Abstract
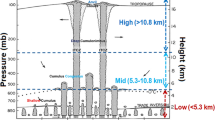
Using the CloudSat data for the Sichuan Basin vortices (SBVs) from June to August (2007–2016) and dividing the data based on whether the SBVs moved eastward, the cloud, precipitation, and thermal structural characteristics of the SVBs were comprehensively analyzed to cultivate a deeper understanding of these vortices. The results show that a direct correlation between vortex structure and precipitation intensity. The variations in radar reflectivity are completely opposite vertical distribution above and below a height of 5 km. The proportion of deep convective clouds is more than 30% of the total vortex depth, and the distribution differences are reflected by the middle and lower clouds. This occurs because stratiform precipitation commonly takes place in the Sichuan Basin. When an SBV moves eastward, the proportion of convective precipitation increases with increasing vortex enhancement. The distribution differences of ice particle parameters embody the effective precipitation mechanisms of sowing and supplying. The locations of intense vortices are indicative of the locations of rainfall centers. The instantaneous precipitation rate increases as the vortex center moves southward. There is a warm central region with a temperature of over 0 °C within 200 km of the vortex center for both type I and type III in the radial direction. The wet region appears below the warm region, and the vertical scope of the wet center is less than 4 km. The ranges and intensities of both the warm and wet centers increase gradually with the eastward development of the SBV.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
(1) The CloudSat data can be downloaded from the link ftp://ftp.cloudsat.cira.colostate.edu/. (2) The ECMWF reanalysis data with a horizontal resolution of 0.75° × 0.75° can be downloaded from the link https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/search?type=dataset. (3) The hourly precipitation product of the CMORPH integrated with the automatic station of China are from the China Meteorological Administration; the Southwest China Vortex Yearbook (2014–2017) data are from the Chengdu Institute of Plateau Meteorological, China Meteorology. These datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Austin R (2004) Level 2 Cloud ice water content product process description and interface control document. Colorado State University, Colorado, pp 1–29
Austin RT, Heymsfield AJ, Stephens GL (2009) Retrieval of ice cloud microphysical parameters using the CloudSat millimeter—wave radar and temperature. J Geophy Res Atmos 114(D8):D00A23. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD010049
Chen SJ, Lorenzo D (1984) Numerical prediction of the heavy rain-fall vortex over eastern Asia monsoon region. J MeteorOL Soc Japan 62(5):730–747. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj1965.62.5_730
Chen ZM, Xu ML, Min WB, Miu Q (2003) Relationship between abnormal activities of southwest vortex and heavy rain the upper reach of Yangtze River during summer of 1998. Plateau Meteorol 22(2):162–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02948883 (in Chinese)
Chen QZ, Huang YW, Wang QW, Tan ZM (2007) The statistical study of the southwest vortexes during 1990–2004. J Nanjing Univ Nat Sci 43(6):633642. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0469-5097.2007.06.008 (in Chinese)
Chengdu Institute of Plateau Meteorological, China Meteorology (2014) Southwest China vortex yearbook of 2013. Science Press, Beijing, pp 1–270 (in Chinese)
Chengdu Institute of Plateau Meteorological, China Meteorology (2015) Southwest China vortex yearbook of 2014. Science Press, Beijing, pp 1–270 (in Chinese)
Chengdu Institute of Plateau Meteorological, China Meteorology (2016) Southwest China vortex yearbook of 2015. Science Press, Beijing, pp 1–270 (in Chinese)
Chengdu Institute of Plateau Meteorological, China Meteorology (2017) Southwest China vortex yearbook of 2016. Science Press, Beijing, pp 1–270 (in Chinese)
Du Q, Qin DY, Zhang P (2013) Observation and analysis of a southwest vortex rainstorm in southern China using FY-2 satellite data. Meteorol Mon 39(7):821–931. https://doi.org/10.7519/j.issn.1000-0526.2013.07.003 (in Chinese)
Feng XY, Liu CH, Fan GZ, Liu XD, Feng CY (2016) Climatology and structures of southwest vortices in the NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. J Clim 29(21):7675–7701. https://doi.org/10.1175/jcli-d-15-0813.1
Fu SM, Zhang JP, Sun JH, Shen XY (2014) A fourteen-year climatology of the southwest vortex in summer. Atmos Ocean Sci Lett 7(6):510–514. https://doi.org/10.3878/AOSL20140047
Gao ST (1987) The dynamic action of the disposition of the fluid fields and the topography on the formation of the south-west vortex. Chin J Atmos Sci 11(3):263–271. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1987.03.05 (in Chinese)
Gao DM, Li YQ, Cheng XL (2018) A numerical study on a heavy rainfall caused by an abnormal-path coupling vortex with the assimilation of southwest China vortex scientific experiment data. Acta Meteorol Sin 76(3):343–360. https://doi.org/10.11676/qxxb2018.008 (in Chinese)
Hao LP, Deng J, Li GP (2013) Characteristics of GPS vapor in a persistent heavy rainfall related to southwest vortex. J Appl Meteor 24(2):230–239. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2013.02.011 (in Chinese)
Kang L, Hao LP, Niu JL (2011) Feature analysis on southwest vortex of triggering rainstorm. Plateau Meteorol 30(6): 1435–1443 http://www.gyqx.ac.cn/article/id/3038 (in Chinese)
Kollia P, Sztrmer W, Zawadzki I, Joe P (2007) Considerations for spaceborne 94 GHz radar observation of precipitation. Geophy Res Lett 34(21):L21803. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL031536
Kuo YH, Cheng LS, Anthes RA (1986) Mesoscale analyses of the Sichuan flood catastrophe, 11–15 July 1981. Mon Weather Rev 114(11):1984–2003. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1986)114%3c1984:MAOTSF%3e2.0.CO;2
Kuo YH, Cheng L, Bao JW (1988) Numerical simulation of the 1981 Sichuan flood. Part I: evolution of a mesoscale southwest vortex. Mon Weather Rev 116(12):2481–2504. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1988)116%3c2481:NSOTSF%3e2.0.CO;2
Li YQ, Xu XD (2016) A review of research and observing experiment on southwest China vortex. Adv Meteorol Sci Technol 6(3):134–140. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-1973.2016.03.018 (in Chinese)
Li GP, Wan J, Lu JH (1991) A potential mechanism of the warm vortex genesis in southwest China. Q J Appl Meteorol 2(1):91–99 (in Chinese)
Li DJ, Li YQ, Liu C, Lin L (2010) Comparative analysis between two summer heavy rain events in Yibin based on the TRMM data. Acta Meteor Sin 68(4):559–568. https://doi.org/10.11676/qxxb2010.054 (in Chinese)
Li C, Li YQ, Jiang XW (2015) Statistical characteristics of the inter-monthly variation of the Sichuan Basin vortex and distribution of daily precipitation. Chin J Atmos Sci 39(6):1191–1203. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1502.14270 (in Chinese)
Lu JH (1988) Apply the thermal wind adjustment theorem to analyse genesis mechanism of the warm south-west vortex of China. Plateau Meteorol 7(4): 345–356. http://www.gyqx.ac.cn/CN/Y1988/V7/I4/345 (in Chinese)
Lu P, Li X, Li Y, Li YQ, Zheng WP (2016) The influence of spatially intensive sounding observation data on the numerical modeling of southwest vortex rainfall. Chin J Atmos Sci 40(4):730–742. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1511.15170 (in Chinese)
Luo ZZ, Stephens G, Emanuel KA, Vane DG, Tourville N, Haynes JM (2008) On the use of CloudSat and MODIS data for estimating hurricane intensity. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 5(1):13–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2007.905341
Ma H, Zheng SB, Hu ZTY, Zheng H (2010) Analyses on satellite cloud images and doppler radar echo features of a MCC rainstorm caused by southwest vortex. Trans Atmos Sci 33(6):688–696. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1037.2010.00186 (in Chinese)
Mace G (2008) A NASA earth system science pathfinder mission, CloudSat standard data products handbook. Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere, Colorado State University
Matrosov SY (2010) CloudSat studies of stratiform precipitating systems observed in the vicinity of the Southern Great Plains Atmospheric Radiation Measurement site. J Appl Meteor Climatol 49(8):1756–1765. https://doi.org/10.1175/2010JAMC2444.1/
Matrosov SY (2011) CloudSat measurements of landfalling hurricanes Gustav and Ike (2008). J Geophys Res 116(D1):D01203. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD014506
Mitrescu C, L’Ecuyer T, Haynes J, Miller S, Turk J (2010) CloudSat precipitation profiling algorithm-model description. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 49(5):991–1003. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JAMC2181.1
Mu D, Li YQ (2017) Statistical characteristics summary of the southwest China vortex. J Arid Meteorol 35(2):175–181. https://doi.org/10.11755/j.issn.1006-7639(2017)-02-0175 (in Chinese)
Pan Y, Li J, Yu RC (2011) Climatic characteristics of the spatial structure of eastward-moving southwest vortex. Clim Environ Res 16(1):60–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-010-1000-5 (in Chinese)
Peng XD, Cheng LS (1994) A case study on the evolution of the low vortex and shear-line on the east side of the plateau. II. Mesoscale numerical simulation. J Lanzhou Univ 30(1):124–131 (in Chinese)
Rao XQ, Wang SG (2019) Diagnostic Analysis on Heavy Rain Process of the Northeast-moving Southwest Vortex. Meteor Environ Res 10(3):1–10. https://doi.org/10.19547/j.issn2152-3940.2019.03.001
Sassen K, Wang ZE (2008) Classifying clouds around the globe with the CloudSat radar: 1-year of results. Geophys Res Lett 35(4):L04805. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007gl032591
Shen GX, He GB (2008) The observed facts analysis of southwest vortex from 2000 to 2007. Plateau Mt Meteorol Res 28(4):59–65. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.16742184.2008.04.010 (in Chinese)
Stephens GG, Vane DG, Boain RJ, Mace GG, Sassen K, Wang ZE, Lllingworth AJ, O’Connor EJ, Rossow WB, Durden S, Miller SD, Austin RT (2002) The CloudSat mission and the A-train: a new dimension of space-based observation of clouds and precipitation. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83(12):1771–1790. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-83-12-1771
Tanelli S, Durden S, Im E, Pak K, Reinke DG, Partain P, Haynes JM, Marchand RT (2008) CloudSat’s cloud profiling radar after two years in orbit: Performance, calibration, and processing. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 46(11):3560–3573. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002030
Wang B, Orlanski I (1987) Study of a heavy rain vortex formed over the eastern flank of the Tibetan Plateau. Mon WeaTHER Rev 115:1370–1393. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1987)115,1370:SOAHRV.2.0.CO;2
Wang ZE, Sassen K (2007) Level 2 cloud scenario classification product process description and interface control document. Version 5.0. Colorado State University pp 5–50
Wang QW, Tan ZM (2015) Multi-scale topographic control of south-west vortex formation in Tibetan Plateau region in an idealized simulation. J Geophys Res- Atmos 119(20):11543–11561. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD021898
Wang W, Kuo YH, Wamer TT (1993) A Diabatically driven mesoscale vortex in the lee of the Tibetan plateau. Mon Weather Rev 121(9):2542–2561. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(1993)121%3c2542:ADDMVI%3e2.0.CO;2
Wang ZS, Wang YH, Liang YG (1996) Numerical experiments on a heavy rainfall caused by southwest vortex. A study on the rainstorm science, operational experiments and theory of weather dynamics. Meteorological Press, Beijing, pp 257–267 (in Chinese)
Wu GX, Chen SJ (1985) The effect of mechanical forcing on the formation of a mesoscale vortex. Q J R Meteorol Soc 111(470):1049–1070. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49711147009
Wu GX, Liu HZ (1999) Complete form of vertical vorticity tendency equation and slantwise vorticity development. Acta Meteorol Sin 57(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.11676/qxxb1999.001 (in Chinese)
Wu DL, Austin RT, Deng M, Durden SL, Heymsfield AJ, Jiang JH, Lambert A, Li JL, Livesey NJ, McFarquhar GM, Pittman JV, Stephens GL, Tanelli S, Vane DG, Waliser DE (2009) Comparisons of global cloud ice from MLS, CloudSat, and correlative data sets. J Geophy Res Atmos 114(D8):D00A24. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD009946
Xu YH (1991) Climate of Southwest China. Meteorological Press, Beijing, pp 56–60
Yan YF, Liu YM, Lu JH (2016) Cloud vertical structure, precipitation, and cloud radiative effects over Tibetan Plateau and its neighboring regions. J Geophys Res 121(10):5864–5877. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD024591
Yan YF, Wang XC, Liu YM (2018) Cloud vertical structures associated with precipitation magnitudes over the Tibetan Plateau and its neighboring regions. Atmos Oceanic Sci Lett 11(1):44–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/16742834.2018.1395680
Zeng HY, Kang P, Wang SG, Zhang XL, Feng XY, Jing JH, Zhou ZH (2020) Influences of southwest vortex on aerosol optical depth variation. Acta Sci Circum 40(2):418–428. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2019.0410 (in Chinese)
Zhang H, Jing X, Li J (2014) Application and evaluation of a new radiation code under McICA scheme in BCC_AGCM2.0.1. Geosci Model Dev 7(3):737–754. https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-7-737-2014
Zhang X, Duan KQ, Shi PH (2015) Cloud vertical profiles from CloudSat data over eastern Tibetan Plateau during summer. Chin J Atmos Sci 39(6):1073–1080. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1502.14196 (in Chinese)
Zhao SX, Fu SM (2007) An analysis on the southwest vortex and its environment fields during heavy rainfall in eastern Sichuan province and Chongqing in September 2004. Chin J Atmos Sci 31(6):1059–1075. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2007.06.03 (in Chinese)
Zhao YC, Wang YH (2010) A case study of plateau vortex inducing southwest vortex and producing extremely heavy rain. Plateau Meteorol 29(4):819–831. https://doi.org/10.3788/gzxb20103906.0998 (in Chinese)
Zhao DJ, Jiang YH, Li Y (2011) Diagnostic analysis and numerical simulation of a torrential rainstorm process caused southwestern low vortex. Plateau Meteorol 30(5):1158–1169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-010-1000-5 (in Chinese)
Zhong R, Zhong LH, Hua LJ, Feng SD (2014) A climatology of the southwest vortex during 1979–2008. Atmos Ocean Sci Lett 7(6):577–583. https://doi.org/10.3878/AOSL20140042
Zhou M, Liu LP, Wang HY (2014) Analysis of the echo structure and its evolution as shown in a severe precipitation event caused by the plateau vortex and the southwest vortex. Acta Meteor Sin 72(3):554–569. https://doi.org/10.11676/qxxb2014.029 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 91937301), the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (Nos. 2019QZKK0105 and 2019QZKK0103), and the Scientific and Technological Research Program of the China Railway Eryuan Engineering Group Co. Ltd. (No. KYY2020066 (20–22)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Clemens Simmer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, S., Li, Y. & Peng, J. Analyzing the structural characteristics of the Sichuan basin vortex based on CloudSat satellite data. Meteorol Atmos Phys 134, 74 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-022-00905-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-022-00905-6