Abstract
A non-fouling electrochemical immunosensor is described for determination of the tumor biomarker carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). It is based on the use of composite wires made by chemical grafting of hyaluronic acid onto polyaniline nanowires. The modified nanowires possess excellent antifouling property both in single protein solutions and in dilute serum samples. The current of immunoelectrode exhibits a linear response in the 0.01 pg mL−1 to 10,000 pg mL−1 CEA concentration range and 0.0075 pg mL−1 detection limit. This work demonstrates that coating an electrode with hyaluronic acid can largely reduce unspecific adsorption of proteins on the electrode surface.

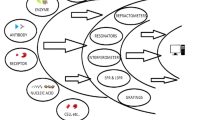
Schematic of a nonfouling electrochemical immunosensor for the carcinoembryonic antigen. It is based on novel composite wires made through the chemical grafting of easily available hyaluronic acid (HA) onto polyaniline (PANI) nanowires. The HA/PANI demonstrated excellent antifouling property both in single protein solutions and human serum samples.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwazawa T, Kanoh T, Matsui S, Monden T (2000) Diagnosis of lung cancer metastasis with CEA extracted from the dissected regional lymph nodes. Lung Cancer 29(1):254–254
Lu W, Cao X, Tao L, Ge J, Dong J, Qian W (2014) A novel label-free amperometric immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen based on ag nanoparticle decorated infinite coordination polymer fibres. Biosens Bioelectron 57:219–225
Yang W, Zhou X, Zhao J, Xu W (2018) A cascade amplification strategy of catalytic hairpin assembly and hybridization chain reaction for the sensitive fluorescent assay of the model protein carcinoembryonic antigen. Microchim Acta 185(2):100
Chen Y, Chu W, Liu W, Guo X, Jin Y, Li B (2018) Paper-based chemiluminescence immunodevice for the carcinoembryonic antigen by employing multi-enzyme carbon nanosphere signal enhancement. Microchim Acta 185(3):187
Zhang Y, Liu W, Ge S, Yan M, Wang S, Yu J, Li N, Song X (2013) Multiplexed sandwich immunoassays using flow-injection electrochemiluminescence with designed substrate spatial-resolved technique for detection of tumor markers. Biosens Bioelectron 41:684–690
Liu R, Zhang S, Wei C, Xing Z, Zhang S, Zhang X (2016) Metal stable isotope tagging: renaissance of radioimmunoassay for multiplex and absolute quantification of biomolecules. Acc Chem Res 49(5):775–783
Hasanzadeh M, Shadjou N (2017) Advanced nanomaterials for use in electrochemical and optical immunoassays of carcinoembryonic antigen. A review. Microchim Acta 184:389–414
Zhu Y, Chandra P, Shim YB (2013) Ultrasensitive and selective electrochemical diagnosis of breast cancer based on a hydrazine-au nanoparticle-aptamer bioconjugate. Anal Chem 85(2):1058–1064
Vaisocherova H, Brynda E, Homola J (2015) Functionalizable low-fouling coatings for label-free biosensing in complex biological media: advances and applications. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(14):3927–3953
Liu B, Liu X, Shi S, Huang R, Su R, Qi W, He Z (2016) Design and mechanisms of antifouling materials for surface plasmon resonance sensors. Acta Biomater 40:100–118
Jiang S, Cao Z (2010) Ultralow-fouling, functionalizable, and hydrolyzable zwitterionic materials and their derivatives for biological applications. Adv Mater 22(9):920–932
Chen S, Li L, Zhao C, Zheng J (2010) Surface hydration: principles and applications toward low-fouling/nonfouling biomaterials. Polymer 51(23):5283–5293
Ma H, Hyun J, Stiller P, Chilkoti A (2004) “Non-fouling” oligo (ethylene glycol)-functionalized polymer brushes synthesized by surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. Adv Mater 16(4):338–341
Rossi NA, Mustafa I, Jackson JK, Burt HM, Horte S, Scott MD, Kizhakkedathu JN (2009) In vitro chelating, cytotoxicity, and blood compatibility of degradable poly(ethylene glycol)-based macromolecular iron chelators. Biomaterials 30(4):638–648
Gombotz WR, Guanghui W, Horbett TA, Hoffman AS (1991) Protein adsorption to poly (ethylene oxide) surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A 25(12):1547–1562
Yamanlar S, Sant S, Boudou T, Picart C, Khademhosseini A (2011) Surface functionalization of hyaluronic acid hydrogels by polyelectrolyte multilayer films. Biomaterials 32(24):5590–5599
Liu X, Huang R, Su R, Qi W, Wang L, He Z (2014) Grafting hyaluronic acid onto gold surface to achieve low protein fouling in surface plasmon resonance biosensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(15):13034–13042
Huang R, Liu X, Ye H, Su R, Qi W, Wang L, He Z (2015) Conjugation of hyaluronic acid onto surfaces via the interfacial polymerization of dopamine to prevent protein adsorption. Langmuir 31(44):12061–12070
Weathers A, Khan ZU, Brooke R, Evans D, Pettes MT, Andreasen JW, Crispin X, Shi L (2015) Significant electronic thermal transport in the conducting polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Adv Mater 27(12):2101–2106
Huang J, Virji S, Weiller BH, Kaner RB (2003) Polyaniline nanofibers: facile synthesis and chemical sensors. J Am Chem Soc 125(2):314–315
Lu X, Zhang W, Wang C, Wen TC, Wei Y (2011) One-dimensional conducting polymer nanocomposites: synthesis, properties and applications. Prog Polym Sci 36(5):671–712
Hao Y, Zhou B, Wang F, Li J, Deng L, Liu YN (2014) Construction of highly ordered polyaniline nanowires and their applications in DNA sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 52:422–426
Sun X, Hui N, Luo X (2017) Reagentless and label-free voltammetric immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen based on polyaniline nanowires grown on porous conducting polymer composite. Microchim Acta 184(3):889–896
Shiny N, Rajeswari R, Natarajan V, Mukundan T (2014) Concentration-dependent growth and morphology of doped polyaniline nanowires. J Exp Nanosci 9(10):982–993
Bryan T, Luo X, Forsgren L, Morozova-Roche LA, Davis JJ (2012) The robust electrochemical detection of a Parkinson's disease marker in whole blood sera. Chem Sci 3(12):3468–3473
Hui N, Sun X, Niu S, Luo X (2017) PEGylated polyaniline nanofibers: antifouling and conducting biomaterial for electrochemical DNA sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(3):2914–2923
Hui N, Sun X, Song Z, Niu S, Luo X (2016) Gold nanoparticles and polyethylene glycols functionalized conducting polyaniline nanowires for ultrasensitive and low fouling immunosensing of alpha-fetoprotein. Biosens Bioelectron 86:143–149
Hui N, Chai F, Lin P, Song Z, Sun X, Li Y, Niu S, Luo X (2016) Electrodeposited conducting polyaniline nanowire arrays aligned on carbon nanotubes network for high performance supercapacitors and sensors. Electrochim Acta 199:234–241
Ombelli M, Costello L, Postle C, Anantharaman V, Meng QC, Composto RJ, Eckmann DM (2011) Competitive protein adsorption on polysaccharide and hyaluronate modified surfaces. Biofouling 27:505–518
Prime K, Whitesides G (1991) Self-assembled organic monolayers: model Systems for Studying Adsorption of proteins at surfaces. Science 252:1164–1167
Ham HO, Park SH, Kurutz JW, Szleifer IG, Messersmith PB (2013) Antifouling Glycocalyx-mimetic Peptoids. J Am Chem Soc 135:13015–13022
Liang RP, Wang ZX, Zhang L, Qiu JD (2012) A label-free amperometric immunosensor for alpha-fetoprotein determination based on highly ordered porous multi-walled carbon nanotubes/silica nanoparticles array platform. Sensors Actuators B Chem 166-167:569–575
Kafka J, Pänke O, Abendroth B, Lisdat F (2008) A label-free DNA sensor based on impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim Acta 53:7467–7474
Wang W, Fan X, Xu S, Davis JJ, Luo X (2015) Low fouling label-free DNA sensor based on polyethylene glycols decorated with gold nanoparticles for the detection of breast cancer biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 71:51–56
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21705088), the Shandong Science and Technology Program (J14LB14), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (ZR2016BM05 and ZR2017BD038), the Qingdao Agricultural University High-level Talent Project (663/1117025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1098 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Hui, N. A nonfouling voltammetric immunosensor for the carcinoembryonic antigen based on the use of polyaniline nanowires wrapped with hyaluronic acid. Microchim Acta 185, 329 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2854-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2854-y