Abstract
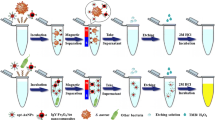
The authors describe a rapid colorimetric assay for Listeria monocytogenes (L. monocytogenes) based on the o-phenylenediamine-mediated deaggregation of gold nanoparticles. Silver nanoclusters are used as an artificial enzyme that can oxidize o-phenylenediamine to form o-benzoquinone diamine. Aptamer and IgY antibodies were chosen to conjugate with magnetic beads and silver nanoclusters, respectively, which can recognize and bind L. monocytogenes at different specific binding sites. This results in the disassembly of colloidal gold nanoparticles which is accompanied by a color change from blue to red, with peaks at 730 and 525 nm, respectively. The method allows L. monocytogenes to be colorimetrically determined in the 10 to 106 cfu·mL−1 concentration range without pre-enrichment, and the limit of detection is as low as 10 cfu·mL−1. Recoveries ranging from 97.4 to 101.3% are found when analyzing spiked food samples. The assay is rapid, sensitive and specific.

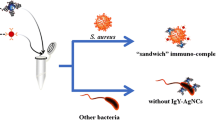
Schematic illustration of a colorimetric method for detection of L. monocytogenes based on silver nanoclusters-catalyzed oxidation of OPD and de-aggregation of GNPs. A color change from blue to red can be observed and correlated to the concentration of L. monocytogenes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cole MB, Jones MV, Holyoak C (1990) The effect of pH, salt concentration and temperature on the survival and growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Appl Bacteriol 69(1):63–72
Sharma H, Mutharasan R (2013) hlyA gene-based sensitive detection of Listeria monocytogenes using a novel cantilever sensor. Anal Chem 85(6):3222–3228
Silk BJ, McCoy MH, Iwamoto M, Griffin PM (2014) Foodborne listeriosis acquired in hospitals. Clin Infect Dis 59(4):532–540
Auvolat A, Besse NG (2016) The challenge of enumerating Listeria monocytogenes in food. Food Microbiol 53(Pt B):135–149
Lee W, Kwon D, Chung B, Jung GY, Au A, Folch A, Jeon S (2014) Ultrarapid detection of pathogenic bacteria using a 3D immunomagnetic flow assay. Anal Chem 86(13):6683–6688
Meng X, Li F, Xiong Y, Xu H (2017) Vancomycin modified PEGylated-magnetic nanoparticles combined with PCR for efficient enrichment and detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Sensors Actuators B Chem 247:546–555
Yang X, Zhou X, Zhu M, Xing D (2017) Sensitive detection of Listeria monocytogenes based on highly efficient enrichment with vancomycin-conjugated brush-like magnetic nano-platforms. Biosens Bioelectron 91:238–245
González-Sálamo J, Socas-Rodríguez B, Hernández-Borges J, Rodríguez-Delgado MÁ (2016) Nanomaterials as sorbents for food sample analysis. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 85:203–220
Wu J, Wei X, Gan J, Huang L, Shen T, Lou J, Liu B, Zhang JX, Qian K (2016) Multifunctional magnetic particles for combined circulating tumor cells isolation and cellular metabolism detection. Adv Funct Mater 26(22):4016–4025
Wen CY, Jiang YZ, Li XY, Tang M, Wu LL, Hu J, Pang DW, Zeng JB (2017) Efficient enrichment and analyses of bacteria at ultralow concentration with quick-response magnetic nanospheres. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(11):9416–9425
Park B, Choi SJ (2017) Sensitive immunoassay-based detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus using capture and labeling particles in a stationary liquid phase lab-on-a-chip. Biosens Bioelectron 90:269–275
Suaifan GA, Alhogail S, Zourob M (2017) Paper-based magnetic nanoparticle-peptide probe for rapid and quantitative colorimetric detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosens Bioelectron 92:702–708
Wang C, Wang J, Li M, Qu X, Zhang K, Rong Z, Xiao R, Wang S (2016) A rapid SERS method for label-free bacteria detection using polyethylenimine-modified Au-coated magnetic microspheres and Au@Ag nanoparticles. Analyst 141(22):6226–6238
Jia F, Xu L, Yan W, Wu W, Yu Q, Tian X, Dai R, Li X (2017) A magnetic relaxation switch aptasensor for the rapid detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa using superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184(5):1539–1545
Srisa-Art M, Boehle KE, Geiss BJ, Henry CS (2018) Highly sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium using a colorimetric paper-based analytical device coupled with immunomagnetic separation. Anal Chem 90(1):1035–1043
Wang W, Liu L, Song S, Xu L, Kuang H, Zhu J, Xu C (2017) Identification and quantification of eight Listeria monocytogene serotypes from Listeria spp. using a gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow assay. Microchim Acta 184(3):715–724
Deng J, Yu P, Wang Y, Yang L, Mao L (2014) Visualization and quantification of neurochemicals with gold nanoparticles: opportunities and challenges. Adv Mater 26(40):6933–6943
Lu S, Zhang X, Chen L, Yang P (2017) Colorimetric visualization of superoxide dismutase in serum via etching of Au nanorods from superoxide radical. Sensors Actuators B Chem 259:1066–1072
Zhang Z, Chen Z, Chen L (2015) Ultrasensitive visual sensing of molybdate based on enzymatic-like etching of gold nanorods. Langmuir 31(33):9253–9259
Zhang L, Huang R, Liu W, Liu H, Zhou X, Xing D (2016) Rapid and visual detection of Listeria monocytogenes based on nanoparticle cluster catalyzed signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 86:1–7
Liu Y, Zhao C, Fu K, Song X, Xu K, Wang J, Li J (2017) Selective turn-on fluorescence detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in food based on charge-transfer between CdSe/ZnS quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. Food Control 80:380–387
Liu Y, Zhao C, Song X, Xu K, Wang J, Li J (2017) Colorimetric immunoassay for rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microchim Acta 184(12):4785–4792
Song Y, Xu G, Wei F, Cen Y, Sohail M, Shi M, Xu X, Ma Y, Ma Y, Hu Q (2018) Aptamer-based fluorescent platform for ultrasensitive adenosine detection utilizing Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185:139
Li XG, Zhang F, Gao Y, Zhou QM, Zhao Y, Li Y, Huo JZ, Zhao XJ (2016) Facile synthesis of red emitting 3-aminophenylboronic acid functionalized copper nanoclusters for rapid, selective and highly sensitive detection of glycoproteins. Biosens Bioelectron 86:270–276
Yang J, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Wang H, Nie J, Qin Z, Li J, Xiao W (2017) Analyte-triggered autocatalytic amplification combined with gold nanoparticle probes for colorimetric detection of heavy-metal ions. Chem Commun 53(54):7477–7480
Li F, Zhang H, Wang Z, Newbigging AM, Reid MS, Li XF, Le XC (2015) Aptamers facilitating amplified detection of biomolecules. Anal Chem 87(1):274–292
Li F, Li J, Tang Y, Wang C, Li XF, Le XC (2016) Targeted enlargement of aptamer functionalized gold nanoparticles for quantitative protein analysis. Proteomes 5(1):1
Lin Y, Ren J, Qu X (2014) Catalytically active nanomaterials: a promising candidate for artificial enzymes. Acc Chem Res 47(4):1097–1105
Nasir M, Nawaz MH, Latif U, Yaqub M, Hayat A, Rahim A (2017) An overview on enzyme-mimicking nanomaterials for use in electrochemical and optical assays. Microchim Acta 184(2):323–342
Yang X, Wang E (2011) A nanoparticle autocatalytic sensor for Ag+ and Cu2+ ions in aqueous solution with high sensitivity and selectivity and its application in test paper. Anal Chem 83(12):5005–5011
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 81602894, 81602895, and 81473018), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2017 T100214 and 2016 M591492), the Development Foundation of Science and Technology in Jilin Province of China (Grant No. 20170204003SF) and Graduate Innovation Fund of Jilin University (Grant No. 2017084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3759 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Wang, J., Song, X. et al. Colorimetric immunoassay for Listeria monocytogenes by using core gold nanoparticles, silver nanoclusters as oxidase mimetics, and aptamer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185, 360 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2896-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2896-1