Abstract
3D magnetic hollow porous CdFe2O4 microspheres (3D MHPS-CdFe2O4) were prepared by a one-step and template-free hydrothermal method. The material was applied for magnetic solid phase extraction of three azo colorants (Acid Red, Congo Red, Sunset Yellow). Compared to conventional CdFe2O4 nanoparticles, the new 3D material exhibits superior extraction capability because of its unique hollow porous structure, high specific surface area, and the strong interaction between 3D microspheres and the colorants. A magnetic solid phase extraction (MPSE) combined with HPLC was established for simultaneous detection of the three azo colorants in food samples. Under optimum conditions, the detection limits are 0.54–1.00 ng mL-1, and good recoveries of 87.0–100.7% were obtained with spiked samples, with relative standard deviation of ≤ 3.8%. The combination of using the new 3D material and MPSE-HPLC results in an efficient, sensitive and inexpensive method for simultaneous determination of such colorants.

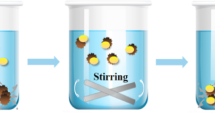
Schematic of the preparation of 3D magnetic hollow porous CdFe2O4 microspheres as solid phase extractant for simultaneous trace detection of three azo colorants in real samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonan S, Fedrizzi G, Menotta S, Elisabetta C (2013) Simultaneous determination of synthetic dyes in foodstuffs and beverages by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode-array detector. Dyes Pigments 99(1):36–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2013.03.029
Yamjala K, Nainar MS, Ramisetti NR (2016) Methods for the analysis of azo dyes employed in food industry-a review. Food Chem 192:813–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.085
Long C, Mai Z, Yang X, Zhu B, Xu X, Huang X, Zou X (2011) A new liquid–liquid extraction method for determination of 6 azo-dyes in chilli products by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem 126(3):1324–1329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.11.089
Tang B, Xi C, Zou Y, Wang G, Li X, Zhang L, Chen D, Zhang J (2014) Simultaneous determination of 16 synthetic colorants in hotpot condiment by high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B 960(Supplement C):87–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.04.026
Rodriguez JA, Escamilla-Lara KA, Guevara-Lara A, Miranda JM, Paez-Hernandez ME (2015) Application of an activated carbon-based support for magnetic solid phase extraction followed by spectrophotometric determination of tartrazine in commercial beverages. Int J Anal Chem 2015:291827. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/291827
de Andrade FI, Florindo Guedes MI, Pinto Vieira ÍG, Pereira Mendes FN, Salmito Rodrigues PA, Costa Maia CS, Marques Ávila MM, de Matos Ribeiro L (2014) Determination of synthetic food dyes in commercial soft drinks by TLC and ion-pair HPLC. Food Chem 157(Supplement C):193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.01.100
Yilmaz UT, Ergun F, Yilmaz H (2014) Determination of the food dye carmine in milk and candy products by differential pulse polarography. J Food Drug Anal 22(3):329–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2013.12.002
Yoshioka N, Ichihashi K (2008) Determination of 40 synthetic food colors in drinks and candies by high-performance liquid chromatography using a short column with photodiode array detection. Talanta 74(5):1408–1413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2007.09.015
Zhang Z, Wang L, Liu X, Zhang D, Zhang L, Li Q (2015) Nano-Al2O3-based micro solid-phase filter membrane extraction for simultaneous determination of tartrazine and sunset yellow in food. RSC Adv 5(105):86445–86452. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA13843D
Liu X, Qi X, Zhang L (2018) 3D hierarchical magnetic hollow sphere-like CuFe2O4 combined with HPLC for the simultaneous determination of Sudan I–IV dyes in preserved bean curd. Food Chem 241(Supplement C):268–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.113
de Araújo Siqueira Bento W, Lima BP, APS P (2015) Simultaneous determination of synthetic colorants in yogurt by HPLC. Food Chem 183(Supplement C):154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.03.050
Wang Q, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Tong Y, Zhang L (2017) Waxberry-like magnetic porous carbon composites prepared from a nickel-organic framework for solid-phase extraction of fluoroquinolones. Microchim Acta 184(10):4107–4115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2438-2
Vasconcelos I, Fernandes C (2017) Magnetic solid phase extraction for determination of drugs in biological matrices. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem 89:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.11.011
Chai W, Wang H, Zhang Y, Ding G (2016) Preparation of polydopamine-coated magnetic nanoparticles for dispersive solid-phase extraction of water-soluble synthetic colorants in beverage samples with HPLC analysis. Talanta 149:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.11.026
Liu F, Zhang S, Wang G, Zhao J, Guo Z (2015) A novel bifunctional molecularly imprinted polymer for determination of Congo red in food. RSC Adv 5(29):22811–22817. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra14719g
Iram M, Guo C, Guan Y, Ishfaq A, Liu H (2010) Adsorption and magnetic removal of neutral red dye from aqueous solution using Fe3O4 hollow nanospheres. J Hazard Mater 181(1–3):1039–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.119
Miao F, Deng Z, Lv X, Gu G, Wan S, Fang X, Zhang Q, Yin S (2010) Fundamental properties of CdFe2O4 semiconductor thin film. Solid State Commun 150(41–42):2036–2039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2010.08.010
Al-Degs YS, El-Barghouthi MI, El-Sheikh AH, Walker GM (2008) Effect of solution pH, ionic strength, and temperature on adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on activated carbon. Dyes Pigments 77(1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2007.03.001
Liu FJ, Liu CT, Li W, Tang AN (2015) Dispersive solid-phase microextraction and capillary electrophoresis separation of food colorants in beverages using diamino moiety functionalized silica nanoparticles as both extractant and pseudostationary phase. Talanta 132:366–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.09.014
Li WJ, Zhou X, Tong SS, Jia Q (2013) Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co- N,N'-methylene bisacrylamide) monolithic column embedded with gamma-alumina nanoparticles microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of synthetic food dyes in soft drink samples. Talanta 105:386–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.10.065
Chen XH, Zhao YG, Shen HY, Zhou LX, Pan SD, Jin MC (2014) Fast determination of seven synthetic pigments from wine and soft drinks using magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1346:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.04.060
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (NSFC51672116). Science and technology foundation of ocean and fisheries of Liaoning province (201408, 201406), General project of scientific research of the education department of Liaoning province (L2015206), Liaoning scientific instruments service sharing information platform ability construction funds (201507A003). The authors also thank their colleagues and other students who participated in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 2987 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Zhang, L. & Liu, T. 3D hollow porous CdFe2O4 microspheres as viable materials for magnetic solid-phase extraction of azo colorants. Microchim Acta 185, 248 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2780-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2780-z