Abstract
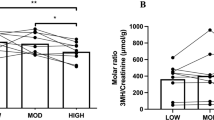
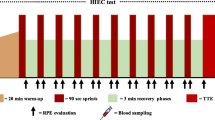
The aim of this study was to identify the relationship between metabolic effort, muscular damage/activity indices, and urinary amino acids profile over the course of a strenuous prolonged endurance activity, as a cycling stage race is, in order to identify possible fatigue markers. Nine professional cyclists belonging to a single team, competing in the Giro d’Italia cycling stage race, were anthropometrically characterized and sampled for blood and urine the day before the race started, and on days 12 and 23 of the race. Diet was kept the same over the race, and power output and energy expenditure were recorded. Sera were assayed for muscle markers (lactate dehydrogenase, aspartate aminotransferase, and creatine kinase activities, and blood urea nitrogen), and creatinine, all corrected for plasma volume changes. Urines were profiled for amino acid concentrations, normalized on creatinine excretion. Renal function, in terms of glomerular filtration rate, was monitored by MDRD equation corrected on body surface area. Creatine kinase activity and blood urea were increased during the race as did serum creatinine while kidney function remained stable. Among the amino acids, taurine, glycine, cysteine, leucine, carnosine, 1-methyl histidine, and 3-methyl histidine showed a net decreased, while homocysteine was increased. Taurine and the dipeptide carnosine (β-alanyl-l-histidine) were significantly correlated with the muscle activity markers and the indices of effort. In conclusion, the metabolic profile is modified strikingly due to the effort. Urinary taurine and carnosine seem useful tools to evaluate the muscle damage and possibly the fatigue status on a long-term basis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amelio I, Cutruzzola F, Antonov A, Agostini M, Melino G (2014) Serine and glycine metabolism in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci 39:191–198. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2014.02.004
Banfi G, Dolci A (2003) Preanalytical phase of sport biochemistry and haematology. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 43:223–230
Blomstrand E (2001) Amino acids and central fatigue. Amino Acids 20:25–34
Bonfanti L, Peretto P, De Marchis S, Fasolo A (1999) Carnosine-related dipeptides in the mammalian brain. Progr Neurobiol 59:333–353
Colombini A, Corsetti R, Graziani R, Lombardi G, Lanteri P, Banfi G (2012a) Evaluation of creatinine, cystatin C and eGFR by different equations in professional cyclists during the Giro d’Italia 3-weeks stage race. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 72:114–120. doi:10.3109/00365513.2011.642305
Colombini A, Corsetti R, Machado M, Graziani R, Lombardi G, Lanteri P, Banfi G (2012b) Serum creatine kinase activity and its relationship with renal function indices in professional cyclists during the Giro d’Italia 3-week stage race. Clin J Sports Med 22:408–413. doi:10.1097/JSM.0b013e31825e66cc
Corsetti R, Lombardi G, Lanteri P, Colombini A, Graziani R, Banfi G (2012) Haematological and iron metabolism parameters in professional cyclists during the Giro d’Italia 3-weeks stage race. Clin Chem Lab Med 50:949–956
Cuisinier C, Ward RJ, Francaux M, Sturbois X, de Witte P (2001) Changes in plasma and urinary taurine and amino acids in runners immediately and 24 h after a marathon. Amino Acids 20:13–23
DeBerardinis RJ, Cheng T (2010) Q’s next: the diverse functions of glutamine in metabolism, cell biology and cancer. Oncogene 29:313–324. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.358
Forslund AH et al (2000) Inverse relationship between protein intake and plasma free amino acids in healthy men at physical exercise. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278:E857–E867
Garibotto G, Sofia A, Saffioti S, Bonanni A, Mannucci I, Verzola D (2010) Amino acid and protein metabolism in the human kidney and in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Nutr 29:424–433. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2010.02.005
Gatti R, De Palo EF (2011) An update: salivary hormones and physical exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 21:157–169. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2010.01252.x
Grasso D et al (2015) Bone-muscle unit activity, salivary steroid hormones profile, and physical effort over a 3-week stage race. Scand J Med Sci Sports 25:70–80
Halson SL (2014) Monitoring training load to understand fatigue in athletes. Sports Med 44:S139–S147. doi:10.1007/s40279-014-0253-z
Harris RC, Wise JA, Price KA, Kim HJ, Kim CK, Sale C (2012) Determinants of muscle carnosine content Amino Acids 43:5–12. doi:10.1007/s00726-012-1233-y
Harvey RJ, Yee BK (2013) Glycine transporters as novel therapeutic targets in schizophrenia, alcohol dependence and pain. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:866–885. doi:10.1038/nrd3893
Iio W, Matsukawa N, Tsukahara T, Toyoda A (2012) The effects of oral taurine administration on behavior and hippocampal signal transduction in rats. Amino Acids 43:2037–2046. doi:10.1007/s00726-012-1282-2
Lamb EJ, Tomson CR, Roderick PJ (2005) Estimating kidney function in adults using formulae. Ann Clin Biochem 42:321–345. doi:10.1258/0004563054889936
Makrides V, Camargo SM, Verrey F (2014) Transport of amino acids in the kidney. Compr Physiol 4:367–403. doi:10.1002/cphy.c130028
Mashiko T, Umeda T, Nakaji S, Sugawara K (2004) Effects of exercise on the physical condition of college rugby players during summer training camp. Br J Sports Med 38:186–190
Meeusen R (2014) Exercise, nutrition and the brain. Sports Med 44:S47–S56. doi:10.1007/s40279-014-0150-5
Mondino A, Bongiovanni G, Fumero S, Rossi L (1972) An improved method of plasma deproteination with sulphosalicylic acid for determining amino acids and related compounds. J Chromatogr 74:255–263
Nagasawa T, Hirano J, Yoshizawa F, Nishizawa N (1998) Myofibrillar protein catabolism is rapidly suppressed following protein feeding. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:1932–1937. doi:10.1271/bbb.62.1932
Nedelec M, McCall A, Carling C, Legall F, Berthoin S, Dupont G (2012) Recovery in soccer: part I—post-match fatigue and time course of recovery. Sports Med 42:997–1015. doi:10.2165/11635270-000000000-00000
Ortenblad N, Young JF, Oksbjerg N, Nielsen JH, Lambert IH (2003) Reactive oxygen species are important mediators of taurine release from skeletal muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 284:C1362–C1373. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00287.2002
Pfaffe T, Cooper-White J, Beyerlein P, Kostner K, Punyadeera C (2011) Diagnostic potential of saliva: current state and future applications. Clin Chem 57:675–687. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2010.153767
Pinto V, Pinho MJ, Soares-da-Silva P (2013) Renal amino acid transport systems and essential hypertension. FASEB J 27:2927–2938. doi:10.1096/fj.12-224998
Ra SG, Maeda S, Higashino R, Imai T, Miyakawa S (2014) Metabolomics of salivary fatigue markers in soccer players after consecutive games. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 39:1120–1126. doi:10.1139/apnm-2013-0546
Sale C, Artioli GG, Gualano B, Saunders B, Hobson RM, Harris RC (2013) Carnosine: from exercise performance to health. Amino Acids 44:1477–1491. doi:10.1007/s00726-013-1476-2
Sanchis-Gomar F, Lippi G (2014) Physical activity—an important preanalytical variable. Biochem Med 24:68–79. doi:10.11613/BM.2014.009
Simundic AM (2012) Practical recommendations for statistical analysis and data presentation in Biochemia Medica journal. Biochem Med 22:15–23
Spriet LL, Whitfield J (2015) Taurine and skeletal muscle function. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 18:96–101. doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000135
Tiao G, Hobler S, Wang JJ, Meyer TA, Luchette FA, Fischer JE, Hasselgren PO (1997) Sepsis is associated with increased mRNAs of the ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway in human skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest 99:163–168. doi:10.1172/JCI119143
Tiedje KE, Stevens K, Barnes S, Weaver DF (2010) Beta-alanine as a small molecule neurotransmitter. Neurochem Int 57:177–188. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2010.06.001
UCI (2012) Union Cycliste Internationale. UCI Anti-doping procedural guidelines 7.0. Storage and Transport of samples. http://www.uci.ch/Modules/BUILTIN/getObject.asp?MenuId=MTI1NzE&ObjTypeCode=FILE&type=FILE&id=Nzc2ODE&LangId=1. Accessed February 2012
WADA (2011) World Anti-doping Agency. Requirements for passport operation from international standard for testing and international standard for laboratories. http://www.wada-ama.org/Documents/Resources/Guidelines/WADA_ABP_OperatingGuidelines_EN_2.1.pdf. Accessed January 2012
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted with Mr. Massimiliano Casavecchia who helped in data storage and handling and with the Cannondale pro-cycling team for availability and logistics. This study has been partially supported by the ITALIAN MINISTRY OF HEALTH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: E. Rawson.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corsetti, R., Barassi, A., Perego, S. et al. Changes in urinary amino acids excretion in relationship with muscle activity markers over a professional cycling stage race: in search of fatigue markers. Amino Acids 48, 183–192 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2077-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-015-2077-z