Abstract
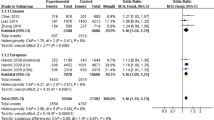
It is reported that CLU rs2279590 polymorphism is significantly associated with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in European ancestry. Recent studies investigated rs2279590 polymorphism in Asian population (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Four studies showed negative association and two studies showed weak association between rs2279590 and AD. We believe that the weak association or no association may be caused by the relatively small sample size in Asian population. Here, we reinvestigated the association in Asian population. Meanwhile, to investigate the genetic heterogeneity of the rs2279590 polymorphism in Asian and Caucasian populations, we searched the PubMed and AlzGene databases and selected 11 independent studies (6 studies in Asian population and 5 studies in Caucasian population) including 20,655 individuals (8,605 cases and 12,050 controls) for meta-analysis. Our results showed significant association between rs2279590 polymorphism and AD in Asian population with P = 2.00E−04 and P = 2.00E−04 using additive and recessive models, respectively. We observed no significant heterogeneity between Asian and Caucasian populations. We believe that our results may be helpful to understand the mechanisms of CLU in AD pathogenesis and will be useful for future genetic studies in AD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ (2005) Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 21(2):263–265
Braskie MN, Jahanshad N, Stein JL, Barysheva M, McMahon KL, de Zubicaray GI et al (2011) Common Alzheimer’s disease risk variant within the CLU gene affects white matter microstructure in young adults. J Neurosci 31(18):6764–6770
Carrasquillo MM, Belbin O, Hunter TA, Ma L, Bisceglio GD, Zou F et al (2010) Replication of CLU, CR1, and PICALM associations with alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 67(8):961–964
Chen LH, Kao PY, Fan YH, Ho DT, Chan CS, Yik PY et al (2012) Polymorphisms of CR1, CLU and PICALM confer susceptibility of Alzheimer’s disease in a southern Chinese population. Neurobiol Aging 33(1):210 (e211–217)
Daimon M, Oizumi T, Karasawa S, Kaino W, Takase K, Tada K et al (2011) Association of the clusterin gene polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 60(6):815–822
Elias-Sonnenschein LS, Helisalmi S, Natunen T, Hall A, Paajanen T, Herukka SK et al (2013) Genetic loci associated with Alzheimer’s disease and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in a Finnish case-control cohort. PLoS ONE 8(4):e59676
Harold D, Abraham R, Hollingworth P, Sims R, Gerrish A, Hamshere ML et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41(10):1088–1093
Hollingworth P, Harold D, Sims R, Gerrish A, Lambert JC, Carrasquillo MM et al (2011) Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 43(5):429–435
Jiang Y, Zhang R, Zheng J, Liu P, Tang G, Lv H et al (2012) Meta-analysis of 125 rheumatoid arthritis-related single nucleotide polymorphisms studied in the past two decades. PLoS ONE 7(12):e51571
Jin C, Li W, Yuan J, Xu W, Cheng Z (2012) Association of the CR1 polymorphism with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in Chinese Han populations: a meta-analysis. Neurosci Lett 527(1):46–49
Kamboh MI, Minster RL, Demirci FY, Ganguli M, Dekosky ST, Lopez OL et al (2012) Association of CLU and PICALM variants with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 33(3):518–521
Komatsu M, Shibata N, Kuerban B, Ohnuma T, Baba H, Arai H (2011) Genetic association between clusterin polymorphisms and Alzheimer’s disease in a Japanese population. Psychogeriatrics 11(1):14–18
Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G, Campion D, Sleegers K, Hiltunen M et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41(10):1094–1099
Liu G, Jiang Y, Wang P, Feng R, Jiang N, Chen X et al (2012) Cell adhesion molecules contribute to Alzheimer’s disease: multiple pathway analyses of two genome-wide association studies. J Neurochem 120(1):190–198
Liu G, Zhang L, Feng R, Liao M, Jiang Y, Chen Z et al (2013a) Lack of association between PICALM rs3851179 polymorphism and Alzheimer’s disease in Chinese population and APOEepsilon4-negative subgroup. Neurobiol Aging 34(4):1310 (e1319–1310)
Liu G, Zhang S, Cai Z, Li Y, Cui L, Ma G et al (2013b) BIN1 gene rs744373 polymorphism contributes to Alzheimer’s disease in East Asian population. Neurosci Lett 544:47–51
Liu G, Zhang S, Cai Z, Ma G, Zhang L, Jiang Y et al (2013c) PICALM gene rs3851179 Polymorphism contributes to Alzheimer’s disease in an Asian population. Neuromol Med 15(2):384–388
Liu G, Wang H, Liu J, Li J, Li H, Ma G et al (2014a) The CLU gene rs11136000 variant is significantly associated with Alzheimer’s disease in Caucasian and Asian populations. Neuromolecular Med 16(1):52–60
Liu G, Yao L, Liu J, Jiang Y, Ma G, Chen Z et al (2014b) Cardiovascular disease contributes to Alzheimer’s disease: evidence from large-scale genome-wide association studies. Neurobiol Aging 35(4):786–792
Logue MW, Schu M, Vardarajan BN, Buros J, Green RC, Go RC et al (2011) A comprehensive genetic association study of Alzheimer disease in African Americans. Arch Neurol 68(12):1569–1579
Miyashita A, Koike A, Jun G, Wang LS, Takahashi S, Matsubara E et al (2013) SORL1 is genetically associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in Japanese, Koreans and Caucasians. PLoS One 8(4):e58618
Naj AC, Jun G, Beecham GW, Wang LS, Vardarajan BN, Buros J et al (2011) Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 43(5):436–441
Seshadri S, Fitzpatrick AL, Ikram MA, DeStefano AL, Gudnason V, Boada M et al (2010) Genome-wide analysis of genetic loci associated with Alzheimer disease. JAMA 303(18):1832–1840
Sweet RA, Seltman H, Emanuel JE, Lopez OL, Becker JT, Bis JC et al (2012) Effect of Alzheimer’s disease risk genes on trajectories of cognitive function in the Cardiovascular Health Study. Am J Psychiatry 169(9):954–962
Thambisetty M, Beason-Held LL, An Y, Kraut M, Nalls M, Hernandez DG et al (2013) Alzheimer risk variant CLU and brain function during aging. Biol Psychiatry 73(5):399–405
Trikalinos TA, Salanti G, Khoury MJ, Ioannidis JP (2006) Impact of violations and deviations in Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium on postulated gene-disease associations. Am J Epidemiol 163(4):300–309
Yu JT, Tan L (2012) The role of clusterin in Alzheimer’s disease: pathways, pathogenesis, and therapy. Mol Neurobiol 45(2):314–326
Yu JT, Li L, Zhu QX, Zhang Q, Zhang W, Wu ZC et al (2010) Implication of CLU gene polymorphisms in Chinese patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Chim Acta 411(19–20):1516–1519
Yu JT, Ma XY, Wang YL, Sun L, Tan L, Hu N (2013) Genetic variation in clusterin gene and Alzheimer’s disease risk in Han Chinese. Neurobiol Aging 34(7):1921 (e1917–1923)
Zhang MD, Gu W, Qiao SB, Zhu EJ, Zhao QM, Lv SZ (2014) Apolipoprotein e gene polymorphism and risk for coronary heart disease in the Chinese population: a meta-analysis of 61 studies including 6634 cases and 6393 controls. PLoS ONE 9(4):e95463
Acknowledgments
We thank Yu, Chen, KOMATSU and Lambert et al. for the genotype data. This work was supported by funding from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 81300945, 31200934, 31171219, 81271213, 81070878, 81271214, and 81261120404), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (No S2012010008222), and the Science and Technology Innovation Fund of Guangdong Medical College (No. STIF 201101).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Zhang, D., Jiang, Y. et al. CLU rs2279590 polymorphism contributes to Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility in Caucasian and Asian populations. J Neural Transm 122, 433–439 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1260-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1260-9