Abstract
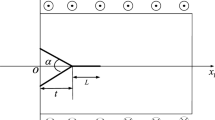
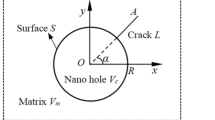
An electrically permeable elliptical nano-hole or nano-crack embedded in an infinite piezoelectric material with surface effect is investigated based on the Gurtin–Murdoch surface/interface model, which is subjected to far-field anti-plane mechanical and in-plane electrical loads. The electric field inside the elliptical nano-hole has been taken into consideration, and exact electroelastic fields near the elliptical nano-hole are obtained by using the technique of conformal mapping. The size-dependent stress and electric displacement intensity factors at the crack tip are derived exactly for both electrically permeable and impermeable boundary conditions when the elliptical nano-hole reduces to the nano-crack. Numerical examples are illustrated to show the surface effects on the stress and electric displacement intensity factors of electrically permeable and impermeable cracks, and on the stress and electric field concentrations around the electrically permeable and impermeable holes. The results indicate that the size dependence of an electrically permeable nano-hole or nano-crack is entirely different from that of the electrically impermeable case.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, R., Qin, Y., Li, C., et al.: Characteristics of output voltage and current of integrated nanogenerators. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 94, 022905 (2009)
Caillier, C., Ayari, A., Gouttenoire, V., et al.: Gold contact to individual metallic carbon nanotubes: A sensitive nanosensor for high-pressure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 173111 (2010)
Khaderbad, M.A., Choi, Y., Hiralal, P., et al.: Electrical actuation and readout in a nanoelectromechanical resonator based on a laterally suspended zinc oxide nanowire. Nanotechnology 23, 025501 (2012)
Cammarata, R.C.: Surface and interface stress effects in thin films. Prog. Sur. Sci. 46, 1–38 (1994)
Cammarata, R.C.: Surface and interface stress effects on interfacial and nanostructured materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 237, 180–184 (1997)
Miller, R.E., Shenoy, V.B.: Size-dependent elastic properties of nanosized structural elements. Nanotechnology 11, 139–147 (2000)
Allara, D.L.: A perspective on surfaces and interfaces. Nature 437, 638–639 (2005)
Wong, E., Sheehan, P.E., Lieber, C.M.: Nanobeam mechanics: elasticity, strength, and toughness of nanorods and nanotubes. Science 277, 1971–1975 (1997)
Poncharal, P., Wang, Z., Ugarte, D., deHeer, W.A.: Electrostatic deflections and electromechanical resonances of carbon nanotubes. Science 283, 1513–1516 (1999)
Scheludko, A.D., Nikolov, A.D.: Measurement of surface tension by pulling a sphere from a liquid. Colloid Polymer Sci. 253, 396–403 (1975)
Deville, G.: Dynamic measurement of the surface tension of liquid helium with a two-dimensional electron probe. J. Low Temp. Phys. 72, 135–151 (1988)
Vázquez, G., Alvarez, E., Navaza, J.M.: Surface Tension of Alcohol + Water from 20 to 50 \(^{\circ }\)C. J. Chem. Eng. Data 40, 611–614 (1995)
Romero, C.M., Paéz, M.S.: Surface tension of aqueous solutions of alcohol and polyols at 298.15K. Phys. Chem. Liquids 44, 61-65 (2006)
Chang, J., Wang, H.P., Zhou, K., Wei, B.: Surface tension measurement of undercooled liquid Ni-based multicomponent alloys. Phil. Mag. Lett. 92, 428–435 (2012)
Gurtin, M.E., Murdoch, A.I.: A continuum theory of elastic material surfaces. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 57, 291–323 (1975)
Gurtin, M.E., Murdoch, A.I.: Surface stress in solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 14, 431–440 (1978)
Sharma, P., Ganti, S.: Effect of surfaces on the size-dependent elastic state of nano-inhomogeneities. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 535–537 (2003)
Duan, H.L., Wang, J., Huang, Z.P.: Size-dependent effective elastic constants of solids containing nano-inhomogeneities with interface stress. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 53, 1574–1596 (2005)
Lim, C.W., Li, Z.R., He, L.H.: Size-dependent, non-uniform elastic field inside a nano-scale spherical inclusion due to interface stress. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 5055–5065 (2006)
Tian, L., Rajapakse, R.K.N.D.: Analytical solution for size-dependent elastic field of a nano-scale circular inhomogeneity. J. Appl. Mech. 74, 568–574 (2007)
Tian, L., Rajapakse, R.K.N.D.: Elastic field of an isotropic matrix with a nano scale elliptical inhomogeneity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 44, 7988–8005 (2007)
Luo, J., Wang, X.: On the anti-plane shear of an elliptic nano inhomogeneity. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 28, 926–934 (2009)
Dong, C.Y., Pan, E.: Boundary element analysis of nano inhomogeneities of arbitrary shapes with surface and interface effects. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 35, 996–1002 (2011)
Wang, G.F., Wang, T.J.: Deformation around a nanosized elliptical hole with surface effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 161901 (2006)
Li, Q., Chen, Y.H.: Surface effect and size dependence on the energy release due to a nanosized hole expansion in plane elastic materials. J. Appl. Mech. 75, 061008 (2008)
Wang, S., Dai, M., Ru, C.Q., Gao, C.F.: Stress field around an arbitrarily shaped nanosized hole with surface tension. Acta Mech. 225, 3453–3462 (2014)
Grekov, M.A., Yazovskaya, A.A.: The effect of surface elasticity and residual surface stress in an elastic body with an elliptic nanohole. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 78, 172–180 (2014)
Xu, J.Y., Dong, C.Y.: Surface and interface stress effects on the interaction of nano-inclusions and nano-cracks in an infinite domain under anti-plane shear. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 111–112, 12–23 (2016)
Chen, T.: Exact size-dependent connections between effective moduli of fibrous piezoelectric nanocomposites with interface effects. Acta Mech. 196, 205–217 (2008)
Xiao, J.H., Xu, Y.L., Zhang, F.C.: Size-dependent effective electroelastic moduli of piezoelectric nanocomposites with interface effect. Acta Mech. 222, 59–67 (2011)
Xiao, J.H., Xu, Y.L., Zhang, F.C.: Evaluation of effective electroelastic properties of piezoelectric coated nano-inclusion composites with interface effect under antiplane shear. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 69, 61–68 (2013)
Fang, X.Q., Huang, M.J., Liu, J.X., Nie, G.Q.: Electro-mechanical coupling properties of piezoelectric nanocomposites with coated elliptical nano-fibers under anti-plane shear. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 064306 (2014)
Fang, X.Q., Huang, M.J., Liu, J.X., Feng, W.J.: Dynamic effective property of piezoelectric composites with coated piezoelectric nano-fibers. Compos. Sci. Tech. 98, 79–85 (2014)
Fang, X.Q., Huang, M.J., Zhu, Z.T., Liu, J.X.: Surface free energy effect on electromechanical behavior of piezoelectric thin film with square nanofibers under antiplane shear. Acta Mech. 226, 149–156 (2015)
Xiao, J.H., Xu, Y.L., Zhang, F.C.: Generalized self-consistent electroelastic estimation of piezoelectric nanocomposites accounting for fiber section shape under antiplane shear. Acta Mech. 227, 1381–1392 (2016)
Fang, X.Q., Zhu, C.S.: Size-dependent nonlinear vibration of nonhomogeneous shell embedded with a piezoelectric layer based on surface/interface theory. Compos. Struct. 160, 1191–1197 (2017)
Zhu, C.S., Fang, X.Q., Liu, J.X., Li, H.Y.: Surface energy effect on nonlinear free vibration behavior of orthotropic piezoelectric cylindrical nano-shells. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 66, 423–432 (2017)
Fang, X.Q., Gupta, V., Liu, J.X.: Effect of couple stress at the interfaces of a nanohole on the anti-plane electro-mechanical behavior. Phil. Mag. Lett. 93, 58–67 (2013)
Nan, H.S., Wang, B.L.: Nanoscale anti-plane cracking of materials with consideration of bulk and surface piezoelectricity effects. Acta Mech. 227, 1445–1452 (2016)
Chiang, C.R., Weng, G.J.: The nature of stress and electric displacement concentration around a strongly oblate cavity in a transversely isotropic piezoelectric material. Int. J. Fract. 134, 319–337 (2005)
Chiang, C.R., Weng, G.J.: Nonlinear behavior and critical state of a penny-shaped dielectric crack in a piezoelectric solid. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 74, 852–860 (2007)
Xiao, J.H., Xu, Y.L., Zhang, F.C.: A rigorous solution for the piezoelectric materials containing elliptic cavity or crack with surface effect. ZAMM Z Angew. Math. Mech. 96, 633–641 (2016)
Kuna, M.: Fracture mechanics of piezoelectric materials-Where are we right now? Eng. Fract. Mech. 77, 309–326 (2010)
Pak, Y.E.: Elliptical inclusion problem in antiplane piezoelectricity: implications for fracture mechanics. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 48, 209–222 (2010)
Mishra, D., Park, C.Y., Yoo, S.H., Pak, Y.E.: Closed-form solution for elliptical inclusion problem in antiplane piezoelectricity with far-field loading at an arbitrary angle. Eur. J. Mech. A. Solids 40, 186–197 (2013)
Wang, G.F., Feng, X.Q., Yu, S.W., Nan, C.W.: Interface effects on effective elastic moduli of nanocrystalline materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 363, 1–8 (2003)
Pan, X.H., Yu, S.W., Feng, X.Q.: A continuum theory of surface piezoelectricity for nanodielectrics. Sci. Chin. -Phys. Mech. Astron. 54, 564–573 (2011)
Chen, T.Y., Chiu, M.S., Weng, C.N.: Derivation of the generalized Young-Laplace equation of curved interfaces in nanoscaled solids. J. Appl. Phys. 100, 074308 (2006)
Zhang, T.Y., Tong, P.: Fracture mechanics for a mode III crack in a piezoelectric material. Int. J. Solids Struct. 33, 343–359 (1996)
Zhang, T.Y., Gao, C.F.: Fracture behaviors of piezoelectric materials. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 41, 339–379 (2004)
Pak, Y.E.: Circular inclusion problem in antiplane piezoelectricity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 29, 2403–2419 (1992)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11502123, 11262012) and the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region of China (Grant No. 2015JQ01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Li, X. Surface effects on an electrically permeable elliptical nano-hole or nano-crack in piezoelectric materials under anti-plane shear. Acta Mech 229, 4251–4266 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-018-2232-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-018-2232-1