Abstract
Objectives
Research across many fields of medicine now points towards the clinical advantages of combining regenerative procedures with platelet-rich fibrin (PRF). This systematic review aimed to gather the extensive number of articles published to date on PRF in the dental field to better understand the clinical procedures where PRF may be utilized to enhance tissue/bone formation.
Materials and methods
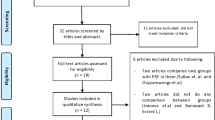
Manuscripts were searched systematically until May 2016 and separated into the following categories: intrabony and furcation defect regeneration, extraction socket management, sinus lifting procedures, gingival recession treatment, and guided bone regeneration (GBR) including horizontal/vertical bone augmentation procedures. Only human randomized clinical trials were included for assessment.
Results
In total, 35 articles were selected and divided accordingly (kappa = 0.94). Overall, the use of PRF has been most investigated in periodontology for the treatment of periodontal intrabony defects and gingival recessions where the majority of studies have demonstrated favorable results in soft tissue management and repair. Little to no randomized clinical trials were found for extraction socket management although PRF has been shown to significantly decrease by tenfold dry sockets of third molars. Very little to no data was available directly investigating the effects of PRF on new bone formation in GBR, horizontal/vertical bone augmentation procedures, treatment of peri-implantitis, and sinus lifting procedures.
Conclusions
Much investigation now supports the use of PRF for periodontal and soft tissue repair. Despite this, there remains a lack of well-conducted studies demonstrating convincingly the role of PRF during hard tissue bone regeneration. Future human randomized clinical studies evaluating the use of PRF on bone formation thus remain necessary.
Clinical relevance
PRF was shown to improve soft tissue generation and limit dimensional changes post-extraction, with little available data to date supporting its use in GBR.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dangaria SJ, Ito Y, Walker C, Druzinsky R, Luan X, Diekwisch TG (2009) Extracellular matrix-mediated differentiation of periodontal progenitor cells. Differentiation 78:79–90. doi:10.1016/j.diff.2009.03.005
Hollander A, Macchiarini P, Gordijn B, Birchall M (2009) The first stem cell-based tissue-engineered organ replacement: implications for regenerative medicine and society. Regen Med 4:147–148. doi:10.2217/17460751.4.2.147
Choukroun J, Adda F, Schoeffler C, Vervelle A (2001) Une opportunité en paro-implantologie: le PRF. Implantodontie 42:e62
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J, Gogly B (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part II: platelet-related biologic features. Oral Surg, Oral Med, Oral Pathol, Oral Radiol Endod 101:e45–e50. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.009
Kang YH, Jeon SH, Park JY, Chung JH, Choung YH, Choung HW, Kim ES, Choung PH (2011) Platelet-rich fibrin is a bioscaffold and reservoir of growth factors for tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng A 17:349–359. doi:10.1089/ten.TEA.2010.0327
He L, Lin Y, Hu X, Zhang Y, Wu H (2009) A comparative study of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on the effect of proliferation and differentiation of rat osteoblasts in vitro. Oral Surg, Oral Med, Oral Pathol, Oral Radiol Endod 108:707–713. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.06.044
Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Diss A, Odin G, Doglioli P, Hippolyte MP, Charrier JB (2009) In vitro effects of Choukroun’s PRF (platelet-rich fibrin) on human gingival fibroblasts, dermal prekeratinocytes, preadipocytes, and maxillofacial osteoblasts in primary cultures. Oral Surg, Oral Med, Oral Pathol, Oral Radiol Endod 108:341–352. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.04.020
Anfossi G, Trovati M, Mularoni E, Massucco P, Calcamuggi G, Emanuelli G (1989) Influence of propranolol on platelet aggregation and thromboxane B2 production from platelet-rich plasma and whole blood. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids 36:1–7
Fijnheer R, Pietersz RN, de Korte D, Gouwerok CW, Dekker WJ, Reesink HW, Roos D (1990) Platelet activation during preparation of platelet concentrates: a comparison of the platelet-rich plasma and the buffy coat methods. Transfusion 30:634–638
Jameson C (2007) Autologous platelet concentrate for the production of platelet gel. Lab Med 38:39–42
Whitman DH, Berry RL, Green DM (1997) Platelet gel: an autologous alternative to fibrin glue with applications in oral and maxillofacial surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55:1294–1299
Marx RE, Carlson ER, Eichstaedt RM, Schimmele SR, Strauss JE, Georgeff KR (1998) Platelet-rich plasma: growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 85:638–646
Marx RE (2004) Platelet-rich plasma: evidence to support its use. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 62:489–496
Anitua E (1999) Plasma rich in growth factors: preliminary results of use in the preparation of future sites for implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 14:529–535
Anitua E, Prado R, Troya M, Zalduendo M, de la Fuente M, Pino A, Muruzabal F, Orive G (2016) Implementation of a more physiological plasma rich in growth factor (PRGF) protocol: anticoagulant removal and reduction in activator concentration. Platelets 27:459–466. doi:10.3109/09537104.2016.1143921
Lucarelli E, Beretta R, Dozza B, Tazzari PL, O’Connel SM, Ricci F, Pierini M, Squarzoni S, Pagliaro PP, Oprita EI, Donati D (2010) A recently developed bifacial platelet-rich fibrin matrix. Eur Cell Mater 20:13–23
Saluja H, Dehane V, Mahindra U (2011) Platelet-rich fibrin: a second generation platelet concentrate and a new friend of oral and maxillofacial surgeons. Ann Maxillofac Surg 1:53–57. doi:10.4103/2231-0746.83158
Kobayashi E, Fluckiger L, Fujioka-Kobayashi M, Sawada K, Sculean A, Schaller B, Miron RJ (2016) Comparative release of growth factors from PRP, PRF, and advanced-PRF. Clin Oral Investig. doi:10.1007/s00784-016-1719-1
Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Del Corso M, Diss A, Mouhyi J, Charrier JB (2010) Three-dimensional architecture and cell composition of a Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin clot and membrane. J Periodontol 81:546–555. doi:10.1902/jop.2009.090531
Toffler M, Toscano N, Holtzclaw D, Corso M, Dohan D (2009) Introducing Choukroun’s platelet rich fibrin (PRF) to the reconstructive surgery milieu. J Implant Adv Clin Dent 1:22–31
Tsay RC, Vo J, Burke A, Eisig SB, Lu HH, Landesberg R (2005) Differential growth factor retention by platelet-rich plasma composites. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:521–528. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2004.09.012
Carlson NE, Roach RB Jr (2002) Platelet-rich plasma: clinical applications in dentistry. J Am Dent Assoc 1939(133):1383–1386
Andrades JA, Han B, Becerra J, Sorgente N, Hall FL, Nimni ME (1999) A recombinant human TGF-beta1 fusion protein with collagen-binding domain promotes migration, growth, and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal cells. Exp Cell Res 250:485–498. doi:10.1006/excr.1999.4528
Lind M, Deleuran B, Thestrup-Pedersen K, Soballe K, Eriksen EF, Bunger C (1995) Chemotaxis of human osteoblasts. Effects of osteotropic growth factors. APMIS 103:140–146
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J, Gogly B (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part III: leucocyte activation: a new feature for platelet concentrates? Oral Surg, Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:e51–e55. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.010
Grando Mattuella L, Poli de Figueiredo JA, Nor JE, de Araujo FB, Medeiros Fossati AC (2007) Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 expression in the pulp of human primary and young permanent teeth. J Endod 33:1408–1412. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2007.08.019
Troost E, Hold GL, Smith MG, Chow WH, Rabkin CS, McColl KE, El-Omar EM (2003) The role of interleukin-1beta and other potential genetic markers as indicators of gastric cancer risk. Can J Gastroenterol 17(Suppl B):8B–12B
Kishimoto T, Akira S, Narazaki M, Taga T (1995) Interleukin-6 family of cytokines and gp130. Blood 86:1243–1254
Kishimoto T (1989) The biology of interleukin-6. Blood 74:1–10
Waters JP, Pober JS, Bradley JR (2013) Tumour necrosis factor in infectious disease. J Pathol 230:132–147. doi:10.1002/path.4187
Murtaugh MP, Johnson CR, Xiao Z, Scamurra RW, Zhou Y (2009) Species specialization in cytokine biology: is interleukin-4 central to the T(H)1-T(H)2 paradigm in swine? Dev Comp Immunol 33:344–352. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2008.06.014
Li Z, Zhang Y, Sun B (2011) Current understanding of Th2 cell differentiation and function. Protein Cell 2:604–611. doi:10.1007/s13238-011-1083-5
Choukroun J, Diss A, Simonpieri A, Girard MO, Schoeffler C, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J, Dohan DM (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part IV: clinical effects on tissue healing. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:e56–e60. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.011
Clark RA (2001) Fibrin and wound healing. Ann N Y Acad Sci 936:355–367
Swartz MK (2011) The PRISMA statement: a guideline for systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J Pediatr Health Care 25:1–2. doi:10.1016/j.pedhc.2010.09.006
Agarwal A, Gupta ND, Jain A (2016) Platelet rich fibrin combined with decalcified freeze-dried bone allograft for the treatment of human intrabony periodontal defects: a randomized split mouth clinical trail. Acta Odontol Scand 74:36–43. doi:10.3109/00016357.2015.1035672
Ajwani H, Shetty S, Gopalakrishnan D, Kathariya R, Kulloli A, Dolas RS, Pradeep AR (2015) Comparative evaluation of platelet-rich fibrin biomaterial and open flap debridement in the treatment of two and three wall intrabony defects. J Int Oral Health 7:32–37
Elgendy EA, Abo Shady TE (2015) Clinical and radiographic evaluation of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite with or without platelet-rich fibrin membrane in the treatment of periodontal intrabony defects. J Indian Soc Periodontol 19:61–65. doi:10.4103/0972-124x.148639
Panda S, Sankari M, Satpathy A, Jayakumar D, Mozzati M, Mortellaro C, Gallesio G, Taschieri S, Del Fabbro M (2016) Adjunctive effect of autologus platelet-rich fibrin to barrier membrane in the treatment of periodontal intrabony defects. J Craniofac Surg 27:691–696. doi:10.1097/scs.0000000000002524
Pradeep AR, Nagpal K, Karvekar S, Patnaik K, Naik SB, Guruprasad CN (2015) Platelet-rich fibrin with 1% metformin for the treatment of intrabony defects in chronic periodontitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol 86:729–737. doi:10.1902/jop.2015.140646
Pradeep AR, Rao NS, Agarwal E, Bajaj P, Kumari M, Naik SB (2012) Comparative evaluation of autologous platelet-rich fibrin and platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of 3-wall intrabony defects in chronic periodontitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol 83:1499–1507. doi:10.1902/jop.2012.110705
Shah M, Patel J, Dave D, Shah S (2015) Comparative evaluation of platelet-rich fibrin with demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft in periodontal infrabony defects: a randomized controlled clinical study. J Indian Soc Periodontol 19:56–60. doi:10.4103/0972-124x.145803
Thorat M, Pradeep AR, Pallavi B (2011) Clinical effect of autologous platelet-rich fibrin in the treatment of intra-bony defects: a controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol 38:925–932. doi:10.1111/j.1600-051X.2011.01760.x
Pradeep AR, Bajaj P, Rao NS, Agarwal E, Naik SB (2012) Platelet-rich fibrin combined with a porous hydroxyapatite graft for the treatment of three-wall intrabony defects in chronic periodontitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. doi:10.1902/jop.2012.110722
Sharma A, Pradeep AR (2011) Treatment of 3-wall intrabony defects in patients with chronic periodontitis with autologous platelet-rich fibrin: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol 82:1705–1712. doi:10.1902/jop.2011.110075
Sharma A, Pradeep AR (2011) Autologous platelet-rich fibrin in the treatment of mandibular degree II furcation defects: a randomized clinical trial. J Periodontol 82:1396–1403. doi:10.1902/jop.2011.100731
Bajaj P, Pradeep AR, Agarwal E, Rao NS, Naik SB, Priyanka N, Kalra N (2013) Comparative evaluation of autologous platelet-rich fibrin and platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of mandibular degree II furcation defects: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontal Res. doi:10.1111/jre.12040
Pradeep AR, Karvekar S, Nagpal K, Patnaik K, Raju A, Singh P (2016) Rosuvastatin 1.2 mg in situ gel combined with 1:1 mixture of autologous platelet-rich fibrin and porous hydroxyapatite bone graft in surgical treatment of mandibular class II furcation defects: a randomized clinical control trial. J Periodontol 87:5–13. doi:10.1902/jop.2015.150131
Agarwal SK, Jhingran R, Bains VK, Srivastava R, Madan R, Rizvi I (2016) Patient-centered evaluation of microsurgical management of gingival recession using coronally advanced flap with platelet-rich fibrin or amnion membrane: a comparative analysis. Eur J Dent 10:121–133. doi:10.4103/1305-7456.175686
Aleksic Z, Jankovic S, Dimitrijevic B, Divnic-Resnik T, Milinkovic I, Lekovic V (2010) The use of platelet-rich fibrin membrane in gingival recession treatment. Srp Arh Celok Lek 138:11–18
Aroca S, Keglevich T, Barbieri B, Gera I, Etienne D (2009) Clinical evaluation of a modified coronally advanced flap alone or in combination with a platelet-rich fibrin membrane for the treatment of adjacent multiple gingival recessions: a 6-month study. J Periodontol 80:244–252. doi:10.1902/jop.2009.080253
Dogan SB, Dede FO, Balli U, Atalay EN, Durmuslar MC (2015) Concentrated growth factor in the treatment of adjacent multiple gingival recessions: a split-mouth randomized clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol 42:868–875. doi:10.1111/jcpe.12444
Eren G, Atilla G (2014) Platelet-rich fibrin in the treatment of localized gingival recessions: a split-mouth randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig 18:1941–1948. doi:10.1007/s00784-013-1170-5
Gupta S, Banthia R, Singh P, Banthia P, Raje S, Aggarwal N (2015) Clinical evaluation and comparison of the efficacy of coronally advanced flap alone and in combination with platelet rich fibrin membrane in the treatment of Miller class I and II gingival recessions. Contemp Clin Dent 6:153–160. doi:10.4103/0976-237x.156034
Jankovic S, Aleksic Z, Klokkevold P, Lekovic V, Dimitrijevic B, Kenney EB, Camargo P (2012) Use of platelet-rich fibrin membrane following treatment of gingival recession: a randomized clinical trial. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 32:e41–e50
Jankovic S, Aleksic Z, Milinkovic I, Dimitrijevic B (2010) The coronally advanced flap in combination with platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and enamel matrix derivative in the treatment of gingival recession: a comparative study. Eur J Esthet Dent 5:260–273
Keceli HG, Kamak G, Erdemir EO, Evginer MS, Dolgun A (2015) The adjunctive effect of platelet-rich fibrin to connective tissue graft in the treatment of buccal recession defects: results of a randomized, parallel-group controlled trial. J Periodontol 86:1221–1230. doi:10.1902/jop.2015.150015
Padma R, Shilpa A, Kumar PA, Nagasri M, Kumar C, Sreedhar A (2013) A split mouth randomized controlled study to evaluate the adjunctive effect of platelet-rich fibrin to coronally advanced flap in Miller’s class-I and II recession defects. J Indian Soc Periodontol 17:631–636. doi:10.4103/0972-124x.119281
Rajaram V, Thyegarajan R, Balachandran A, Aari G, Kanakamedala A (2015) Platelet rich fibrin in double lateral sliding bridge flap procedure for gingival recession coverage: an original study. J Indian Soc Periodontol 19:665–670. doi:10.4103/0972-124x.164764
Thamaraiselvan M, Elavarasu S, Thangakumaran S, Gadagi JS, Arthie T (2015) Comparative clinical evaluation of coronally advanced flap with or without platelet rich fibrin membrane in the treatment of isolated gingival recession. J Indian Soc Periodontol 19:66–71. doi:10.4103/0972-124x.145790
Tunaliota M, Ozdemir H, Arabaciota T, Gurbuzer B, Pikdoken L, Firatli E (2015) Clinical evaluation of autologous platelet-rich fibrin in the treatment of multiple adjacent gingival recession defects: a 12-month study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 35:105–114. doi:10.11607/prd.1826
Femminella B, Iaconi MC, Di Tullio M, Romano L, Sinjari B, D’Arcangelo C, De Ninis P, Paolantonio M (2016) Clinical comparison of platelet-rich fibrin and a gelatin sponge in the management of palatal wounds after epithelialized free gingival graft harvest: a randomized clinical trial. J Periodontol 87:103–113. doi:10.1902/jop.2015.150198
Moraschini V, Barboza Edos S (2016) Use of platelet-rich fibrin membrane in the treatment of gingival recession: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Periodontol 87:281–290. doi:10.1902/jop.2015.150420
De Risi V, Clementini M, Vittorini G, Mannocci A, De Sanctis M (2015) Alveolar ridge preservation techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis of histological and histomorphometrical data. Clin Oral Implants Res 26:50–68. doi:10.1111/clr.12288
Jambhekar S, Kernen F, Bidra AS (2015) Clinical and histologic outcomes of socket grafting after flapless tooth extraction: a systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials. J Prosthet Dent 113:371–382. doi:10.1016/j.prosdent.2014.12.009
Moraschini V, Barboza ED (2016) Quality assessment of systematic reviews on alveolar socket preservation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2016.03.010
Chappuis V, Engel O, Reyes M, Shahim K, Nolte LP, Buser D (2013) Ridge alterations post-extraction in the esthetic zone: a 3D analysis with CBCT. J Dental Res 92:195s–201s. doi:10.1177/0022034513506713
Girish Rao S, Bhat P, Nagesh KS, Rao GH, Mirle B, Kharbhari L, Gangaprasad B (2013) Bone regeneration in extraction sockets with autologous platelet rich fibrin gel. J Maxillofac Oral Surgery 12:11–16. doi:10.1007/s12663-012-0370-x
Suttapreyasri S, Leepong N (2013) Influence of platelet-rich fibrin on alveolar ridge preservation. J Craniofac Surg 24:1088–1094. doi:10.1097/SCS.0b013e31828b6dc3
Hoaglin DR, Lines GK (2013) Prevention of localized osteitis in mandibular third-molar sites using platelet-rich fibrin. Int J Dent 2013:875380. doi:10.1155/2013/875380
Hauser F, Gaydarov N, Badoud I, Vazquez L, Bernard JP, Ammann P (2013) Clinical and histological evaluation of postextraction platelet-rich fibrin socket filling: a prospective randomized controlled study. Implant Dent 22:295–303. doi:10.1097/ID.0b013e3182906eb3
Tajima N, Ohba S, Sawase T, Asahina I (2013) Evaluation of sinus floor augmentation with simultaneous implant placement using platelet-rich fibrin as sole grafting material. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 28:77–83. doi:10.11607/jomi.2613
Mazor Z, Horowitz RA, Del Corso M, Prasad HS, Rohrer MD, Dohan Ehrenfest DM (2009) Sinus floor augmentation with simultaneous implant placement using Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin as the sole grafting material: a radiologic and histologic study at 6 months. J Periodontol 80:2056–2064. doi:10.1902/jop.2009.090252
Simonpieri A, Choukroun J, Del Corso M, Sammartino G, Dohan Ehrenfest DM (2011) Simultaneous sinus-lift and implantation using microthreaded implants and leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin as sole grafting material: a six-year experience. Implant Dent 20:2–12. doi:10.1097/ID.0b013e3181faa8af
Inchingolo F, Tatullo M, Marrelli M, Inchingolo AM, Scacco S, Inchingolo AD, Dipalma G, Vermesan D, Abbinante A, Cagiano R (2010) Trial with platelet-rich fibrin and Bio-Oss used as grafting materials in the treatment of the severe maxillar bone atrophy: clinical and radiological evaluations. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 14:1075–1084
Tatullo M, Marrelli M, Cassetta M, Pacifici A, Stefanelli LV, Scacco S, Dipalma G, Pacifici L, Inchingolo F (2012) Platelet rich fibrin (P.R.F.) in reconstructive surgery of atrophied maxillary bones: clinical and histological evaluations. Int J Med Sci 9:872–880. doi:10.7150/ijms.5119
Zhang Y, Tangl S, Huber CD, Lin Y, Qiu L, Rausch-Fan X (2012) Effects of Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin on bone regeneration in combination with deproteinized bovine bone mineral in maxillary sinus augmentation: a histological and histomorphometric study. J Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg 40:321–328. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2011.04.020
Choukroun J, Diss A, Simonpieri A, Girard MO, Schoeffler C, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J, Dohan DM (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part V: histologic evaluations of PRF effects on bone allograft maturation in sinus lift. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Rad Endod 101:299–303. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2005.07.012
Ali S, Bakry SA, Abd-Elhakam H (2015) Platelet-rich fibrin in maxillary sinus augmentation: a systematic review. J Oral Implantol 41:746–753. doi:10.1563/aaid-joi-D-14-00167
Roy S, Driggs J, Elgharably H, Biswas S, Findley M, Khanna S, Gnyawali U, Bergdall VK, Sen CK (2011) Platelet-rich fibrin matrix improves wound angiogenesis via inducing endothelial cell proliferation. Wound Repair Regen 19:753–766. doi:10.1111/j.1524-475X.2011.00740.x
Chen FM, Wu LA, Zhang M, Zhang R, Sun HH (2011) Homing of endogenous stem/progenitor cells for in situ tissue regeneration: promises, strategies, and translational perspectives. Biomaterials 32:3189–3209. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.12.032
Steed DL, Donohoe D, Webster MW, Lindsley L (1996) Effect of extensive debridement and treatment on the healing of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetic Ulcer Study Group. J Am Coll Surg 183:61–64
Wieman TJ, Smiell JM, Su Y (1998) Efficacy and safety of a topical gel formulation of recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB (becaplermin) in patients with chronic neuropathic diabetic ulcers. A phase III randomized placebo-controlled double-blind study. Diabetes Care 21:822–827
White AP, Vaccaro AR, Hall JA, Whang PG, Friel BC, McKee MD (2007) Clinical applications of BMP-7/OP-1 in fractures, nonunions and spinal fusion. Int Orthop 31:735–741. doi:10.1007/s00264-007-0422-x
Miron RJ, Zhang YF (2012) Osteoinduction: a review of old concepts with new standards. J Dent Res 91:736–744. doi:10.1177/0022034511435260
Young CS, Ladd PA, Browning CF, Thompson A, Bonomo J, Shockley K, Hart CE (2009) Release, biological potency, and biochemical integrity of recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor-BB (rhPDGF-BB) combined with Augment(TM) Bone Graft or GEM 21S beta-tricalcium phosphate (beta-TCP). J Control Release 140:250–255. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.06.030
Park YJ, Lee YM, Lee JY, Seol YJ, Chung CP, Lee SJ (2000) Controlled release of platelet-derived growth factor-BB from chondroitin sulfate-chitosan sponge for guided bone regeneration. J Control Release 67:385–394
Wissink MJ, Beernink R, Poot AA, Engbers GH, Beugeling T, van Aken WG, Feijen J (2000) Improved endothelialization of vascular grafts by local release of growth factor from heparinized collagen matrices. J Control Release 64:103–114
Delgado JJ, Evora C, Sanchez E, Baro M, Delgado A (2006) Validation of a method for non-invasive in vivo measurement of growth factor release from a local delivery system in bone. J Control Release 114:223–229
Oe S, Fukunaka Y, Hirose T, Yamaoka Y, Tabata Y (2003) A trial on regeneration therapy of rat liver cirrhosis by controlled release of hepatocyte growth factor. J Control Release 88:193–200
Sculean A, Gruber R, Bosshardt DD (2014) Soft tissue wound healing around teeth and dental implants. J Clin Periodontol 41(Suppl 15):S6–22. doi:10.1111/jcpe.12206
Adamson R (2009) Role of macrophages in normal wound healing: an overview. J Wound Care 18:349–351. doi:10.12968/jowc.2009.18.8.43636
Miron RJ, Bosshardt DD (2016) OsteoMacs: key players around bone biomaterials. Biomaterials 82:1–19. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.12.017
Sinder BP, Pettit AR, McCauley LK (2015) Macrophages: their emerging roles in bone. J Bone Miner Res 30:2140–2149. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2735
Subash D, Shoba K, Aman S, Bharkavi SK (2016) Revitalization of an immature permanent mandibular molar with a necrotic pulp using platelet-rich fibrin: a case report. J Clin Diagn Res 10:Zd21–zd23. doi:10.7860/jcdr/2016/21793.8902
Rebentish PD, Umashetty G, Kaur H, Doizode T, Kaslekar M, Chowdhury S (2016) Platelet-rich fibrin: a boon in regenerative endodontics. Minerva Stomatol 65:385–392
Kim JH, Woo SM, Choi NK, Kim WJ, Kim SM, Jung JY (2017) Effect of platelet-rich fibrin on odontoblastic differentiation in human dental pulp cells exposed to lipopolysaccharide. J Endod 43:433–438. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2016.11.002
Bakhtiar H, Esmaeili S, Fakhr Tabatabayi S, Ellini MR, Nekoofar MH, Dummer PM (2017) Second-generation platelet concentrate (platelet-rich fibrin) as a scaffold in regenerative endodontics: a case series. J Endod 43:401–408. doi:10.1016/j.joen.2016.10.016
Pradeep K, Kudva A, Narayanamoorthy V, Cariappa KM, Saraswathi MV (2016) Platelet-rich fibrin combined with synthetic nanocrystalline hydroxy apatite granules in the management of radicular cyst. Niger J Clin Pract 19:688–691. doi:10.4103/1119-3077.188711
Mirkovic S, Djurdjevic-Mirkovic T, Pugkar T (2015) Application of concentrated growth factors in reconstruction of bone defects after removal of large jaw cysts--the two cases report. Vojnosanit Pregl 72:368–371
Meshram VS, Lambade PN, Meshram PV, Kadu A, Tiwari MS (2015) The autologous platelet rich fibrin: a novel approach in osseous regeneration after cystic enucleation: a pilot study. Indian J Dent Res 26:560–564. doi:10.4103/0970-9290.176915
Dar M, Hakim T, Shah A, Najar L, Yaqoob G, Lanker F (2016) Use of autologous platelet-rich fibrin in osseous regeneration after cystic enucleation: a clinical study. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res 6:S29–s32. doi:10.1016/j.jobcr.2016.04.004
Arunachalam LT, Merugu S, Sudhakar U (2012) A novel surgical procedure for papilla reconstruction using platelet rich fibrin. Contemp Clin Dent 3:467–470. doi:10.4103/0976-237x.107443
Ghanaati S, Booms P, Orlowska A, Kubesch A, Lorenz J, Rutkowski J, Landes C, Sader R, Kirkpatrick C, Choukroun J (2014) Advanced platelet-rich fibrin: a new concept for cell-based tissue engineering by means of inflammatory cells. J Oral Implantol 40:679–689. doi:10.1563/aaid-joi-D-14-00138
Choukroun J, Ghanaati S (2017) Reduction of relative centrifugation force within injectable platelet-rich-fibrin (PRF) concentrates advances patients’ own inflammatory cells, platelets and growth factors: the first introduction to the low speed centrifugation concept. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. doi:10.1007/s00068-017-0767-9
El Bagdadi K, Kubesch A, Yu X, Al-Maawi S, Orlowska A, Dias A, Booms P, Dohle E, Sader R, Kirkpatrick CJ, Choukroun J, Ghanaati S (2017) Reduction of relative centrifugal forces increases growth factor release within solid platelet-rich-fibrin (PRF)-based matrices: a proof of concept of LSCC (low speed centrifugation concept). Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. doi:10.1007/s00068-017-0785-7
Kobayashi E, Fluckiger L, Fujioka-Kobayashi M, Sawada K, Sculean A, Schaller B, Miron RJ (2016) Comparative release of growth factors from PRP, PRF, and advanced-PRF. Clin Oral Investig 20:2353–2360. doi:10.1007/s00784-016-1719-1
Fujioka-Kobayashi M, Miron RJ, Hernandez M, Kandalam U, Zhang Y, Choukroun J (2017) Optimized platelet-rich fibrin with the low-speed concept: growth factor release, biocompatibility, and cellular response. J Periodontol 88:112–121. doi:10.1902/jop.2016.160443
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Joseph Choukroun is the founder of Process of PRF company and the developer and inventor of PRF protocol in Nice, France. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was fully funded by the Cell Biology Laboratory at Nova Southeastern University, College of Dental Medicine.
Ethical approval
No ethical approval was required for this study as human participants or animals were not utilized in this study.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not required as no human or animal subjects were utilized in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miron, R.J., Zucchelli, G., Pikos, M.A. et al. Use of platelet-rich fibrin in regenerative dentistry: a systematic review. Clin Oral Invest 21, 1913–1927 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2133-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2133-z