Summary.
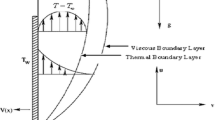
An analysis has been carried out to obtain the thermal-diffusion and the diffusion-thermo effects on the mixed free-forced convective and mass transfer steady laminar boundary-layer flow over an accelerating surface with a heat source in the presence of suction and blowing. The fluid viscosity is assumed to vary as an inverse linear function of temperature. The partial differential equations governing the problem under consideration have been transformed by a similarity transformation into a system of ordinary differential equations which is solved numerically by applying the shooting method. The results for an impermeable accelerating surface are discussed. The effects of the variable viscosity parameter θ r , the thermal diffusion parameter Sr, the diffusion-thermo parameter Df, suction or blowing parameter m, heat flux parameter s and Schmidt number Sc have been examined on the flow field of a hydrogen-air mixture as a non-chemical reacting fluid pair. The effects of varying these parameters are studied in the case of a surface with prescribed wall temperature and a surface with prescribed wall heat flux.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seddeek, M. Thermal-diffusion and diffusion-thermo effects on mixed free-forced convective flow and mass transfer over an accelerating surface with a heat source in the presence of suction and blowing in the case of variable viscosity. Acta Mechanica 172, 83–94 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-004-0139-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-004-0139-5