Abstract
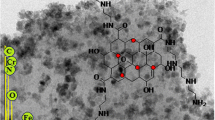
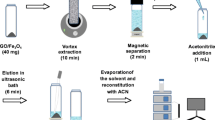
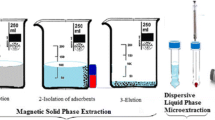
An amino acid derived ionic liquid, Fe3O4 nanoparticles and graphene oxide (GO) were used to prepare a material for the magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) of the ions Al(III), Cr(III), Cu(II) and Pb(II). The material was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectral (FT-IR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), magnetic analysis and isoelectric point (pI) analysis. It is shown to be a viable sorbent for the separation of these metal ions. Single factor experiments were carried out to optimize adsorption including pH values, ionic strength, temperature and solution volume. Following desorption with 0.1 M HCl, the ions were quantified by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Under the optimum conditions, the method provides a linear range from 10 to 170 μg· L−1 for Al(III); from 4.0 to 200 μg· L−1 for Cr(III); from 5.0 to 170 μg· L−1 for Cu(II); and from 5.0 to 200 μg· L−1 for Pb(II). The limits of detection (LOD) are 6.2 ng L−1 for Al(III); 1.6 ng L−1 for Cr(III); 0.52 ng L−1 for Cu(II); and 30 ng L−1 for Pb(II). Method performance was investigated by determination of these ions in (spiked) environmental water and gave recoveries in the range of 89.1%–117.8%.

The graph shows that Al(III), Cr(III), Cu(II), Pb(II) are not adsorbed quantitatively by Fe3O4-SiO2. On the other hand, Cr(III) and Pb(II) are adsorbed quantitatively by Fe3O4-SiO2-GO while Al(III) and Cu(II) are not quantitatively retained. However, 3D–Fe3O4-SiO2-GO-AAIL adsorb all these 4 metal ions quantitatively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saleh TA, Tuzen M, Sarı A (2017) Magnetic activated carbon loaded with tungsten oxide nanoparticles for aluminum removal from waters. J Env Chem Eng 5:2853–2860
Li N, Chen J, Shi YP (2017) Magnetic polyethyleneimine functionalized reduced graphene oxide as a novel magnetic solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the determination of polar acidic herbicides in rice. Anal Chim Acta 949:23–34
Tuzen M, Sahiner S, Hazer B (2016) Solid phase extraction of lead, cadmium and zinc on biodegradable polyhydroxybutyrate diethanol amine (PHB-DEA) polymer and their determination in water and food samples. Food Chem 210:115–120
Chen SQ, Qin XX, Gu WX, Zhu XS (2016) Speciation analysis of Mn(II)/Mn(VII) using Fe3O4@ionic liquids-β-cyclodextrin polymer magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with ICP-OES. Talanta 161:325–332
Ebrahimpour E, Amiri A, Baghayeri M, Rouhi M, Lakouraj MM (2017) Poly (indole-co-thiophene)@Fe3O4 as novel adsorbents for the extraction of aniline derivatives from water samples. Microchem J 131:174–181
Farmany A, Mortazavi SS, Mahdavi H (2016) Ultrasond-assisted synthesis of Fe3O4/SiO2 core/shell with enhanced adsorption capacity for diazinon removal. J Magn Magn Mater 416:75–80
Liao NN, Liu ZS, Zhang WJ, Gong SG, Ren DM, Ke LJ, Lin K, Yang H, He F, Jiang HL (2016) Preparation of a novel Fe3O4/graphene oxide hybrid for adsorptive removal of methylene blue from water. J Macromol Sci Part A Pure Appl Chem 53:276–281
Farzin L, Shamsipur M, Sheibani S (2016) Solid phase extraction of hemin from serum of breast cancer patients using an ionic liquid coated Fe3O4/graphene oxide nanocomposite, and its quantitation by using FAAS. Microchim Acta 183:1–9
Fan YC, Chen ML, Shentu C, El-Sepai F (2009) Ionic liquids extraction of Para red and Sudan dyes from chilli powder, chilli oil and food additive combined with high performance liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 650:65–69
Zhang Y, Zhou H, Zhang ZH, Wu XL, Chen WG, Zhu Y, Fang CF, Zhao YG (2017) Three-dimensional ionic liquid functionalized magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite for the magnetic dispersive solid phase extraction of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in vegetable oils. J Chromatogr A 1489:29–38
Fukumoto K, Masahiro Yoshizawa A, Ohno H (2005) Room temperature ionic liquids from 20 natural amino acids. J Am Chem Soc 127:2398–2399
Varyani M, Khatri PK, Jain SL (2016) Amino acid ionic liquid bound copper Schiff base catalyzed highly efficient three component A3-coupling reaction. Catal Commun 77:113–117
Liu YT, Tian AL, Wang X, Qi J, Wang FK, Ma Y, Ito Y, Wei Y (2015) Fabrication of chiral amino acid ionic liquid modified magnetic multifunctional nanospheres for centrifugal chiral chromatography separation of racemates. J Chromatogr A 1400:40–46
Wang WN, Ma RY, Wu QH, Wang C, Wang Z (2013) Magnetic microsphere-confined graphene for the extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from environmental water samples coupled with high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence analysis. J Chromatogr A 1293:20–27
Moghadam F, Kamio E, Matsuyama H (2017) High CO2 separation performance of amino acid ionic liquid-based double network ion gel membranes in low CO2 concentration gas mixtures under humid conditions. J Membr Sci 525:290–297
Wen Q, Wang YZ, Xu KJ, Li N, Zhang HM, Yang Q, Zhou YG (2014) Magnetic solid-phase extraction of protein by ionic liquid-coated Fe@graphene oxide. Talanta 119:341–347
Huang C, Gjelstad A, Pedersen BP (2015) Selective electromembrane extraction based on isoelectric point: fundamental studies with angiotensin II antipeptide as model analyte. J Membr Sci 481:115–123
Mehdinia A, Shoormeij Z, Jabbari A (2017) Trace determination of lead(II) ions by using a magnetic nanocomposite of the type Fe3O4/TiO2/PPy as a sorbent, and FAAS for quantitation. Microchim Acta 184:1–9
Habila MA, Alothman ZA, El-Toni AM, Labis JP, Li XM, Zhang F, Soylak M (2016) Mercaptobenzothiazole-functionalized magnetic carbon nanospheres of type Fe3O4@SiO2@C for the preconcentration of nickel, copper and lead prior to their determination by ICP-MS. Microchim Acta 183:2377–2384
Saleh TA, Sarı A, Tuzen M (2017) Optimization of parameters with experimental design for the adsorption of mercury using polyethylenimine modified-activated carbon. J Env Chem Eng 5:1079–1088
Zhan F, Gao F, Wang X, Xie LQ, Gao F, Wang QX (2016) Determination of lead(II) by adsorptive stripping voltammetry using a glassy carbon electrode modified with β-cyclodextrin and chemically reduced graphene oxide composite. Microchim Acta 183:1169–1176
Li L, Wu M, Feng YY, Zhao FQ, Zeng BZ (2016) Doping of three-dimensional porous carbon nanotube-graphene-ionic liquid composite into polyaniline for the headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography determination of alcohols. Anal Chim Acta 948:48–54
Taha M, Khan I, Joao AP (2016) Coordination abilities of Good’s buffer ionic liquids toward europium(III) ion in aqueous solution. J Chem Thermodyn 94:152–159
Kato M, Maezawa Y, Takeda S, Hagiwara Y, Kogo R (2006) Pre-combustion CO2, capture using ceramic absorbent and methane steam reforming. J Ceram Soc Jpn 113:252–254
Jean PS (2016) On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem Eng J 300:254–263
Yao M, Bard AJ (2015) Measurement of temperature-dependent stability constants of cu(I) and cu(II) chloride complexes by voltammetry at a Pt Ultramicroelectrode. Anal Chem 87:3498–3504
Wen SP, Zhu XS, Wu XY, Qin XX (2014) Directly suspended droplet microextraction coupled with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry for the speciation of chromium(III)/chromium(VI). Anal Methods 6:9777–9782
Yang JL, Liu JZ, Wu CX, Kerr PG, Wong P-K, Wu YH (2016) Bioremediation of agricultural solid waste leachates with diverse species of cu (II) and cd (II) by periphyton. Bioresour Technol 221:214–221
Breza M, Manova A (1999) On the structure of lead(II) complexes in aqueous solutions. II-Tetranuclear clusters Polyhedron 30:2085–2090
Peng XQ, Zhang W, Gai LG, Jiang HH, Wang Y, Zhao LC (2015) Dedoped Fe3O4/PPy nanocomposite with high anti-interfering ability for effective separation of Ag(I) from mixed metal-ion solution. Chem Eng J 280:197–205
Chen JP, Zhu XS (2016) Magnetic solid phase extraction using ionic liquid-coated core-shell magnetic nanoparticles followed by high-performance liquid chromatography for determination of Rhodamine B in food samples. Food Chem 200:10–15
Chullasat K, Nurerk P, Kanatharana P, Sukchuay T, Bunkoed O (2017) Hybrid monolith sorbent of polypyrrole-coated graphene oxide incorporated into a polyvinyl alcohol cryogel for extraction and enrichment of sulfonamides from water samples. Anal Chim Acta 961:59–66
Sang HB, Liang P, Du D (2008) Determination of trace aluminum in biological and water samples by cloud point extraction preconcentration and graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry detection. J Hazard Mater 154:1127–1132
Sohrabi MR, Matbouie Z, Asgharinezhad AA, Dehghani A (2013) Solid phase extraction of cd (II) and Pb (II) using a magnetic metal-organic framework, and their determination by FAAS. Microchim Acta 180:589–597
Taghizadeh M, Asgharinezhad AA, Pooladi M, Barzin M, Abbaszadeh A, Tadjarodi A (2013) A novel magnetic metal organic framework nanocomposite for extraction and preconcentration of heavy metal ions, and its optimization via experimental design methodology. Microchim Acta 180:1073–1084
Wang Y, Xie J, Wu Y, Hu X (2014) A magnetic metal-organic framework as a new sorbent for solid-phase extraction of copper(II), and its determination by electrothermal AAS. Microchim Acta 181:949–956
Maryam R, Somayeh AB, Behruz B (2017) Dissolvable layered double hydroxide as an efficient nanosorbent for centrifugeless air-agitated dispersive solid-phase extraction of potentially toxic metal ions from bio-fluid samples. Anal Chim Acta 957:1–9
Karadas C, Kara D (2017) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic drop for preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of copper by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem 220:242–248
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21375117) and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Weixi Gu and Xiashi Zhu declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 764 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, W., Zhu, X. Nanoparticles of type Fe3O4-SiO2-graphene oxide and coated with an amino acid-derived ionic liquid for extraction of Al(III), Cr(III), Cu(II), Pb(II) prior to their determination by ICP-OES. Microchim Acta 184, 4279–4286 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2469-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2469-8