K, Wagle N, Wargo J, Chong K, Morton DL, Stemke-Hale K, Chen G, Noble M, Meyerson M, Ladbury JE, Davies MA, Gershenwald JE, Wagner SN, Hoon DS, Schadendorf D, Lander ES, Gabriel SB, Getz G, Garraway LA, Chin L (2012) A landscape of driver mutations in melanoma. Cell 150(2):251–263. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.024
Ding L, Kim M, Kanchi KL, Dees ND, Lu C, Griffith M, Fenstermacher D, Sung H, Miller CA, Goetz B, Wendl MC, Griffith O, Cornelius LA, Linette GP, McMichael JF, Sondak VK, Fields RC, Ley TJ, Mule JJ, Wilson RK, Weber JS (2014) Clonal architectures and driver mutations in metastatic melanomas. PLoS One 9(11), e111153. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111153
Huang HT, Chen SM, Pan LB, Yao J, Ma HT (2015) Loss of function of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling genes leads to genome instability of human lung cancer. Oncol Rep 33(1):283–291. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3584
Iossifov I, O’Roak BJ, Sanders SJ, Ronemus M, Krumm N, Levy D, Stessman HA, Witherspoon KT, Vives L, Patterson KE, Smith JD, Paeper B, Nickerson DA, Dea J, Dong S, Gonzalez LE, Mandell JD, Mane SM, Murtha MT, Sullivan CA, Walker MF, Waqar Z, Wei L, Willsey AJ, Yamrom B, Lee YH, Grabowska E, Dalkic E, Wang Z, Marks S, Andrews P, Leotta A, Kendall J, Hakker I, Rosenbaum J, Ma B, Rodgers L, Troge J, Narzisi G, Yoon S, Schatz MC, Ye K, McCombie WR, Shendure J, Eichler EE, State MW, Wigler M (2014) The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder. Nature 515(7526):216–221. doi:10.1038/nature13908
Acknowledgements
We thank the families for their generous contributions. We thank the data review support from ExAC consortium. This work was supported in part by a grant from the Simons Foundation.
Conflicts of interest
Megan Cho, Kyle Retterer, Leandra Folk, Patrik Vitazka, and Jane Juusola are employees of GeneDx. Wendy Chung is a consultant to BioReference Laboratories. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shang, L., Cho, M.T., Retterer, K. et al. Mutations in ARID2 are associated with intellectual disabilities. Neurogenetics 16, 307–314 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-015-0454-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-015-0454-0