Abstract
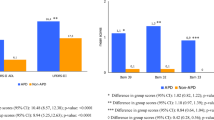
It is currently controversial if and in which terms Parkinson’s disease (PD) and restless legs syndrome (RLS) are linked in co-morbid association. In a cohort of 106 de novo PD patients (67 male and 39 female, aged 42–83 years), 15 of them developed RLS, which was prospectively assessed at 6-month intervals from the starting of dopamine(DA)ergic therapy. The incidence rate of total RLS was 47 per 1,000 case/person per year and 37 per 1,000 case/person per year after the exclusion of possible “secondary” forms of the disorder (n = 3). These figures are higher than those reported in an incidence study conducted in German general population (Study of Health in Pomerania), in which the method of ascertainment of RLS similar to ours has been used. An incidence rate of total RLS significantly higher than that reported in the above-mentioned study was found in the age ranges 55–64 years and in the age range 45–74 years standardized to European general population 2013 (70 and 53 per 1,000 case/person per year, respectively, p < 0.01). Ten out of 12 patients (83.3 %) developed RLS within 24 months from the starting of DAergic medication (median latency 7.5 months). These findings support the view that sustained DAergic therapy could represent the critical factor inducing an increased incidence of RLS in patients with PD and that the latter disease should be regarded as the condition predisposing to the occurrence of the former and not viceversa as previously hypothesized. The mechanism underlying the increased incidence of RLS remains unclear and deserves further investigation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RP, Picchietti D, Hening WA, Trenkwalder C, Walters AS, Montplaisir J (2003) Restless legs syndrome: diagnostic criteria, special considerations and epidemiology. A report from the restless leg syndrome diagnosis and epidemiology workshop at the National Institutes of Health. Sleep Med 4:101–119
American Sleep Disorders Association (1997) International Classification of Sleep Disorders: Diagnosis and Coding Manual—Revised, Rochester
Angelini M, Negrotti A, Marchesi E, Bonavina G, Calzetti S (2011) A study of prevalence of restless legs syndrome in previously untreated Parkinson’s disease patients: absence of co-morbid association. J Neurol Sci 310:286–288
Bhalsing K, Suresh K, Muthane UB, Pal PKr (2013) Prevalence and profile of Restless Legs Syndrome in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders: A case-control study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19:426–430
Braga-Neto P, Silva junior FP, Monte FS, de Bruin PFC, de Bruin VMS (2004) Snoring and excessive daytime sleepiness in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 217:41–45
Budhiraja P, Budhiraja R, Goodwin JL, Allen RP, Newman AB, Koo BB, Quan SF (2012) Incidence of Restless Legs Syndrome and its correlates. J Clin Sleep Med 8:119–124
Calzetti S, Negrotti A, Bonavina G, Angelini M, Marchesi E (2009) Absence of co-morbidity of Parkinson’s disease and restless legs syndrome: a case-control study in patients attending a movement disorders clinic. Neurol Sci 30:119–122
Clemens S, Reye D, Hochman S (2006) Restless legs syndrome: revisiting the dopamine hypothesis from the spinal cord perspective. Neurology 67:125–130
Gjerstad MD, Tysnes OB, Larsen JP (2011) Increased risk of leg motor restlessness but not RLS in early Parkinson disease. Neurology 77:1941–1946
Gomez-Esteban JC, Zarranz JJ, Tijero B, Velasco F, Barcena J, Rouco I, Lezcano E, Lachen MC, Jauregui A, Ugarte A (2007) Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 22:1912–1916
Guerreiro TM, Nishikawa DRC, Ferreira LC, Melo HA, Prado RCP (2010) Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease—Clinical characteristics and biochemical correlations. Arq Neuropsichiatr 68:869–872
Kaynak D, Kiziltan G, Kaynak G, Benbir G, Uysal O (2005) Sleep and sleepiness in patients with Parkinson’s disease before and after dopaminergic treatment. Eur J Neurol 12:199–207
Krishnan PR, Bathia M, Behari M (2003) Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease: a case-controlled study. Mov Disord 18:181–185
Kumar S, Bathia M, Behari M (2002) Sleep disorders in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 17:775–781
Langston JW, Forno LS (1978) The hypothalamus in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 3:129–133
Lee JE, Shin HW, Kim KS, Sohn YH (2009) Factors contributing to the development of restless legs syndrome in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 24:579–582
Loo H-V, Tan EK (2008) Case-control study of restless legs syndrome and quality of sleep in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 266:145–149
Nomura T, Inoue Y, Miyake M, Yasui K, Nakashima K (2006a) Prevalence and clinical characteristics of restless legs syndrome in Japanese patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 21:380–384
Nomura T, Inoue Y, Nakashima K (2006b) Clinical characteristics of restless legs syndrome in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 250:39–44
Ohajon MM, O’Hara R, Vitiello MV (2012) Epidemiology of restless legs syndrome: a synthesis of the literature. Sleep Med Rev 16:283–295
Ondo WG, Vuong KD, Jankovic J (2002) Exploring the relationship between Parkinson disease and restless legs syndrome. Arch Neurol 59:421–424
Peralta CM, Frauscher B, Seppi K, Wolf E, Wenning GK, Hogl B, Poewe W (2009) Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 24:2076–2080
Shin H-Y, Youn J, Yoon WT, Kim JS, Cho JW (2013) Restless legs syndrome in Korean patients with drug-naïve Parkinson’s disease: a nation-wide study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19:355–358
Suzuki K, Miyamoto M, Miyamoto T, Tatsumoto M, Watanabe Y, Suzuki S, Iwanami M, Sada T, Kadowaki T, Numao A (2012) Nocturnal disturbances and restlessness in Parkinson’s disease: Using the Japanese version of the Parkinson’s disease sleep scale-2. J Neurol Sci 318:76–81
Szentkiralyi A, Fendrich K, Hoffman W, Happe S, Berger K (2011) Incidence of restless legs syndrome in two population-based cohort studies in Germany. Sleep Med 12:815–820
Tan EK, Lum SY, Wong MC (2002) Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 196:33–36
The International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group (2003) Validation of the International Restless Legs Syndrome Study Group rating scale for restless legs syndrome. Sleep Med 4:121–132
Tomlison CL, Stowe R, Patel S, Rick C, Gray R, Clarke CE (2010) Systematic review of levodopa dose equivalency reporting in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 25:2649–2653
Verbaan D, van Rooden SM, van Hilten JJ, Rijsman RM (2010) Prevalence and clinical profile of Restless Legs Syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 25:2142–2147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calzetti, S., Angelini, M., Negrotti, A. et al. A long-term prospective follow-up study of incident RLS in the course of chronic DAergic therapy in newly diagnosed untreated patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 121, 499–506 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1132-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-013-1132-8