Abstract
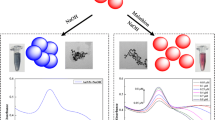
A method is described for the determination of the pesticide chlorothalonil (CLT). It is based on the finding that citrate-capped gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) undergo aggregation on exposure to chlorothalonil. This is accompanied by a visually detectable color change from wine red to blue. The effect is due to the interaction of the cyano group of chlorothalonil with gold nanoparticles. The assay may also be performed by using a spectrometer. The ratio of absorbances at 700 nm and 520 nm (A700/A520) linearly drops in the 5 to 100 ng·mL−1 CLT concentration range, with a 3.6 ng·mL−1 detection limit. This is below the Chinese guideline value for cucumber. The method is rather simple and does not require any modification of the AuNPs or the utilization of antibody. It was successfully applied to the determination of CLT in (spiked) cucumber samples. Recoveries ranged from 80.4 to 97.4%, and the analytical results compared well with those obtained by HPLC.

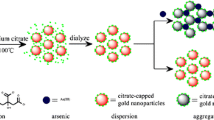
Schematic of the assay. The strong interaction of the cyano group of acetamiprid with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) via Au-N bond induces the aggregation of gold nanoparticles, and this is accompanied by a color change from red to purple.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
He Q, Xu XH, Zhang F, Tai YK, Luo YF, He J, Hong Q, Jiang JD, Yan X (2017) Production of chlorothalonil hydrolytic dehalogenase fromagro-industrial wastewater and its application in raw food cleaning. J Sci Food Agric 97(8):2582–2587. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8079
Zhang H, Nie Y, Zhang SQ, Wang WZ, Li HD, Wang FE, Lv X, Chen ZL (2016) Monitoring and probabilistic risk assessment of chlorothalonil residues in vegetables from Shandong province (China). Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 80:41–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2016.05.035
Guerreiro AD, Rola RC, Rovani MT, da Costa SR, Sandrini JZ (2017) Antifouling biocides: impairment of bivalve immune system by chlorothalonil. Aquat Toxicol 189:194–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.06.012
Lv P, Zhang J, Shi TZ, Dai LL, Li XQ, Wu XW, Li XD, Tang J, Wang Y, Li QX, Hua RM (2017) Procyanidolic oligomers enhance photodegradation of chlorothalonil in water via reductive dechlorination. Appl Catal B Environ 217:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.05.065
Tang LW, Dong JJ, Ren LW, Zhu QF, Huang WW, Liu YM, Lu DN (2017) Biodegradation of chlorothalonil by Enterobacter cloacae TUAH-1. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 121:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.03.029
Rahman MM, Park JH, Abd El-Aty AM, Choi JH, Bae HR, Yang A, Park KH, Shim JH (2013) Single-step modified QuEChERS for determination of chlorothalonil in shallot (Allium ascalonicum) using GC-mu ECD and confirmation via mass spectrometry. Biomed Chromatogr 27(4):416–421. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.2808
Zhou X, Zang XH, Wang DY, Cui PL, Wang Z (2009) Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction method coupled with gas chromatography for determination of Chlorothalonil, Captan and Folpet residues in grape samples. Chin J Anal Chem 37(1):41–45
Catala-Icardo M, Gomez-Benito C, Simo-Alfonso EF, Herrero-Martinez JM (2017) Determination of azoxystrobin and chlorothalonil using a methacrylate-based polymer modified with gold nanoparticles as solid-phase extraction sorbent. Anal Bioanal Chem 409(1):243–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9993-y
Yamamoto A, Miyamato L, Kitagawa M, Moriwaki H, Miyakoda H, Kawasaki H, Arakawa R (2009) Analysis of Chlorothalonil by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry using negative-ion atmospheric pressure photoionization. Anal Sci 25(5):693–697. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.25.693
Anastassiades M, Mastovska K, Lehotay SJ (2003) Evaluation of analyte protectants to improve gas chromatographic analysis of pesticides. J Chromatogr A 1015(1–2):163–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(03)01208-1
Jahn C, Schwack W (2001) Determination of cutin-bound residues of chlorothalonil by immunoassay. J Agric Food Chem 49(3):1233–1238
Watanabe E, Miyake S, Ito S, Baba K, Eun H, Ishizaka M, Endo S (2006) Reliable enzyme immunoassay detection for chlorothalonil: fundamental evaluation for residue analysis and validation with gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1129(2):273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.06.095
Okazaki F, Hirakawa Y, Yamaguchi-Murakami Y, Harada A, Watanabe E, Iwasa S, Narita H, Miyake S (2014) Development of direct competitive ELISA for residue analysis of fungicide chlorothalonil in vegetables. J Food Hyg Soc JPN 55(2):65–72
Hirakawa Y, Yamasaki T, Watanabe E, Okazaki F, Murakami-Yamaguchi Y, Oda M, Iwasa S, Narita H, Miyake S (2015) Development of an Immunosensor for determination of the fungicide Chlorothalonil in vegetables, using surface Plasmon resonance. J Agric Food Chem 63(28):6325–6330. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01980
Lan M, Guo Y, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Gui W, Zhu G (2016) Multi-residue detection of pesticides using a sensitive immunochip assay based on nanogold enhancement. Anal Chim Acta 938:146–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.07.044
Wu S, Li DD, Wang JM, Zhao YQ, Dong SJ, Wang XY (2017) Gold nanoparticles dissolution based colorimetric method for highly sensitive detection of organophosphate pesticides. Sensors Actuators B Chem 238:427–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.07.067
Yang LM, Zhang XH, Li HP, Jiang L (2017) Hyaluronan-tyrosine-gold nanoparticles as an enzyme-free colorimetric probe for the detection of phosphorothiolate pesticides. Anal Methods 9(43):6139–6147. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ay01969f
Zhan L, Yang T, Zhen SJ, Huang CZ (2017) Cytosine triphosphate-capped silver nanoparticles as a platform for visual and colorimetric determination of mercury(II) and chromium(III). Microchim Acta 184(9):3171–3178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2250-z
Jiang GY, Zhu WY, Shen X, Xu L, Li XX, Wang R, Liu CY, Zhou XM (2017) Colorimetric and visual determination of adenosine triphosphate using a boronic acid as the recognition element, and based on the deaggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184(11):4305–4312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2454-2
Sang Y, Xu YJ, Xu LL, Cheng W, Li XM, Wu JL, Ding SJ (2017) Colorimetric and visual determination of microRNA via cycling signal amplification using T7 exonuclease. Microchim Acta 184(7):2465–2471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2238-8
Hou F, Zhao LW, Liu FM (2016) Determination of Chlorothalonil residue in cabbage by a modified QuEChERS-based extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 9(3):656–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0228-1
Diogenes ICN, de Carvalho IMM, Longhnotti E, Lopes LGF, Temperini MLA, Andrade GFS, Moreira IS (2007) A study of pyridinethiolate derivative complexes adsorbed on gold by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J Electroanal Chem 605(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2007.03.007
Lokesh KS, De Wael K, Adriaens A (2010) Self-assembled supramolecular Array of polymeric Phthalocyanine on gold for the determination of hydrogen peroxide. Langmuir 26(22):17665–17673. https://doi.org/10.1021/la102740s
Holze R (2013) Competition of anchoring groups in adsorption on gold electrodes-a comparative spectroelectrochemical study of 4-mercaptobenzonitrile and aromatic nitriles. J Solid State Electrochem 17(7):1869–1879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-013-2076-5
Xu Q, Du S, Jin GD, Li HB, Hu XY (2011) Determination of acetamiprid by a colorimetric method based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 173(3–4):323–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0562-y
Dong L, Hou CJ, Yang M, Fa HB, Wu HX, Shen CH, Huo DQ (2016) Highly sensitive colorimetric and fluorescent sensor for cyanazine based on the inner filter effect of gold nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 18(6):164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3398-x
Meyer J, Nickel A, Ohmann R, Lokamani TC, Ryndyk DA, Garmshausen Y, Hecht S, Moresco F, Cuniberti G (2015) Tuning the formation of discrete coordination nanostructures. Chem Commun 51(63):12621–12624. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc02723c
Yang K, Pan L, Gong L, Liu Q, Li Z, Wu L, He Y (2018) Colorimetric and visual determination of au(III) ions using PEGylated gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(2):95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2648-7
Tiwari A, Aryal S, Pilla S, Gong S (2009) An amperometric urea biosensor based on covalently immobilized urease on an electrode made of hyperbranched polyester functionalized gold nanoparticles. Talanta 78(4–5):1401–1407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2009.02.038
Kazos EA, Nanos CG, Stalikas CD, Konidari CN (2008) Simultaneous determination of chlorothalonil and its metabolite 4-hydroxychlorothalonil in greenhouse air: dissipation process of chlorothalonil. Chemosphere 72(10):1413–1419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.05.044
Ji RD, Zhao ZM, Chen ML, Wang LX, Zhu XY (2015) Study on fluorescence spectra of Chlorothalonil residues and the interaction between Chlorothalonil and Chinese herbal medicines. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 35(2):415–419. https://doi.org/10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2015)02-0415-05
Hirakawa Y, Yamasaki T, Watanabe E, Okazaki F, Murakami-Yamaguchi Y, Oda M, Iwasa S, Narita H, Miyake S (2015) Development of an Immunosensor for determination of the fungicide Chlorothalonil in vegetables, using surface Plasmon resonance. J Agric Food Chem 63(28):6325–6330. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01980
Okazaki F, Hirakawa Y, Yamaguchi-Murakami Y, Harada A, Watanabe E, Iwasa S, Narita H, Miyake S (2014) Development of direct competitive ELISA for residue analysis of fungicide Chlorothalonil in vegetables. J Food Hyg Soc JPN 55(2):65–72. https://doi.org/10.3358/shokueishi.55.65
Watanabe E, Miyake S, Ito S, Baba K, Eun H, Ishizaka M, Endo S (2006) Reliable enzyme immunoassay detection for chlorothalonil: fundamental evaluation for residue analysis and validation with gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1129(2):273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.06.095
Yang XD, Zhang GP, Wang FY, Wang YB, Hu XF, Li QM, Jia GC, Liu Z, Wang Y, Deng RG, Zeng XY (2015) Development of a colloidal gold-based strip test for the detection of chlorothalonil residues in cucumber. Food Agric Immunol 26(5):729–737. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540105.2015.1018875
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0400902) and the Construction of Science and Technology Innovation Team of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry (JNKST201620).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.39 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Han, P., Gong, W. et al. Colorimetric determination of the pesticide chlorothalonil based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185, 354 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2890-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2890-7