Abstract
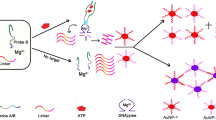
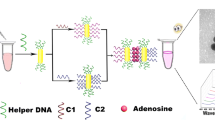
An aptamer based assay is described for the colorimetric detection of adenosine. The presence of adenosine triggers the deformation of hairpin DNA oligonucleotide (HP1) containing adenosine aptamer and then hybridizes another unlabeled hairpin DNA oligonucleotide (HP2). This leads to the formation of a double strand with a blunt 3′ terminal. After exonuclease III (Exo III)-assisted degradation, the guanine-rich strand (GRS) is released from HP2. Hence, the adenosine-HP1 complex is released to the solution where it can hybridize another HP2 and initiate many cycles of the digestion reaction with the assistance of Exo III. This leads to the generation of a large number of GRS strands after multiple cycles. The GRS stabilize the red AuNPs against aggregation in the presence of potassium ions. If, however, GRS forms a G-quadruplex, it loses its ability to protect gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) from salt-induced AuNP aggregation. Therefore, the color of the solution changes from red to blue which can be visually observed. This colorimetric assay has a 0.13 nM detection limit and a wide linear range that extends from 5 nM to 1 μM.

Schematic presentation of a colorimetric aptamer biosensor for adenosine detection based on DNA cycling amplification and salt-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Latini S, Pedata F (2001) Adenosine in the central nervous system: release mechanisms and extracellular concentrations. J Neurochem 79:463–484
Cunha RA (2001) Adenosine as a neuromodulator and as a homeostatic regulator in the nervous system: different roles, different sources and different receptors. Neurochem Int 38:107–125
Nguyen MD, Venton BJ (2015) Fast-scan cyclic voltammetry for the characterization of rapid adenosine release. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 13:47–54
Borea PA, Gessi S, Merighi S, Varani K (2016) Adenosine as a multi-signalling guardian angel in human diseases: when, where and how does it exert its protective effects? Trends Pharmacol Sci 37:419–434
Yin D, Liu YY, Wang TX, Hu ZZ, Qu WM, Chen JF, Cheng NN, Huang ZL (2016) Paeoniflorin exerts analgesic and hypnotic effects via adenosine a(1) receptors in a mouse neuropathic pain model. Psychopharmacology 233:281–293
Majetschak M (2016) Multiple ways of targeting the adenosine/adenosine receptor axis in lung inflammation and injury. Crit Care Med 44(2016):853–854
Zhu Y, Hu XC, Shi S, Gao RR, Huang HL, Zhu YY, Lv XY, Yao TM (2016) Ultrasensitive and universal fluorescent aptasensor for the detection of biomolecules (ATP, adenosine and thrombin) based on DNA/ag nanoclusters fluorescence light-up system. Biosens Bioelectron 79:205–212
Hashemian Z, Khayamian T, Saraji M, Shirani MP (2016) Aptasensor based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer for the analysis of adenosine in urine samples of lung cancer patients. Biosens Bioelectron 79:334–340
Song YY, Xu GH, Wei FD, Cen Y, Sohail M, Shi ML, Xu XM, Ma YS, Ma YJ, Hu Q (2018) Aptamer-based fluorescent platform for ultrasensitive adenosine detection utilizing Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185:139
Li LL, Ge PH, Selvin PR, Lu Y (2012) Direct detection of adenosine in undiluted serum using a luminescent aptamer sensor attached to a terbium complex. Anal Chem 84:7852–7856
Shi HW, Wu MS, Du Y, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2014) Electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based on bipolar electrode for detection of adenosine in cancer cells. Biosens Bioelectron 55:459–463
Fang HF, Pajski ML, Ross AE, Venton BJ (2013) Quantitation of dopamine, serotonin and adenosine content in a tissue punch from a brain slice using capillary electrophoresis with fast-scan cyclic voltammetry detection. Anal Methods-Uk 5:2704–2711
Jeon JS, Kim HT, Kim MG, Oh MS, Hong SR, Yoon MH, Cho SM, Shin HC, Shim JH, Ramadan A, Abd El-Aty AM (2016) Simultaneous determination of watersoluble whitening ingredients and adenosine in different cosmetic formulations by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with photodiode array detection. Int J Cosmet Sci 38:286–293
Fu LJ, Amato NJ, Wang PC, McGowan SJ, Niedernhofer LJ, Wang YS (2015) Simultaneous quantification of methylated cytidine and adenosine in cellular and tissue RNA by nano-flow liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled with the stable isotope-dilution method. Anal Chem 87:7653–7659
Zhang C, Man BY, Jiang SZ, Yang C, Liu M, Chen CS, Xu SC, Qiu HW, Li Z (2015) SERS detection of low-concentration adenosine by silver nanoparticles on silicon nanoporous pyramid arrays structure. Appl Surf Sci 347:668–672
Yao G, Liang R, Huang C, Zhang L, Qiu J (2015) Enzyme-free surface Plasmon resonance aptasensor for amplified detection of adenosine via target-triggering strand displacement cycle and au nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 871:28–34
Ye SJ, Li HX, Cao W (2011) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection of adenosine based on triplex DNA biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2215–2220
Chen JW, Liu XP, Feng KJ, Liang Y, Jiang JH, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2008) Detection of adenosine using surface-enhanced Raman scattering based on structure-switching signaling aptamer. Biosens Bioelectron 24:66–71
Yan FF, Wang F, Chen ZL (2011) Aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for label-free voltammetric detection of thrombin and adenosine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 160:1380–1385
Wang YT, Feng JJ, Tan ZA, Wang HY (2014) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of adenosine with dual backfillers. Biosens Bioelectron 60:218–223
Li F, Zhang J, Cao X, Wang LH, Li D, Song SP, Ye BC, Fan CH (2009) Adenosine detection by using gold nanoparticles and designed aptamer sequences. Analyst 134:1355–1360
Chen SJ, Huang YF, Huang CC, Lee KH, Lin ZH, Chang HT (2008) Colorimetric determination of urinary adenosine using aptamer-modified gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 23:1749–1753
Liu JW, Lu Y (2004) Adenosine-dependent assembly of aptazyme-functionalized gold nanoparticles and its application as a colorimetric biosensor. Anal Chem 76:1627–1632
Ding YN, Yang BC, Liu H, Liu ZX, Zhang X, Zheng XW, Liu QY (2018) FePt-au ternary metallic nanoparticles with the enhanced peroxidase-like activity for ultrafast colorimetric detection of H2O2. Sensors Actuators B Chem 259:775–783
Liu DB, Wang Z, Jiang XY (2011) Gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric and fluorescent detection of ions and small organic molecules. Nanoscale 3:1421–1433
Liu JW, Lu Y (2003) A colorimetric lead biosensor using DNAzyme-directed assembly of gold nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 125:6642–6643
Liu DB, Qu WS, Chen WW, Zhang W, Wang Z, Jiang XY (2010) Highly sensitive, colorimetric detection of mercury(II) in aqueous media by quaternary ammonium group-capped gold nanoparticles at room temperature. Anal Chem 82:9606–9610
Nam JM, Wise AR, Groves JT (2005) Colorimetric bio-barcode amplification assay for cytokines. Anal Chem 77:6985–6988
Liu QY, Yang YT, Li H, Zhu RR, Shao Q, Yang SG, Xu JJ (2015) NiO nanoparticles modified with 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-carboxyl pheyl)-porphyrin: promising peroxidase mimetics for H2O2 and glucose detection. Biosens Bioelectron 64:147–153
Klajn R, Stoddart JF, Grzybowski BA (2010) Nanoparticles functionalised with reversible molecular and supramolecular switches. Chem Soc Rev 39:2203–2237
Du LL, Zhang Y, Du Y, Yang DZ, Gao FL, Tang DQ (2015) A novel label-free aptasensor based on target-induced structure switching of aptamer-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. RSC Adv 5:100960–100967
Gao FL, Du Y, Yao JW, Zhang YZ, Gao J (2015) A novel electrochemical biosensor for DNA detection based on exonuclease III-assisted target recycling and rolling circle amplification. RSC Adv 5:9123–9129
Wang X, Xu GH, Wei FD, Ma YS, Ma YJ, Song YY, Cen Y, Hu Q (2017) Highly sensitive and selective aptasensor for detection of adenosine based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer from carbon dots to nano-graphite. J Colloid Interf Sci 508:455–461
Song YY, Tang T, XWang X, Xu GH, Wei FD, Wu YZ, Song Q, Ma YJ, Ma YS, Cen Y, Hu Q (2017) Highly selective and sensitive detection of adenosine utilizing signal amplification based on silver ions-assisted cation exchange reaction with CdTe quantum dots. Sensors Actuators B Chem 247:305–311
Liu HY, Bai YF, Qin J, Wang HY, Wang YZ, Chen ZZ, Feng F (2018) Exonuclease I assisted fluorometric aptasensor for adenosine detection using 2-AP modified DNA. Sensors Actuators B Chem 256:413–419
Ahn JK, Kim HY, Baek S, Park HG (2017) A new s-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase-linked method for adenosine detection based on DNA-templated fluorescent Cu/Ag nanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron 93:330–334
Xu L, Shen X, Li BZ, Zhu CH, Zhou XM (2017) G-quadruplex based Exo III-assisted signal amplification aptasensor for the colorimetric detection of adenosine. Anal Chim Acta 980:58–64
Shen J, Wang HY, Li CX, Zhao YY, Yu XJ, Luo XL (2017) Label-free electrochemical aptasensor for adenosine detection based on cascade signal amplification strategy. Biosens Bioelectron 90:356–362
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Scientific Research Project of Beijing Educational Committee (Grant No. KM201710028009), Youth Innovative Research Team of Capital Normal University, and Capacity Building for Sci-Tech Innovation-Fundamental Scientific Research Funds (025185305000/195).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1069 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, C., Gao, L. & Chen, Z. Colorimetric adenosine aptasensor based on DNA cycling amplification and salt-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185, 488 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3031-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3031-z