Abstract
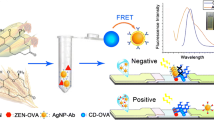
A lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) was developed for the determination of fumonisin mycotoxins. The fluorescence of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs), observed at excitation/emission wavelengths of 365/525 nm, is suppressed by the addition of silver nanoparticles (SNPs) or gold nanoparticles (GNPs) because SNPs overlap the excitation bands of the QDs, and GNPs overlap the emission bands. The fluorescence of the QDs is recovered upon addition of fumonisins, allowing for the sensitive detection in “positive mode” of the target mycotoxin by monitoring the changes of the QDs fluorescence intensity. The SNPs are found to be the most effective quenchers, while the use of GNPs allows for an efficient recovery of fluorescence and can be employed in the LFIA. The method was successfully applied to the fluorometric determination of fumonisins in spiked maize flour samples. The visual detection limit is at the ng·mL−1 level. This is four times lower compared to the colorimetric LFIA based on the use of the conventional gold NPs.

Schematic of the fluorescence quenching lateral flow immunoassay that uses fluorescent quantum dots (QD) and metal nanoparticles (NP) as the quencher: the binding of NP-labelled antibody to the antigen (purple triangle) modulates QD luminescence at the Test line, allowing for ‘positive mode’ detection of fumonisins. The NP accumulation at Control line assures validity of the test.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
St John A, Price CP (2014) Existing and emerging Technologies for Point-of-Care Testing. Clin Biochem Rev 35:155–167
Posthuma-Trumpie GA, Korf J, van Amerongen A (2009) Lateral flow (immuno)assay: its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:569–582
Huang X, Aguilar ZP, Xu H, Lai W, Xiong Y (2016) Membrane-based lateral flow immunochromatographic strip with nanoparticles as reporters for detection: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 75:166–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.08.032
Quesada-González D, Merkoçi A (2015) Nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 73:47–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.05.050
Xu Y, Liu M, Kong N, Liu J (2016) Lab-on-paper micro- and nano-analytical devices: fabrication, modification, detection and emerging applications. Microchim Acta 183:1521–1542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1841-4
Yao J, Li L, Li P, Yang M (2017) Quantum dots: from fluorescence to chemiluminescence, bioluminescence, electrochemiluminescence, and electrochemistry. Nanoscale 9:13364–13383. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR05233B
Li J, Zhu JJ (2013) Quantum dots for fluorescent biosensing and bio-imaging applications. Analyst 138:2506–2515. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AN36705C
Wu P, Hou X, JJ X, Chen HY (2016) Ratiometric fluorescence, electrochemiluminescence, and photoelectrochemical chemo/biosensing based on semiconductor quantum dots. Nano 8:8427–8442. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nr01912a
Bai Y, Tian C, Wei X, Wang Y, Wang D, Shi X (2012) A sensitive lateral flow test strip based on silica nanoparticle/CdTe quantum dot composite reporter probes. RSC Adv 2:1778–1781
Berlina AN, Taranova NA, Zherdev AV, Vengerov YY, Dzantiev BB (2013) Quantum dot-based lateral flow immunoassay for detection of chloramphenicol in milk. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:4997–5000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-6876-3
Di Nardo F, Anfossi L, Giovannoli C, Passini C, Goftman VV, Goryacheva IY, Baggiani C (2016) A fluorescent immunochromatographic strip test using quantum dots for fumonisins detection. Talanta 150:463–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.12.072
Xie Y, Zhang L, Yang X, Le T (2017) Development of a quantum dot-based immunochromatography test strip for rapid screening of oxytetracycline and 4-epi-oxytetracycline in edible animal tissues. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 34:371–378. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2016.1277038
Chou KF, Dennis AM (2015) Förster resonance energy transfer between quantum dot donors and quantum dot acceptors. Sensors (Basel) 15:13288–13325. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150613288
Stanisavljevic M, Krizkova S, Vaculovicova M, Kizek R, Adam V (2015) Quantum dots-fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based nanosensors and their application. Biosens Bioelectron 74:562–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.06.076
Algar WR, Krull UJ (2008) Quantum dots as donors in fluorescence resonance energy transfer for the bioanalysis of nucleic acids, proteins, and other biological molecules. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1609–1618
Esteve-Turrillas FA, Abad-Fuentes A (2013) Applications of quantum dots as probes in immunosensing of small-sized analytes. Biosens Bioelectron 41:12–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.09.025
Zhang H, Lv J, Jia Z (2017) Efficient fluorescence resonance energy transfer between quantum dots and gold nanoparticles based on porous silicon photonic crystal for DNA detection. Sensors (Basel) 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051078
Kattke MD, Gao EJ, Sapsford KE, Stephenson LD, Kumar A (2011) FRET-based quantum dot immunoassay for rapid and sensitive detection of aspergillus amstelodami. Sensors (Basel) 11:6396–6410. https://doi.org/10.3390/s110606396
Mayilo S, Kloster MA, Wunderlich M, Lutich A, Klar TA, Nichtl A, Kurzinger K, Stefani FD, Feldmann J (2009) Long-range fluorescence quenching by gold nanoparticles in a sandwich immunoassay for cardiac troponin T. Nano Lett 9:4558–4563. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl903178n
Ao L, Gao F, Pan B, He R, Cu D (2006) Fluoroimmunoassay for antigen based on fluorescence quenching signal of gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 78:1104–1106. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac051323m
Zhao W, Ji W, Zhang Y, Du L, Wang S (2016) A competitive fluorescence quenching-based immunoassay for bisphenol a employing functionalized silica nanoparticles and nanogold RSC advance 45. Issue in Progress. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA26366B
Shi CY, Deng N, Liang JJ, Zhou KN, QQ F, Tang Y (2015) A fluorescent polymer dots positive readout fluorescent quenching lateral flow sensor for ractopamine rapid detection. Anal Chim Acta 854:202–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.11.005
Fu Q, Tang Y, Shi C, Zhang X, Xiang J, Liu X (2013) A novel fluorescence-quenching immunochromatographic sensor for detection of the heavy metal chromium. Biosens Bioelectron 49:399–402
Fu Q, Liang J, Lan C, Zhou K, Shi C, Tang Y (2014) Development of a novel dual-functional lateral-flow sensor for on-site detection of small molecule analytes. Sensors Actuators B Chem 203:683–689
Chen X, Xu Y, Yu J, Li J, Zhou X, Wu C, Ji Q, Ren Y, Wang L, Huang Z et al (2014) Antigen detection based on background fluorescence quenching immunochromatographic assay. Anal Chim Acta 841:44–50.9
Zhang G, Chen M, Liu D, Xiong Y, Feng R, Zhong P, Lai W (2016) Quantitative detection of 2-adrenergic agonists using fluorescence quenching by immunochromatographic assay. Anal Methods 8:627–631
Morales-Narváez E, Naghdi T, Zor E, Merkoçi A (2015) Photoluminescent lateral-flow immunoassay revealed by graphene oxide: highly sensitive paper-based pathogen detection. Anal Chem 87:8573–8577
Jiang H, Li X, Xiong Y, Pei K, Nie L, Xiong Y (2017) Silver nanoparticle-based fluorescence-quenching lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive detection of Ochratoxin a in grape juice and wine. Toxins 9:83. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9030083
Speranskaya ES, Beloglazova NV, Lenain P, De Saeger S, Wang Z, Zhang S, Hens Z, Knopp D, Potapkin DV, Goryacheva IY (2014) Polymer-coated fluorescent CdSe-based quantum dots for application in immunoassay. Biosens Bioelectron 53:225–231
International Agency for Research on Cancer (1993). Monographs on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk of chemicals to humans. 82: 301–366
Di Nardo F, Baggiani C, Giovannoli C, Spano G, Anfossi L (2017) Multicolor immunochromatographic strip test based on gold nanoparticles for the determination of aflatoxin B1 and fumonisins. Microchim Acta 184:1295–1304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2121-7
Turner NW, Bramhmbhatt H, Szabo-Vezse M, Poma A, Coker R, Piletsky SA (2015) Analytical methods for determination of mycotoxins: an update (2009-2014). Anal Chim Acta 2015 Dec 11 901:12–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.10.013
Anfossi L, Calderara M, Baggiani C, Giovannoli C, Arletti E, Giraudi G (2010) Development and application of a quantitative lateral flow immunoassay for fumonisins in maize. Anal Chim Acta 682:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.09.045
Chauhan R, Singh J, Sachdev T, Basu T, Malhotra BD (2016) Recent advances in mycotoxins detection. Biosens Bioelectron 81:532–545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.03.004
Beloglazova NV, Speranskaya ES, De Saeger S, Hens Z, Abé S, Goryacheva IY (2012) Quantum dot based rapid tests for zearalenone detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 403:3013–3024
Bao Q, Zhang D, Qi P (2011) Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticle and graphene oxide nanosheet composites as a bactericidal agent for water disinfection. J Colloid Interface Sci 360:463–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2011.05.009
Hanagodimatha SM, Evalea BG, Manoharab SR (2009) Nonlinear fluorescence quenching of newly synthesized coumarin derivative by aniline in binary mixtures. Spectrochim Acta A 74:943–948
Lu S, Li G, Lv Z, Qiu N, Kong W, Gong P, Chen G, Xia L, Guo X, You J et al (2016) Facile and ultrasensitive fluorescence sensor platform for tumor invasive biomaker β-glucuronidase detection and inhibitor evaluation with carbon quantum dots based on inner-filter effect. Biosens Bioelectron 85:358–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.05.021
Yen CW, de Puig H, Tam JO, Gómez-Márquez J, Bosch I, Hamad-Schifferli K, Gehrke L (2015) Multicolored silver nanoparticles for multiplexed disease diagnostics: distinguishing dengue, yellow fever, and Ebola viruses. Lab Chip 15:1638. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5lc00055f
Mirasoli M, Buragina A, Dolci LS, Simoni P, Anfossi L, Giraudi G, Roda A (2012) Chemiluminescence-based biosensor for fumonisins quantitative detection in maize samples. Biosens Bioelectron 32:283–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.11.039
Lattanzio VM, Nivarlet N, Lippolis V, Della Gatta S, Huet AC, Delahaut P, Granier B, Visconti A (2012) Multiplex dipstick immunoassay for semi-quantitative determination of Fusarium mycotoxins in cereals. Anal Chim Acta 2012 Mar 9 718:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.12.060
Wang YK, Shi YB, Zou Q, Sun JH, Chen ZF, Wang H, Li SQ, Yian YX (2013) Development of a rapid and simultaneous immunochromatographic assay for the determination of zearalenone and fumonisin B1 in corn, wheat and feedstuff samples. Food Control 31:180–188
Wu S, Duan N, Li X, Tan G, Ma X, Xia Y, Wang Z, Wang H (2013) Homogenous detection of fumonisin B(1) with a molecular beacon based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between NaYF4: Yb, Ho upconversion nanoparticles and gold nanoparticles. Talanta 116:611–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.07.016
Wang Z, Li H, Li C, Yu Q, Shen J, De Saeger S (2014) Development and application of a quantitative fluorescence-based immunochromatographic assay for fumonisin b1 in maize. J Agric Food Chem 2014(62):6294–6298
Zangheri M, Di Nardo F, Anfossi L, Giovannoli C, Baggiani C, Roda A, Mirasoli M (2015) A multiplex chemiluminescent biosensor for type B-fumonisins and aflatoxin B1 quantitative detection in maize flour. Analyst 140:358–365. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4an01613k
Ren W, Huang Z, Xu Y, Li Y, Ji Y, Su B (2015) Urchin-like gold nanoparticle-based immunochromatographic strip test for rapid detection of fumonisin B1 in grains. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:7341–7348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8896-7
Chen X, Huang Y, Ma X, Jia F, Guo X, Wang Z (2015) Impedimetric aptamer-based determination of the mold toxin fumonisin B1. Microchim Acta 182:1709–1714
Yu Q, Li H, Li C, Zhang S, Shen J, Wang Z (2015) Gold nanoparticles-based lateral flow immunoassay with silver staining for simultaneous detection of fumonisin B1 and deoxynivalenol. Food Control 54:347–352
Foubert A, Beloglazova NV, Gordienko A, Tessier MD, Drijvers E, Hens Z, De Saeger S (2017) Development of a rainbow lateral flow immunoassay for the simultaneous detection of four mycotoxins. J Agric Food Chem 65:7121–7130
Wang C, Hou F, Ma Y (2015) Simultaneous quantitative detection of multiple tumor markers with a rapid and sensitive multicolor quantum dots based immunochromatographic test strip. Biosens Bioelectron 68:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.12.051
Acknowledgements
Russian Ministry of Science and Education, project 4.1063.2017/4.6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 655 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anfossi, L., Di Nardo, F., Cavalera, S. et al. A lateral flow immunoassay for straightforward determination of fumonisin mycotoxins based on the quenching of the fluorescence of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots by gold and silver nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185, 94 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2642-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2642-0