Summary
Background. Intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring has become standard in the management of neurocritical patients. A variety of monitoring techniques and devices are available, each offering advantages and disadvantages. Analysis of large populations has never been performed.
Patients and methods. A prospective study was designed to evaluate the Camino® fiberoptic intraparenchymal cerebral pressure monitor for complications and accuracy.
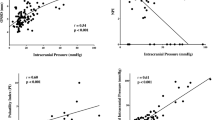
Results. Between 1992–2004 one thousand consecutive patients had a fiberoptic ICP monitor placed. The most frequent indication for monitoring was severe head injury (697 cases). The average duration of ICP monitoring was 184.6 ± 94.3 hours; the range was 16–581 hours. Zero drift (range, −17 to 21 mm Hg; mean 7.3 ± 5.1) was recorded after the devices were removed from 624 patients. Mechanical complications such as: breakage of the optical fiber (n = 17); dislocations of the fixation screw (n = 15) or the probe (n = 13); and failure of ICP recording for unknown reasons (n = 4) were found in 49 Camino® devices.
Conclusions. The Camino ICP sensor remains one of the most popular ICP monitoring devices for use in critical neurosurgical patients. The system offers reliable ICP measurements in an acceptable percentage of device complications and the advantage of in vivo recalibration. The incidence of technical complications was low and similar to others devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RCE Anderson P Kan P Klimo DL Brockmeyer ML Walker JR Kestle (2004) ArticleTitleComplications of intracranial pressure monitoring in children with head trauma. J Neurosurg (Pediatrics) 101 53–58
S Bavetta JS Noris M Wyatt JC Sutcliffe PJ Hamlyn (1997) ArticleTitleProspective study of zero drift in fiberoptic pressure monitors used in clinical practice. J Neurosurg 86 927–930 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiA3MvpvFI%3D Occurrence Handle9171170
M Blaha D Lazar (2005) ArticleTitleTraumatic brain injury and haemorrhagic complications after intracranial pressure monitoring. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76 IssueID1 147 Occurrence Handle10.1136/jnnp.2003.030817 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2cnjt1Gruw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle15608024
A Bekar S Goren E Korfali K Aksoy S Boyaci (1998) ArticleTitleComplications of brain tissue pressure monitoring with a fiberoptic device. Neurosurg Rev 21 254–259 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01105781 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7msFGmtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10068186
Brain Trauma Foundation, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Joint Section on Neurotrauma and Critical Care: Guidelines for the management of severe head injury. J Trauma 2000; 17: 449–555
LR Chambers PJ Kane MS Choksey AD Mendelow (1993) ArticleTitleAn evaluation of the Camino ventricular bolt system in clinical practice. Neurosurgery 33 866–868 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuD1cfosFc%3D Occurrence Handle8264885
G Citerio PJD Andrews (2004) ArticleTitleIntracranial pressure. Part two: Clinical applications and technology. Intensive Care Med 30 1882–1885 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00134-004-2377-3 Occurrence Handle15243685
M Czosnyka K Czosnyka JD Pickard (1996) ArticleTitleLaboratory testing of three intracranial pressure microtransducers: technical report. Neurosurgery 38 219–223 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymA2MvgsVU%3D Occurrence Handle8747977
M Czosnyka Z Czosnyka JD Pickard (1997) ArticleTitleLaboratory testing of the Spiegelberg brain pressure monitor: a technical report. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63 732–735 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2Fnslarug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9416806
JW Davis IC Davis LD Bennink SE Hysell BV Curtis KL Kaups JF Bilello (2004) ArticleTitlePlacement of intracranial pressure monitors: are “normal” coagulation parameters necessary? J Trauma 57 1173–1177 Occurrence Handle15625446
WP Gray JD Palmer J Gill M Gardner F Iannotti (1996) ArticleTitleA clinical study of parenchymal and subdural miniature straingauge transducers for monitoring intracranial pressure. Neurosurgery 39 IssueID5 927–931 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiD287ntFM%3D Occurrence Handle8905747
J Guillaume P Janny (1951) ArticleTitleManometric intracranienne continue: Interet de la methode et premiers resultants. Rev Neurol (Paris) 84 131–142 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Cy6D2svpt10%3D
LL Guyot C Dowling FG Diaz DB Michael (1998) ArticleTitleCerebral Monitoring devices: Analysis of complications. Acta Neurochir [Suppl] 71 47–49 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvlt1WlsQ%3D%3D
DG Jacobs A Westerband (1998) ArticleTitleAntibiotic prophylaxis for intracranial pressure monitors. J Natl Med Assoc 90 417–423 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czltVeqtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9685777
RL Jensen YS Hahn E Ciro (1997) ArticleTitleRisk factors of intracranial pressure monitoring in children with fiberoptic devices: A critical review. Surg Neurol 47 16–22 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiC3sblsFw%3D Occurrence Handle8986159
R Keays G Alexander R Williams (1993) ArticleTitleThe safety and value of extradural intracranial pressure monitors in fulminant hepatic failure. J Hepatol 18 205–209 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-8278(05)80247-8 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuD3Mvis1A%3D Occurrence Handle8409336
JM Lang J Beck M Zimmermann V Seifert A Raabe (2003) ArticleTitleClinical evaluation of intraparenchymal Spiegelberg pressure sensor. Neurosurgery 52 1455–1459 Occurrence Handle12762891
N Lundberg (1961) ArticleTitleContinuous recording and control of ventricular fluid pressure in neurosurgical practice. Acta Psychiatr Scand 36 IssueID[Suppl 149] 1–193
NF Maartens L Lustgarten V Josan TZ Aziz (2002) ArticleTitleHow safe is twistdrill craniostomy? Br J Neurosurg 16 290–293 Occurrence Handle10.1080/02688690220148897 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38vkslamtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle12201400
RM Martínez-Mañas E Ferrer C García-Amorena (1999) ArticleTitleClinical experience of intracranial pressure monitoring. Retrospective study in 239 Camino® monitored patients. Neurocirugía 10 291–296
MH Morgalla M Cuno H Mettenleiter BE Will L Krasznai M Skalej M Bitzer EH Grote (1997) ArticleTitleICP monitoring with are-usable transducer: Experimental and clinical evaluation of the Gaeltec ICT/b pressure probe. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 139 569–573 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiA1M7osFQ%3D
MH Morgalla K Dietz M Deininger EH Grote (2002) ArticleTitleThe problem of Long-Term ICP drift assessment: Improvement by use of the ICP drift index. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144 57–61 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s701-002-8274-2 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FotVCjtw%3D%3D
E Münch R Weigel P Schmiedek L Schürer (1998) ArticleTitleThe CAMINO intracranial pressure device in clinical practice: reliability, handling characteristics and complications. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140 1113–1120
RC Ostrup TG Luerssen LF Marshall MH Zornow (1987) ArticleTitleContinuous monitoring of intracranial pressure with a miniaturized fiberoptic device. J Neurosurg 67 206–209 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiB2MzjslY%3D Occurrence Handle3598682
MA Poca J Sahuquillo M Arribas M Báguena S Amorós E Rubio (2002) ArticleTitleFiberoptic intraparenchymal brain pressure monitoring with the Camino V420 monitor: Reflections on our experience in 163 severely head-injured patients. J Trauma 19 439–448
VC Prabhu HH Kaufman JL Voelker SC Aronoff M Niewiadomska-Bugaj S Mascaro GR Hobbs (1999) ArticleTitleProphylactic antibiotics with intracranial pressure monitors and external ventricular drains: a review of the evidence. Surg Neurol 52 226–237 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MvjvFSqtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10511079
L Schürer E Münch A Piepgras R Weigel L Schilling P Schmiedek (1997) ArticleTitleAssessment of the CAMINO intracranial pressure device in clinical practice. Acta Neurochir [Suppl] 70 296–298
S Shapiro R Bowman J Callahan C Wolfa (1996) ArticleTitleThe fiberoptic intraparenchymal cerebral pressure monitor in 244 patients. Surg Neurol 45 278–282 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymB387jtlc%3D Occurrence Handle8638226
DF Signorini A Shad IR Piper PFX Statham (1998) ArticleTitleA clinical evaluation of the Codman MicroSensor for intracranial pressure monitoring. Br J Neurosurg 12 IssueID3 223–227 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvmtlektw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11013684
R Stendel J Heidenreich A Schilling R Akhavan-Sigari R Kurth T Picht T Pietilä O Suess C Kern J Meisel M Brock (2003) ArticleTitleClinical evaluation of a new intracranial pressure monitoring device. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145 185–193 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3s7hslOqtQ%3D%3D
A Valentin T Lang R Karnik HP Ammerer J Ploder J Slany (2003) ArticleTitleIntracranial pressure monitoring and case mix-adjusted mortality in intracranial hemorrhage. Crit Care Med 31 IssueID5 1539–1542 Occurrence Handle12771630
Y Yau IR Piper RE Clutton IR Whittle (2000) ArticleTitleExperimental evaluation of the Spiegelberg intracranial pressure and intracranial compliance monitor. J Neurosurg 93 1072–1077 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FnslKmsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11117854
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelabert-González, M., Ginesta-Galan, V., Sernamito-García, R. et al. The Camino intracranial pressure device in clinical practice. Assessment in a 1000 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148, 435–441 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0683-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0683-3