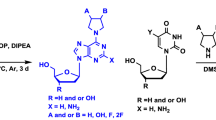
Abstract
In this work, we report the synthesis of an alternate nucleo-alpha,epsilon-peptide based on l-lysine moieties, an in vitro study of its biological activity, and spectroscopical binding studies between the novel nucleopeptide and Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase as well as RNA. An alternate homothymine hexamer was synthesized by a straightforward solid phase route starting from commercial materials, purified by RP-HPLC and characterized by ESI-MS. The efficiency of the novel nucleo-alpha,epsilon-peptide in interfering with the reverse transcription of eukaryotic mRNA and the noteworthy enzymatic resistance demonstrated by specific assays are in favor of the employment of this nucleopeptide in novel biomedical strategies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ac2O:
-
Acetic anhydride
- DBU:
-
1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undecene
- DIEA:
-
N,N-Diisopropylethylamine
- DMF:
-
N,N-Dimethylformamide
- Fmoc:
-
9-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl
- HATU:
-
O-(7-Azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate
- PyBOP:
-
Benzotriazole-1-yl-oxy-tris-pyrrolidino-phosphonium hexafluorophosphate
- PTFE:
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene
- TAE:
-
Tris–acetate–EDTA
- TFA:
-
Trifluoroacetic acid
- TMP:
-
2,4,6-Trimethylpyridine
References
Boiziau C, Thuong NT, Toulmé JJ (1992) Mechanisms of the inhibition of reverse transcription by antisense oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:768–772
Briones C, Martin-Gago JA (2006) Nucleic acids and their analogs as nanomaterials for biosensor development. Curr Nanosci 2:257–273
Chan EW, Lee CK, Dale PJ, Nortridge KR, Hom SS, Seed TM (1981) Antiviral properties of polyinosinic acids containing thio and methyl substitutions. J Gen Virol 52:291–299
Fukui T, De Clercq E (1982) Inhibition of murine leukaemia virus reverse transcriptase by 2-halogenated polyadenylic acids. Biochem J 203:755–760
Gangamani BP, Kumar VA, Ganesh KN (1999) Chiral analogues of peptide nucleic acids: synthesis of 4-aminoprolyl nucleic acids and DNA complementation studies using UV/CD spectroscopy. Tetrahedron 55:177–192
Georgiadis MM, Jessen SM, Ogata CM, Telesnitsky A, Goff SP, Hendrickson WA (1995) Mechanistic implications from the structure of a catalytic fragment of Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase. Structure 3:879–892
Haimaa G, Lohse A, Buchardt O, Nielsen PE (1996) Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) containing thymine monomers derived from chiral amino acids: hybridization and solubility properties of d-lysine PNA. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 35:1939–1942
Helene C, Le Doan T (1991) Oligonucleotides: problems and frontiers of practical applications. Trends Biotechnol 9:339–340
Huang H, Chopra R, Verdine GL, Harrison SC (1998) Structure of a covalently trapped catalytic complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: implications for drug resistance. Science 282:1669–1675
Kotewicz ML, Sampson CM, D’Alessio JM, Gerard GF (1988) Isolation of cloned Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase lacking ribonuclease H activity. Nucleic Acids Res 16:265–277
Krzyzanowska D, Lisowski M, Kochman M (1998) UV-difference and CD spectroscopy studies on juvenile hormone binding to its carrier protein. J Pept Res 51:96–102
Kurreck J (2003) Antisense technologies. Improvement through novel chemical modifications. Eur J Biochem 270:1628–1644
Maga G, Ubiali D, Salvetti R, Pregnolato M, Spadari S (2000) Selective interaction of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase nonnucleoside inhibitor efavirenz and its thio-substituted analog with different enzyme–substrate complexes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:1186–1194
Molling K, Bolognesi DP, Bauer H, Busen W, Plassmann HW, Hausen P (1971) Association of viral reverse transcriptase with an enzyme degrading the RNA moiety of RNA–DNA hybrids. Nat New Biol 234:240–243
Motakis D, Parniak MA (2002) A tight-binding mode of inhibition is essential for anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virucidal activity of nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:1851–1856
Nielsen PE, Egholm M, Berg RM, Buchardt O (1991) Sequence selective recognition of DNA by strand displacement with thymine-substituted polyamide. Science 254:1497–1500
Ray A, Nordén B (2000) Peptide nucleic acid (PNA): its medical and biotechnical applications and promise for the future. FASEB J 14:1041–1060
Rittinger K, Divita G, Goody RS (1995) Human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase substrate-induced conformational changes and the mechanism of inhibition by nonnucleoside inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8046–8049
Rocchi R, Borin G, Marchiori F, Moroder L, Peggion E, Scoffone E, Crescenzi V, Quadrifoglio F (1972) Interaction of S-protein with S-peptide and with synthetic S-peptide analogs. A spectroscopic and calorimetric investigation. Biochemistry 11:50–57
Roviello GN, Moccia M, Sapio R, Valente M, Bucci EM, Castiglione M, Pedone C, Perretta G, Benedetti E, Musumeci D (2006) Synthesis, characterization and hybridization studies of new nucleo-gamma-peptides based on diaminobutyric acid. J Pept Sci 12:829–835
Roviello GN, Musumeci D, Moccia M, Castiglione M, Sapio R, Valente M, Bucci EM, Perretta G, Pedone C (2007) dabPNA: design, synthesis and DNA binding studies. Nucleos Nucleot Nucleic Acids 26:1307–1310
Roviello GN, Musumeci D, Bucci EM, Castiglione M, Cesarani A, Pedone C, Piccialli G (2008) Evidences for complex formation between l-dabPNA and aegPNA. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:4757–4760
Roviello GN, Musumeci D, Moccia M, Castiglione M, Cesarani A, Bucci EM, Saviano M, Pedone C, Benedetti E (2009a) Evidences of complex formation between DABA-based nucleo-gamma-peptides with alternate configuration backbone. J Pept Sci 15:147–154
Roviello GN, Musumeci D, Castiglione M, Bucci EM, Pedone C, Benedetti E (2009b) Solid phase synthesis and RNA-binding studies of a serum resistant nucleo-ε-peptide. J Pept Sci 15:155–160
Roviello GN, Musumeci D, Pedone C, Bucci EM (2009c) Synthesis, characterization and hybridization studies of an alternate nucleo-ε/γ-peptide: complexes formation with natural nucleic acids. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-008-0214-7
Sforza S, Haaima G, Marchelli R, Nielsen PE (1999) Chiral peptide nucleic acids (PNAs): helix handedness and DNA recognition. Eur J Org Chem 1:197–204
Sforza S, Galaverna G, Dossena A, Corradini R, Marchelli R (2002) Role of chirality and optical purity in nucleic acid recognition by PNA and PNA analogs. Chirality 14:591–598
Uhlmann E, Peyman A, Breipohl G, Will DW (1998) PNA: synthetic polyamide nucleic acids with unusual binding properties. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 37:2796–2823
Williams KJ, Loeb LA, Fry M (1990) Synthesis of DNA by human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase is preferentially blocked at template oligo(deoxyadenosine) tracts. J Biol Chem 265:18682–18689
Wu L, Huang MH, Zhao JL, Yang MS (2005) Study of MMLV RT-binding with DNA using surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 37:634–642
Yang SS, Cragg GM, Newman DJ, Bader JP (2001) Natural product-based anti-HIV drug discovery and development facilitated by the NCI developmental therapeutics program. J Nat Prod 64:265–277
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Andrea De Cristofaro and Mr. Leopoldo Zona for their invaluable assistance. We are also grateful to the institutions that supported our laboratory (Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche and Università degli Studi di Napoli ‘Federico II’) and MIUR (FIRB RBRN07BMCT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roviello, G.N., Gaetano, S.D., Capasso, D. et al. Synthesis, spectroscopic studies and biological activity of a novel nucleopeptide with Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase inhibitory activity. Amino Acids 38, 1489–1496 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0361-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0361-5