Abstract
Since the discovery of SOX9 mutations in the severe human skeletal malformation syndrome campomelic dysplasia in 1994, Sox9 was shown to be both required and sufficient for chondrocyte specification and differentiation. At the same time, its distant relatives Sox5 and Sox6 were shown to act in redundancy with each other to robustly enhance its functions. The Sox trio is currently best known for its ability to activate the genes for cartilage-specific extracellular matrix components. Sox9 and Sox5/6 homodimerize through domains adjacent to their Sry-related high-mobility-group DNA-binding domain to increase the efficiency of their cooperative binding to chondrocyte-specific enhancers. Sox9 possesses a potent transactivation domain and thereby recruits diverse transcriptional co-activators, histone-modifying enzymes, subunits of the mediator complex, and components of the general transcriptional machinery, such as CBP/p300, Med12, Med25, and Wwp2. This information helps us begin to unravel the mechanisms responsible for Sox9-mediated transcription. We review here the discovery of this master chondrogenic trio and its roles in chondrogenesis in vivo and at the molecular level, and we discuss how these pioneering studies open the way for many additional studies that are needed to further increase our understanding of the transcriptional regulatory machinery operating in chondrogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horton W, Miyashita T, Kohno K, Hassell JR, Yamada Y (1987) Identification of a phenotype-specific enhancer in the first intron of the rat collagen II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8864–8868
Savagner P, Krebsbach PH, Hatano O, Miyashita T, Liebman J, Yamada Y (1995) Collagen II promoter and enhancer interact synergistically through Sp1 and distinct nuclear factors. DNA Cell Biol 14:501–510
Krebsbach PH, Nakata K, Bernier SM, Hatano O, Miyashita T, Rhodes CS, Yamada Y (1996) Identification of a minimum enhancer sequence for the type II collagen gene reveals several core sequence motifs in common with the link protein gene. J Biol Chem 271:4298–4303
Lefebvre V, Garofalo S, Zhou G, Metsaranta M, Vuorio E, De Crombrugghe B (1994) Characterization of primary cultures of chondrocytes from type II collagen/beta-galactosidase transgenic mice. Matrix Biol 14:329–335
Mukhopadhyay K, Lefebvre V, Zhou G, Garofalo S, Kimura JH, de Crombrugghe B (1995) Use of a new rat chondrosarcoma cell line to delineate a 119-base pair chondrocyte-specific enhancer element and to define active promoter segments in the mouse pro-alpha 1(II) collagen gene. J Biol Chem 270:27711–27719
Foster JW, Dominguez-Steglich MA, Guioli S, Kowk G, Weller PA, Stevanovic M, Weissenbach J, Mansour S, Young ID, Goodfellow PN et al (1994) Campomelic dysplasia and autosomal sex reversal caused by mutations in an SRY-related gene. Nature 372:525–530
Wagner T, Wirth J, Meyer J, Zabel B, Held M, Zimmer J, Pasantes J, Bricarelli FD, Keutel J, Hustert E et al (1994) Autosomal sex reversal and campomelic dysplasia are caused by mutations in and around the SRY-related gene SOX9. Cell 79:1111–1120
Zhao Q, Eberspaecher H, Lefebvre V, De Crombrugghe B (1997) Parallel expression of Sox9 and Col2a1 in cells undergoing chondrogenesis. Dev Dyn 209:377–386
Bell DM, Leung KK, Wheatley SC, Ng LJ, Zhou S, Ling KW, Sham MH, Koopman P, Tam PP, Cheah KS (1997) SOX9 directly regulates the type-II collagen gene. Nat Genet 16:174–178
Ng LJ, Wheatley S, Muscat GE, Conway-Campbell J, Bowles J, Wright E, Bell DM, Tam PP, Cheah KS, Koopman P (1997) SOX9 binds DNA, activates transcription, and coexpresses with type II collagen during chondrogenesis in the mouse. Dev Biol 183:108–121
Leung KK, Ng LJ, Ho KK, Tam PP, Cheah KS (1998) Different cis-regulatory DNA elements mediate developmental stage- and tissue-specific expression of the human COL2A1 gene in transgenic mice. J Cell Biol 141:1291–1300
Lefebvre V, Huang W, Harley VR, Goodfellow PN, de Crombrugghe B (1997) SOX9 is a potent activator of the chondrocyte-specific enhancer of the pro alpha1(II) collagen gene. Mol Cell Biol 17:2336–2346
Lefebvre V, Li P, de Crombrugghe B (1998) A new long form of Sox5 (L-Sox5), Sox6 and Sox9 are coexpressed in chondrogenesis and cooperatively activate the type II collagen gene. EMBO J 17:5718–5733
Bernard P, Tang P, Liu S, Dewing P, Harley VR, Vilain E (2003) Dimerization of SOX9 is required for chondrogenesis, but not for sex determination. Hum Mol Genet 12:1755–1765
Sock E, Pagon RA, Keymolen K, Lissens W, Wegner M, Scherer G (2003) Loss of DNA-dependent dimerization of the transcription factor SOX9 as a cause for campomelic dysplasia. Hum Mol Genet 12:1439–1447
Bridgewater LC, Lefebvre V, de Crombrugghe B (1998) Chondrocyte-specific enhancer elements in the Col11a2 gene resemble the Col2a1 tissue-specific enhancer. J Biol Chem 273:14998–15006
Bridgewater LC, Walker MD, Miller GC, Ellison TA, Holsinger LD, Potter JL, Jackson TL, Chen RK, Winkel VL, Zhang Z et al (2003) Adjacent DNA sequences modulate Sox9 transcriptional activation at paired Sox sites in three chondrocyte-specific enhancer elements. Nucleic Acids Res 31:1541–1553
Han Y, Lefebvre V (2008) L-Sox5 and Sox6 drive expression of the aggrecan gene in cartilage by securing binding of Sox9 to a far-upstream enhancer. Mol Cell Biol 28:4999–5013
Jenkins E, Moss JB, Pace JM, Bridgewater LC (2005) The new collagen gene COL27A1 contains SOX9-responsive enhancer elements. Matrix Biol 24:177–184
Nagy A, Kenesi E, Rentsendorj O, Molnar A, Szenasi T, Sinko I, Zvara A, Oommen ST, Barta E, Puskas LG et al (2011) Evolutionarily conserved, growth plate zone-specific regulation of the matrilin-1 promoter: L-Sox5/Sox6 and Nfi factors bound near TATA finely tune activation by Sox9. Mol Cell Biol 31:686–699
Rentsendorj O, Nagy A, Sinko I, Daraba A, Barta E, Kiss I (2005) Highly conserved proximal promoter element harbouring paired Sox9-binding sites contributes to the tissue- and developmental stage-specific activity of the matrilin-1 gene. Biochem J 389:705–716
Xie WF, Zhang X, Sakano S, Lefebvre V, Sandell LJ (1999) Trans-activation of the mouse cartilage-derived retinoic acid-sensitive protein gene by Sox9. J Bone Miner Res 14:757–763
Bi W, Huang W, Whitworth DJ, Deng JM, Zhang Z, Behringer RR, de Crombrugghe B (2001) Haploinsufficiency of Sox9 results in defective cartilage primordia and premature skeletal mineralization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6698–6703
Bi W, Deng JM, Zhang Z, Behringer RR, de Crombrugghe B (1999) Sox9 is required for cartilage formation. Nat Genet 22:85–89
Akiyama H, Chaboissier MC, Martin JF, Schedl A, de Crombrugghe B (2002) The transcription factor Sox9 has essential roles in successive steps of the chondrocyte differentiation pathway and is required for expression of Sox5 and Sox6. Genes Dev 16:2813–2828
Smits P, Li P, Mandel J, Zhang Z, Deng JM, Behringer RR, de Croumbrugghe B, Lefebvre V (2001) The transcription factors L-Sox5 and Sox6 are essential for cartilage formation. Dev Cell 1:277–290
Smits P, Dy P, Mitra S, Lefebvre V (2004) Sox5 and Sox6 are needed to develop and maintain source, columnar, and hypertrophic chondrocytes in the cartilage growth plate. J Cell Biol 164:747–758
Akiyama H, Stadler HS, Martin JF, Ishii TM, Beachy PA, Nakamura T, de Crombrugghe B (2006) Misexpression of Sox9 in mouse limb bud mesenchyme induces polydactyly and rescues hypodactyly mice. Matrix Biol 26:224–233
Haudenschild DR, Chen J, Pang N, Lotz MK, D’Lima DD (2011) Rho kinase-dependent activation of SOX9 in chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 62:191–200
Huang W, Zhou X, Lefebvre V, de Crombrugghe B (2000) Phosphorylation of SOX9 by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A enhances SOX9’s ability to transactivate a Col2a1 chondrocyte-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol 20:4149–4158
Huang W, Chung UI, Kronenberg HM, de Crombrugghe B (2001) The chondrogenic transcription factor Sox9 is a target of signaling by the parathyroid hormone-related peptide in the growth plate of endochondral bones. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:160–165
Hattori T, Coustry F, Stephens S, Eberspaecher H, Takigawa M, Yasuda H, de Crombrugghe B (2008) Transcriptional regulation of chondrogenesis by coactivator Tip60 via chromatin association with Sox9 and Sox5. Nucleic Acids Res 36:3011–3024
Hattori T, Eberspaecher H, Lu J, Zhang R, Nishida T, Kahyo T, Yasuda H, de Crombrugghe B (2006) Interactions between PIAS proteins and SOX9 result in an increase in the cellular concentrations of SOX9. J Biol Chem 281:14417–14428
Oh HJ, Kido T, Lau YF (2007) PIAS1 interacts with and represses SOX9 transactivation activity. Mol Reprod Dev 74:1446–1455
Akiyama H, Kim JE, Nakashima K, Balmes G, Iwai N, Deng JM, Zhang Z, Martin JF, Behringer RR, Nakamura T et al (2005) Osteo-chondroprogenitor cells are derived from Sox9 expressing precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14665–14670
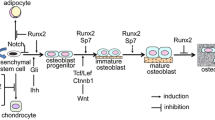
Komori T, Yagi H, Nomura S, Yamaguchi A, Sasaki K, Deguchi K, Shimizu Y, Bronson RT, Gao YH, Inada M, Sato M, Okamoto R, Kitamura Y, Yoshiki S, Kishimoto T (1997) Targeted disruption of Cbfa1 results in a complete lack of bone formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell 89:755–764
Otto F, Thornell AP, Crompton T, Denzel A, Gilmour KC, Rosewell IR, Stamp GW, Beddington RS, Mundlos S, Olsen BR, Selby PB, Owen MJ (1997) Cbfa1, a candidate gene for cleidocranial dysplasia syndrome, is essential for osteoblast differentiation and bone development. Cell 89:765–771
Day TF, Guo X, Garrett-Beal L, Yang Y (2005) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate skeletogenesis. Dev Cell 8:739–750
Hill TP, Spater D, Taketo MM, Birchmeier W, Hartmann C (2005) Canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling prevents osteoblasts from differentiating into chondrocytes. Dev Cell 8:727–738
Akiyama H, Lyons JP, Mori-Akiyama Y, Yang X, Zhang R, Zhang Z, Deng JM, Taketo MM, Nakamura T, Behringer RR et al (2004) Interactions between Sox9 and beta-catenin control chondrocyte differentiation. Genes Dev 18:1072–1087
Topol L, Chen W, Song H, Day TF, Yang Y (2009) Sox9 inhibits Wnt signaling by promoting beta-catenin phosphorylation in the nucleus. J Biol Chem 284:3323–3333
Zhou G, Zheng Q, Engin F, Munivez E, Chen Y, Sebald E, Krakow D, Lee B (2006) Dominance of SOX9 function over RUNX2 during skeletogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:19004–19009
Cheng A, Genever PG (2010) SOX9 determines RUNX2 transactivity by directing intracellular degradation. J Bone Miner Res 25:2404–2413
Amano K, Hata K, Muramatsu S, Wakabayashi M, Takigawa Y, Ono K, Nakanishi M, Takashima R, Kogo M, Matsuda A et al (2011) Arid5a cooperates with sox9 to stimulate chondrocyte-specific transcription. Mol Biol Cell 22:1300–1311
Huang W, Lu N, Eberspaecher H, De Crombrugghe B (2002) A new long form of c-Maf cooperates with Sox9 to activate the type II collagen gene. J Biol Chem 277:50668–50675
Kawakami Y, Tsuda M, Takahashi S, Taniguchi N, Esteban CR, Zemmyo M, Furumatsu T, Lotz M, Belmonte JC, Asahara H (2005) Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha regulates chondrogenesis via association with Sox9. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2414–2419
Takigawa Y, Hata K, Muramatsu S, Amano K, Ono K, Wakabayashi M, Matsuda A, Takada K, Nishimura R, Yoneda T (2010) The transcription factor Znf219 regulates chondrocyte differentiation by assembling a transcription factory with Sox9. J Cell Sci 123:3780–3788
Hata K, Nishimura R, Muramatsu S, Matsuda A, Matsubara T, Amano K, Ikeda F, Harley VR, Yoneda T (2008) Paraspeckle protein p54 links Sox9-mediated transcription with RNA processing during chondrogenesis in mice. J Clin Invest 118:3098–3108
Furumatsu T, Tsuda M, Yoshida K, Taniguchi N, Ito T, Hashimoto M, Asahara H (2005) Sox9 and p300 cooperatively regulate chromatin-mediated transcription. J Biol Chem 280:35203–35208
Tsuda M, Takahashi S, Takahashi Y, Asahara H (2003) Transcriptional co-activators CREB-binding protein and p300 regulate chondrocyte-specific gene expression via association with Sox9. J Biol Chem 278:27224–27229
Zhou R, Bonneaud N, Yuan CX, de Santa Barbara P, Boizet B, Schomber T, Scherer G, Roeder RG, Poulat F, Berta P (2002) SOX9 interacts with a component of the human thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein complex. Nucleic Acids Res 30:3245–3252
Rau MJ, Fischer S, Neumann CJ (2006) Zebrafish Trap230/Med12 is required as a coactivator for Sox9-dependent neural crest, cartilage and ear development. Dev Biol 296:83–93
Nakamura Y, Yamamoto K, He X, Otsuki B, Kim Y, Murao H, Soeda T, Tsumaki N, Deng JM, Zhang Z et al (2011) Wwp2 is essential for palatogenesis mediated by the interaction between Sox9 and mediator subunit 25. Nat Commun 2:251
Lee HK, Park UH, Kim EJ, Um SJ (2007) MED25 is distinct from TRAP220/MED1 in cooperating with CBP for retinoid receptor activation. EMBO J 26:3545–3557
Rana R, Surapureddi S, Kam W, Ferguson S, Goldstein JA (2011) Med25 is required for RNA polymerase II recruitment to specific promoters, thus regulating xenobiotic and lipid metabolism in human liver. Mol Cell Biol 31:466–481
Youn HS, Park UH, Kim EJ, Um SJ (2011) PTOV1 antagonizes MED25 in RAR transcriptional activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 404:239–244
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Akiyama is a recipient of the 2010 JSBMR Distinguished Scientist Award.
About this article
Cite this article
Akiyama, H., Lefebvre, V. Unraveling the transcriptional regulatory machinery in chondrogenesis. J Bone Miner Metab 29, 390–395 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-011-0273-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-011-0273-9