Abstract
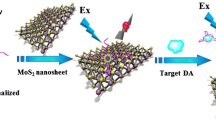
A method is described for the rapid fluorometric determination of dopamine (DA) by using molybdenum disulfide quantum dots (MoS2 QDs) that were fabricated via an ammonium hydroxide etching method. The probe has a fluorescence (with excitation/emission peaks at 267/380 nm) that is quenched by DA with high selectivity over various interferences. This is attributed to a reaction that occurs between DA and the molybdate ions in pH 9 solutions of MoS2 QDs. The formation of organic molybdate complexes and of dopamine-quinone results in strong quenching of the fluorescence of the QDs which is due to both electron transfer and an inner filter effect. Under the optimum conditions, the assay works in the 0.1–100 μM DA concentration range, with two linear ranges and a 10 nM detection limit. The method was applied to the determination of DA in spiked artificial urine samples, where it gave recoveries ranging from 97.6 to 102.2%, demonstrating that the method a promising tool for rapid and selective detection of DA.

MoS2 QDs are facilely synthesized via the etching effect of ammonium hydroxide for highly selective fluorometric detection of dopamine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li B-R, Hsieh Y-J, Chen Y-X, Chung Y-T, Pan C-Y, Chen Y-T (2013) An ultrasensitive nanowire-transistor biosensor for detecting dopamine release from living PC12 cells under hypoxic stimulation. J Am Chem Soc 135(43):16034–16037
Yildirim A, Bayindir M (2014) Turn-on fluorescent dopamine sensing based on in situ formation of visible light emitting Polydopamine nanoparticles. Anal Chem 86(11):5508–5512
De Benedetto GE, Fico D, Pennetta A, Malitesta C, Nicolardi G, Lofrumento DD, De Nuccio F, La Pesa V (2014) A rapid and simple method for the determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin in mouse brain homogenate by HPLC with fluorimetric detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 98:266–270
Wen D, Liu W, Herrmann A-K, Haubold D, Holzschuh M, Simon F, Eychmueller A (2016) Simple and sensitive colorimetric detection of dopamine based on assembly of cyclodextrin-modified au nanoparticles. Small 12(18):2439–2442
Anithaa AC, Lavanya N, Asokan K, Sekar C (2015) WO3 nanoparticles based direct electrochemical dopamine sensor in the presence of ascorbic acid. Electrochim Acta 167:294–302
Xu Q, Yoon J (2011) Visual detection of dopamine and monitoring tyrosinase activity using a pyrocatechol violet-Sn4+ complex. Chem Commun 47(46):12497–12499
Diaz-Diestra D, Thapa B, Beltran-Huarac J, Weiner BR, Morell G (2017) L-cysteine capped ZnS:Mn quantum dots for room-temperature detection of dopamine with high sensitivity and selectivity. Biosens Bioelectron 87:693–700
Yang Q, Wang Y, Wang J, Liu F, Hu N, Pei H, Yang W, Li Z, Suo Y, Wang J (2018) High effective adsorption/removal of illegal food dyes from contaminated aqueous solution by Zr-MOFs (UiO-67). Food Chem 254:241–248
Wang B, M-m C, H-q Z, Wen W, Zhang X-h, S-f W (2017) A simple and sensitive fluorometric dopamine assay based on silica-coated CdTe quantum dots. Microchim Acta 184(9):3189–3196
Zhou X, Ma P, Wang A, Yu C, Qian T, Wu S, Shen J (2015) Dopamine fluorescent sensors based on polypyrrole/graphene quantum dots core/shell hybrids. Biosens Bioelectron 64:404–410
Rasheed PA, Lee J-S (2017) Recent advances in optical detection of dopamine using nanomaterials. Microchim Acta 184(5):1239–1266
Dong H, Tang S, Hao Y, Yu H, Dai W, Zhao G, Cao Y, Lu H, Zhang X, Ju H (2016) Fluorescent MoS2 quantum dots: ultrasonic preparation, up-conversion and down-conversion bioimaging, and photodynamic therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(5):3107–3114
Zhang W, Shi S, Wang Y, Yu S, Zhu W, Zhang X, Zhang D, Yang B, Wang X, Wang J (2016) Versatile molybdenum disulfide based antibacterial composites for in vitro enhanced sterilization and in vivo focal infection therapy. Nano 8(22):11642–11648
Cao H, Wang H, Huang Y, Sun Y, Shi S, Tang M (2017) Quantification of gold(III) in solution and with a test stripe via the quenching of the fluorescence of molybdenum disulfide quantum dots. Microchim Acta 184(1):91–100
Wang Y, Ni Y (2014) Molybdenum disulfide quantum dots as a photoluminescence sensing platform for 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol detection. Anal Chem 86(15):7463–7470
Gu W, Yan Y, Zhang C, Ding C, Xian Y (2016) One-step synthesis of water-soluble MoS2 quantum dots via a hydrothermal method as a fluorescent probe for hyaluronidase detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(18):11272–11279
Mohammadi S, Maeki M, Mohamadi RM, Ishida A, Tani H, Tokeshi M (2015) An instrument-free, screen-printed paper microfluidic device that enables bio and chemical sensing. Analyst 140(19):6493–6499
Wang J, Yang Q, Zhang L, Liu M, Hu N, Zhang W, Zhu W, Wang R, Suo Y, Wang J (2018) A hybrid monolithic column based on layered double hydroxide-alginate hydrogel for selective solid phase extraction of lead ions in food and water samples. Food Chem 257:155–162
Xu S, Li D, Wu P (2015) One-pot, facile, and versatile synthesis of monolayer MoS2/WS2 quantum dots as Bioimaging probes and efficient electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv Funct Mater 25(7):1127–1136
Wang Y, Ou JZ, Balendhran S, Chrimes AF, Mortazavi M, Yao DD, Field MR, Latham K, Bansal V, Friend JR, Zhuiykov S, Medhekar NV, Strano MS, Kalantar-zadeh K (2013) Electrochemical control of photoluminescence in two-dimensional MoS2 nanoflakes. ACS Nano 7(11):10083–10093
Kibsgaard J, Chen Z, Reinecke BN, Jaramillo TF (2012) Engineering the surface structure of MoS2 to preferentially expose active edge sites for electrocatalysis. Nat Mater 11(11):963–969
Yin Z, Zhang X, Cai Y, Chen J, Wong JI, Tay Y-Y, Chai J, Wu J, Zeng Z, Zheng B, Yang HY, Zhang H (2014) Preparation of MoS2-MoO3 hybrid nanomaterials for light-emitting diodes. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(46):12560–12565
Chikan V, Kelley DF (2002) Size-dependent spectroscopy of MoS2 nanoclusters. J Phys Chem B 106(15):3794–3804
Zhang W, Wang Y, Zhang D, Yu S, Zhu W, Wang J, Zheng F, Wang S, Wang J (2015) A one-step approach to the large-scale synthesis of functionalized MoS2 nanosheets by ionic liquid assisted grinding. Nano 7(22):10210–10217
Li BL, Chen LX, Zou HL, Lei JL, Luo HQ, Li NB (2014) Electrochemically induced Fenton reaction of few-layer MoS2 nanosheets: preparation of luminescent quantum dots via a transition of nanoporous morphology. Nano 6(16):9831–9838
Chen M, Zheng Y, Gao J, Li C, Yu C, Wang Q (2017) Fluorometric determination of dopamine by using a terbium (III) inorganic-organic network. Microchim Acta 184(7):2275–2280
Devi JSA, Anulekshmi AH, Salini S, Aparna RS, George S (2017) Boronic acid functionalized nitrogen doped carbon dots for fluorescent turn-on detection of dopamine. Microchim Acta 184(10):4081–4090
Wang F, Hao Q, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Lei W (2016) Fluorescence quenchometric method for determination of ferric ion using boron-doped carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183(1):273–279
Xu H, Yang X, Li G, Zhao C, Liao X (2015) Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots for selective detection of Tartrazine in food samples. J Agric Food Chem 63(30):6707–6714
Sahoo D, Mandal A, Mitra T, Chakraborty K, Bardhan M, Dasgupta AK (2018) Nanosensing of pesticides by zinc oxide quantum dot: an optical and electrochemical approach for the detection of pesticides in water. J Agric Food Chem 66(2):414–423
Guo X, Wu F, Ni Y, Kokot S (2016) Synthesizing a nano-composite of BSA-capped Au nanoclusters/graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets as a new fluorescent probe for dopamine detection. Anal Chim Acta 942:112–120
Yue X, Liu L, Li Z, Yang Q, Zhu W, Zhang W, Wang J (2018) Highly specific and sensitive determination of propyl gallate in food by a novel fluorescence sensor. Food Chem 256:45–52
Liao X, Lang H, Xu W, Shen Y (2003) Determination of polyphenols in tea by ammonium molybdate spectrophotometry. Chin J Anal Lab 05:70–72 (in Chinese)
Tang Z, Lin Z, Li G, Hu Y (2017) Amino nitrogen quantum dots-based nanoprobe for fluorescence detection and imaging of cysteine in biological samples. Anal Chem 89(7):4238–4245
Zhao J, Zhao L, Lan C, Zhao S (2016) Graphene quantum dots as effective probes for label-free fluorescence detection of dopamine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 223:246–251
Acknowledgments
This research was financed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21675127), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Northwest A&F University of China (2014YB093, 2452015257) and the Development Project of Qinghai Key Laboratory (2017-ZJ-Y10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 7179 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Zhang, W., Huang, L. et al. Fluorometric determination of dopamine by using molybdenum disulfide quantum dots. Microchim Acta 185, 234 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2771-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2771-0