Abstract
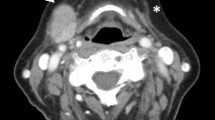
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibroinflammatory condition of unknown etiology. Although the salivary glands are currently considered among the most commonly affected among them, oral and maxillofacial surgeons are generally not familiar with the condition. Enlargement of the major salivary glands may be the first identifiable sign of IgG4-RD. A salivary gland biopsy along with IgG4 serum level assessment may help differentiate IgG4-related sialadenitis (IgG4-RS) from malignancies, infectious diseases, and obstructive conditions. Greater knowledge and higher levels of awareness of IgG4-RS may contribute to the expansion of differential diagnostic and treatment approaches. This case report describes a patient with bilateral submandibular salivary gland swelling who was diagnosed as having IgG4-RS on the basis of the histopathologic findings of a submandibular salivary gland biopsy and subsequent IgG4 levels.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fujita A, Sakai O, Chapman M, Sugimoto H (2012) IgG4-related disease of the head and neck: CT and MR imaging manifestations. Radiographics 32:1945–1958
Stone J, Zen Y, Deshpande V (2012) IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med 366:539–551
Maehara T, Pillai S, Stone J, Nakamura S (2019) Clinical features and mechanistic insights regarding IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis: a review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 48:908–916
Gagnier J, Kienle G, Altman D, Moher D, Sox H, Riley D (2013) The CARE guidelines: consensus-based clinical case report guideline development. J Diet Suppl 10:381–390
Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, Stone J (2011) The clinical and pathological features of IgG4-related disease. Curr Rheumatol Rep 13:473–481
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, Matsui S, Sumida T, Mimori T, Tanaka Y, Tsubota K, Yoshino T, Kawa S, Suzuki R, Takegami T, Tomosugi N, Kurose N, Ishigaki Y, Azumi A, Kojima M, Nakamura S, Inoue D (2012) A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol 22:1–14
Carruthers M, Khosroshahi A, Augustin T, Deshpande V, Stone J (2014) The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis 74:14–18
Khosroshahi A, Cheryk L, Carruthers M, Edwards J, Bloch D, Stone J (2013) Brief report: Spuriously low serum IgG4 concentrations caused by the prozone phenomenon in patients with IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol 66:213–217
Yu G (2017) Differential diagnosis of multiple enlargement of salivary glands. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 46:6
Masaki Y, Kurose N, Umehara H (2011) IgG4-related disease: a novel lymphoproliferative disorder discovered and established in Japan in the 21st century. J Clin Exp Hematop 51:13–20
Liu Y, Xue M, Wang Z et al (2019) Salivary gland involvement disparities in clinical characteristics of IgG4-related disease: a retrospective study of 428 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 59:634–640
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not needed.
Informed consent
Patient’s signed consent was obtained prior to the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoud, R., Ianculovici, C., Kleinman, S. et al. IgG4-related sialadenitis — a rare bilateral submandibular gland enlargement: case report. Oral Maxillofac Surg 26, 673–677 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-021-01020-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-021-01020-3