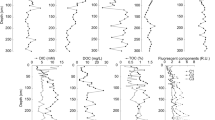
Abstract
In deep-sea cold seeps, microbial communities are shaped by geochemical components in seepage solutions. In the present study, we report the composition of microbial communities and potential metabolic activities in the surface sediment of Jiaolong cold seep at the northern South China Sea. Pyrosequencing of 16S rRNA gene amplicons revealed that a majority of the microbial inhabitants of the surface layers (0–6 cm) were sulfur oxidizer bacteria Sulfurimonas and archaeal methane consumer ANME-1, while sulfate reducer bacteria SEEP-SRB1, ANME-1 and ANME-2 dominated the bottom layers (8–14 cm). The potential ecological roles of the microorganisms were further supported by the presence of functional genes for methane oxidation, sulfur oxidation, sulfur reduction and nitrate reduction in the metagenomes. Metagenomic analysis revealed a significant correlation between coverage of 16S rRNA gene of sulfur oxidizer bacteria, functional genes involved in sulfur oxidation and nitrate reduction in different layers, indicating that sulfur oxidizing may be coupled to nitrate reducing at the surface layers of Jiaolong seeping site. This is probably related to the sulfur oxidizers of Sulfurimonas and Sulfurovum, which may be the capacity of nitrate reduction or associated with unidentified syntrophic nitrate-reducing microbes in the surface of the cold seep.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bankevich A et al (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477
Boetius A, Wenzhofer F (2013) Seafloor oxygen consumption fuelled by methane from cold seeps. Nat Geosci 6:725–734
Boetius A et al (2000) A marine microbial consortium apparently mediating anaerobic oxidation of methane. Nature 407:623–626
Cambon-Bonavita MA et al (2009) Diversity and distribution of methane-oxidizing microbial communities associated with different faunal assemblages in a giant pockmark of the Gabon continental margin. Deep Sea Res Part II 56:2248–2258
Caporaso JG, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, DeSantis TZ, Andersen GL, Knight R (2010a) PyNAST: a flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 26:266–267
Caporaso JG et al (2010b) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Castresana J (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17:540–552
Cui HP, Su X, Chen F, Wei SP, Chen SH, Wang JL (2016) Vertical distribution of archaeal communities in cold seep sediments from the Jiulong metane reef area in the South China Sea. Biosci J 32:1059–1068
Devol AH (2015) Denitrification, anammox, and N2 production in marine sediments. In: Carlson CA, Giovannoni SJ (eds) Annual review of marine science, vol 7, pp 403–423
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Feng D et al (2015) Using Bathymodiolus tissue stable carbon, nitrogen and sulfur isotopes to infer biogeochemical process at a cold seep in the South China Sea. Deep Sea Res Part I 104:52–59
Haas BJ et al (2011) Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome Res 21:494–504
Hallam SJ, Girguis PR, Preston CM, Richardson PM, DeLong EF (2003) Identification of methyl coenzyme M reductase A (mcrA) genes associated with methane-oxidizing archaea. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5483–5491
Han X et al (2005) Jiulong methane reef: first direct evidence of methane seepage in the South China Sea. Geophysical Research Abstracts, 7, 4055, European Geosciences Union
Han XQ et al (2008) Jiulong methane reef: microbial mediation of seep carbonates in the South China Sea. Mar Geol 249:243–256
Huang XQ, Madan A (1999) CAP3: a DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res 9:868–877
Hyatt D, LoCascio PF, Hauser LJ, Uberbacher EC (2012) Gene and translation initiation site prediction in metagenomic sequences. Bioinformatics 28:2223–2230
Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma K, Miyata T (2002) MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res 30:3059–3066
Kennedy J, Flemer B, Jackson SA, Lejon DP, Morrissey JP, O’Gara F, Dobson AD (2010) Marine metagenomics: new tools for the study and exploitation of marine microbial metabolism. Mar Drugs 8:608–628
Kleindienst S, Ramette A, Amann R, Knittel K (2012) Distribution and in situ abundance of sulfate-reducing bacteria in diverse marine hydrocarbon seep sediments. Environ Microbiol 14:2689–2710
Knittel K, Boetius A (2009) Anaerobic oxidation of methane: progress with an unknown process. Annu Rev Microbiol 63:311–334
Knittel K, Losekann T, Boetius A, Kort R, Amann R (2005) Diversity and distribution of methanotrophic archaea at cold seeps. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:467–479
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359
Lanoil BD, Sassen R, La Duc MT, Sweet ST, Nealson KH (2001) Bacteria and archaea physically associated with Gulf of Mexico gas hydrates. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5143–5153
Letunic I, Bork P (2016) Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res 44:W242–W245
Levin LA (2005) Ecology of cold seep sediments: interactions of fauna with flow, chemistry and microbes. In: Gibson RN, Atkinson RJA, Gordon JDM (eds) Oceanography and marine biology—an annual review, vol 43. Oceanography and marine biology. Crc Press-Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, pp 1–46
Li H et al (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079
Li X, Liu F, Hu Z, Zhou H, Wang C, Chen C (2014) Chinese JIAOLONG’s first scientific cruise in 2013. J Ship Mech 18:344–354
Losekann T, Knittel K, Nadalig T, Fuchs B, Niemann H, Boetius A, Amann R (2007) Diversity and abundance of aerobic and anaerobic methane oxidizers at the Haakon Mosby Mud Volcano, Barents Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3348–3362
Mason OU, Case DH, Naehr TH, Lee RW, Thomas RB, Bailey JV, Orphan VJ (2015) Comparison of archaeal and bacterial diversity in methane seep carbonate nodules and host sediments, Eel River Basin and Hydrate Ridge, USA. Microb Ecol 70:766–784
McDonald IR, Murrell JC (1997) The particulate methane monooxygenase gene pmoA and its use as a functional gene probe for methanotrophs. FEMS Microbiol Lett 156:205–210
McGlynn SE, Chadwick GL, Kempes CP, Orphan VJ (2015) Single cell activity reveals direct electron transfer in methanotrophic consortia. Nature 526:531–535
Meyer B, Kuever J (2007) Phylogeny of the alpha and beta subunits of the dissimilatory adenosine-5′-phosphosulfate (APS) reductase from sulfate-reducing prokaryotes—origin and evolution of the dissimilatory sulfate-reduction pathway. Microbiology 153:2026–2044
Mino S, Kudo H, Arai T, Sawabe T, Takai K, Nakagawa S (2014) Sulfurovum aggregans sp. nov., a hydrogen-oxidizing, thiosulfate-reducing chemolithoautotroph within the Epsilonproteobacteria isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimney, and an emended description of the genus Sulfurovum. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3195–3201
Niemann H et al (2006) Novel microbial communities of the Haakon Mosby mud volcano and their role as a methane sink. Nature 443:854–858
Nunoura T, Takaki Y, Kazama H, Hirai M, Ashi J, Imachi H, Takai K (2012) Microbial diversity in deep-sea methane seep sediments presented by SSU rRNA gene tag sequencing. Microbes Environ 27:382–390
Orphan VJ et al (2001a) Comparative analysis of methane-oxidizing archaea and sulfate-reducing bacteria in anoxic marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1922–1934
Orphan VJ, House CH, Hinrichs KU, McKeegan KD, DeLong EF (2001b) Methane-consuming archaea revealed by directly coupled isotopic and phylogenetic analysis. Science 293:484–487
Orphan VJ, House CH, Hinrichs KU, McKeegan KD, DeLong EF (2002) Multiple archaeal groups mediate methane oxidation in anoxic cold seep sediments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7663–7668
Patel RK, Jain M (2012) NGS QC toolkit: a toolkit for quality control of next generation sequencing data. PLoS One 7(2):e30619
Paull CK et al (1984) Biological communities at the Florida escarpment resemble hydrothermal vent taxa. Science 226:965–967
Pop Ristova P, Wenzhofer F, Ramette A, Felden J, Boetius A (2015) Spatial scales of bacterial community diversity at cold seeps (Eastern Mediterranean Sea). ISME J 9:1306–1318
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2009) FastTree: computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol Biol Evol 26:1641–1650
Quast C et al (2012) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D590–D596
Ruff SE, Arnds J, Knittel K, Amann R, Wegener G, Ramette A, Boetius A (2013) Microbial communities of deep-sea methane seeps at Hikurangi continental margin (New Zealand). PLoS One 8(9):e72627
Ruff SE, Biddle JF, Teske AP, Knittel K, Boetius A, Ramette A (2015) Global dispersion and local diversification of the methane seep microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:4015–4020
Sibuet M, Olu K (1998) Biogeography, biodiversity and fluid dependence of deep-sea cold-seep communities at active and passive margins. Deep Sea Res Part II 45:517–567
Sievert SM et al (2008) Genome of the epsilonproteobacterial chemolithoautotroph Sulfurimonas denitrificans. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1145–1156
Simon C, Daniel R (2011) Metagenomic analyses: past and future trends. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:1153–1161
Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J (2008) A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML Web servers. Syst Biol 57:758–771
Suess E (2005) RV SONNE Cruise report SO177, Sino-German cooperative project, South China Sea continental margin: geological methane budget and environmental effects of methane emissions and gashydrates. IFM-GEOMAR reports
Takai K, Suzuki M, Nakagawa S, Miyazaki M, Suzuki Y, Inagaki F, Horikoshi K (2006) Sulfurimonas paralvinellae sp. nov., a novel mesophilic, hydrogen- and sulfur-oxidizing chemolithoautotroph within the Epsilonproteobacteria isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent polychaete nest, reclassification of Thiomicrospira denitrificans as Sulfurimonas denitrificans comb. nov. and emended description of the genus Sulfurimonas. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1725–1733
Taylor B, Hayes DE (2013) Origin and history of the South China Sea basin. In: Wefer G, Billett D, Hebbeln D, Jørgensen BB, Schlüter M, van Weering TCE (eds) Ocean margin systems. Springer, Berlin, pp 457–477
Tian R-M, Wang Y, Bougouffa S, Gao Z-M, Cai L, Bajic V, Qian P-Y (2014) Genomic analysis reveals versatile heterotrophic capacity of a potentially symbiotic sulfur-oxidizing bacterium in sponge. Environ Microbiol 16:3548–3561
Tringe SG, Rubin EM (2005) Metagenomics: DNA sequencing of environmental samples. Nat Rev Genet 6:805–814
Vigneron A, Cruaud P, Pignet P, Caprais JC, Cambon-Bonavita MA, Godfroy A, Toffin L (2013) Archaeal and anaerobic methane oxidizer communities in the Sonora Margin cold seeps, Guaymas Basin (Gulf of California). ISME J 7:1595–1608
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267
Wang FP et al (2014a) Methanotrophic archaea possessing diverging methane-oxidizing and electron-transporting pathways. ISME J 8:1069–1078
Wang Y, Tian RM, Gao ZM, Bougouffa S, Qian PY (2014b) Optimal eukaryotic 18S and universal 16S/18S ribosomal RNA primers and their application in a study of symbiosis. PLoS One 9(3):e90053
Zhang Y et al (2012) Microbial diversity in cold seep sediments from the northern South China Sea. Geosci Front 3:301–316
Acknowledgements
The team members of the Jiaolong manned submersible are thankful for their efforts in the sampling cruise. The present study was supported by National Science Foundation of China (nos. 41476104 and 31460001), The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0302500) and the Strategic Priority Research Program B of Chinese Academy of Sciences, nos. XDB06010201 and XDB06010102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by L. Huang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Qiu, JW., Qian, PY. et al. The vertical distribution of prokaryotes in the surface sediment of Jiaolong cold seep at the northern South China Sea. Extremophiles 22, 499–510 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-018-1012-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-018-1012-0