Abstract
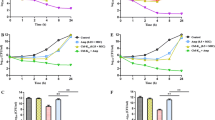
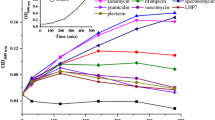
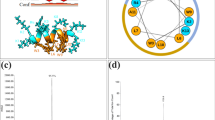
Drug-resistant microorganism infections cause serious disease and can lead to mortality and morbidity. In particular, Staphylococcus aureus induces pyrogenic and toxigenic infections, and drug-resistance occurs rapidly. Multidrug-resistant S. aureus, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus and methicillin-sensitive S. aureus, can also cause immunodeficiency and immune deficiency syndrome from lipoteichoic acid. However, antimicrobial peptides, such as KW4, have strong antimicrobial activity, low cytotoxicity, and high neutralization activity against endotoxin substances from Gram-negative bacteria. The objective of this study was to use a synthetic KW4 antimicrobial peptide to evaluate the inhibition of drug-resistance development, antimicrobial activity, and neutralizing activity in S. aureus Gram-positive bacteria. The KW4 peptide showed strong antimicrobial activity against drug-resistant S. aureus strains and significantly increased the anti-neutralizing activity of lipoteichoic acid in S. aureus 1630 drug-resistant bacteria. In addition, S. aureus ATCC 29213 did not develop resistance to KW4 as with other antibiotic drugs. These results suggest that the KW4 peptide is an effective antibiotic and anti-neutralizing agent against multidrug-resistant S. aureus strains.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertsch M, Mayburd AL, Kassner RJ (2003) The identification of hydrophobic sites on the surface of proteins using absorption difference spectroscopy of bromophenol blue. Anal Biochem 313:187–195
Bishayi B, Bandyopadhyay D, Majhi A, Adhikary R (2015) Effect of exogenous MCP-1 on TLR-2 neutralized murine macrophages and possible mechanisms of CCR-2/TLR-2 and MCP-1 signalling during Staphylococcus aureus infection. Immunobiology 220:350–362
Choo EJ, Chambers HF (2016) Treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Infect Chemother 48:267–273
Gelaw KA, Aweke AM, Astawesegn FH, Demissie BW, Zeleke LB (2017) Surgical site infection and its associated factors following cesarean section: a cross sectional study from a public hospital in Ethiopia. Patient Safety Surg 11:18
Gopal R, Na H, Seo CH, Park Y (2012) Antifungal activity of (KW)n or (RW)n peptide against Fusarium solani and Fusarium oxysporum. Int J Mol Sci 13:15042–15053
Gopal R, Lee JK, Lee JH, Kim YG, Oh GC, Seo CH, Park Y (2013) Effect of repetitive lysine–tryptophan motifs on the eukaryotic membrane. Int J Mol Sci 14:2190–2202
Hoerr V, Zbytnuik L, Leger C, Tam PP, Kubes P, Vogel HJ (2012) Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial infections give rise to a different metabolic response in a mouse model. J Proteome Res 11:3231–3245
Horn KS, Danziger LH, Rodvold KA, Glowacki RC (2017) Pharmacokinetic drug evaluation of ceftobiprole for the treatment of MRSA. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 13:463–472
Kane CD, Bernlohr DA (1996) A simple assay for intracellular lipid-binding proteins using displacement of 1-anilinonaphthalene 8-sulfonic acid. Anal Biochem 233:197–204
Kang SS, Sim JR, Yun CH, Han SH (2016) Lipoteichoic acids as a major virulence factor causing inflammatory responses via Toll-like receptor 2. Arch Pharmacal Res 39:1519–1529
Kasetty G, Kalle M, Morgelin M, Brune JC, Schmidtchen A (2015) Anti-endotoxic and antibacterial effects of a dermal substitute coated with host defense peptides. Biomaterials 53:415–425
Koch L, Frommhold D, Buschmann K, Kuss N, Poeschl J, Ruef P (2014) LPS- and LTA-induced expression of IL-6 and TNF-alpha in neonatal and adult blood: role of MAPKs and NF-kappaB. Mediators Inflamm 2014:283126
Lau G, Wald R, Sladen R, Mazer CD (2015) Acute kidney injury in cardiac surgery and cardiac intensive care. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 19:270–287
Lee JK, Park SC, Hahm KS, Park Y (2013) Antimicrobial HPA3NT3 peptide analogs: placement of aromatic rings and positive charges are key determinants for cell selectivity and mechanism of action. Biochem Biophys Acta 1828:443–454
Lee JK, Seo CH, Luchian T, Park Y (2015) Antimicrobial Peptide CMA3 derived from the CA-MA hybrid peptide: antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities with low cytotoxicity and mechanism of action in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 60:495–506
Mohamed MF, Abdelkhalek A, Seleem MN (2016) Evaluation of short synthetic antimicrobial peptides for treatment of drug-resistant and intracellular Staphylococcus aureus. Sci Rep 6:29707
Morita S, Tagai C, Shiraishi T, Miyaji K, Iwamuro S (2013) Differential mode of antimicrobial actions of arginine-rich and lysine-rich histones against Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus. Peptides 48:75–82
Murray KP, Zhao JJ, Davis SL, Kullar R, Kaye KS, Lephart P, Rybak MJ (2013) Early use of daptomycin versus vancomycin for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia with vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentration > 1 mg/L: a matched cohort study. Clin Infect Dis 56:1562–1569
Ogawa M, Mimuro H, Yoshikawa Y, Ashida H, Sasakawa C (2011) Manipulation of autophagy by bacteria for their own benefit. Microbiol Immunol 55:459–471
Pareja ME, Colombo MI (2013) Autophagic clearance of bacterial pathogens: molecular recognition of intracellular microorganisms. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 3:54
Pasupuleti M, Schmidtchen A, Chalupka A, Ringstad L, Malmsten M (2009) End-tagging of ultra-short antimicrobial peptides by W/F stretches to facilitate bacterial killing. PLoS ONE 4:e5285
Pietrocola G, Arciola CR, Rindi S, Di Poto A, Missineo A, Montanaro L, Speziale P (2011) Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in innate immune defense against Staphylococcus aureus. Int J Artif Org 34:799–810
Purrello SM, Garau J, Giamarellos E, Mazzei T, Pea F, Soriano A, Stefani S (2016) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: a review of the currently available treatment options. J Glob Antimicrob Res 7:178–186
Ragle BE, Karginov VA, Bubeck Wardenburg J (2010) Prevention and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia with a beta-cyclodextrin derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:298–304
Ray A, Cot M, Puzo G, Gilleron M, Nigou J (2013) Bacterial cell wall macroamphiphiles: pathogen-/microbe-associated molecular patterns detected by mammalian innate immune system. Biochimie 95:33–42
Sganga G, Tascini C, Sozio E, Colizza S (2017) Early recognition of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus surgical site infections using risk and protective factors identified by a group of Italian surgeons through Delphi method. World J Emerg Surg 12:25
Sydnor ER, Perl TM (2011) Hospital epidemiology and infection control in acute-care settings. Clin Microbiol Rev 24:141–173
van Hal SJ, Jensen SO, Vaska VL, Espedido BA, Paterson DL, Gosbell IB (2012) Predictors of mortality in Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Clin Microbiol Rev 25:362–386
Vestergaard M, Leng B, Haaber J, Bojer MS, Vegge CS, Ingmer H (2016) Genome-wide identification of antimicrobial intrinsic resistance determinants in Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol 7:2018
Yeom JH, Lee B, Kim D, Lee JK, Kim S, Bae J, Park Y, Lee K (2016) Gold nanoparticle-DNA aptamer conjugate-assisted delivery of antimicrobial peptide effectively eliminates intracellular Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Biomaterials 104:43–51
Zahringer U, Lindner B, Inamura S, Heine H, Alexander C (2008) TLR2—promiscuous or specific? A critical re-evaluation of a receptor expressing apparent broad specificity. Immunobiology 213:205–224
Zivkovic A, Sharif O, Stich K, Doninger B, Biaggio M, Colinge J, Bilban M, Mesteri I, Hazemi P, Lemmens-Gruber R, Knapp S (2011) TLR 2 and CD14 mediate innate immunity and lung inflammation to staphylococcal Panton-Valentine leukocidin in vivo. J Immunol 186:1608–1617
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Government (No. 2016R1A2A1A05005440), Global Research Laboratory (GRL) Grant (No. NRF-2014K1A1A2064460) and Institute for Information & communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2017-0-01714, Development of Antimicrobial Peptide using Deep Learning).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest associated with the manuscript.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any other authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: J. G. López.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Jk., Park, Y. Anti-endotoxin mechanism of the KW4 peptide in inflammation in RAW 264.7 cells induced by LTA and drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus 1630. Amino Acids 50, 363–372 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2518-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2518-y