Abstract
The authors describe an amperometric assay for the detection of prostate specific antigen (PSA) that combines the advantages of using a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) and of a nanocomposite composed of graphene nanoplatelets (graphene sheets; GS), gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and chitosan (Chit). The GS-AuNP composite was synthesized by a single-step reduction of GS and HAuCl4 solution. The MIP was synthesized by electropolymerization of dopamine and characterized by scanning electron microscopy and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). Sensitivity is strongly improved by the magnified current obtained by using the GS-AuNP hybrid. Chit was further employed as a film-forming material to prevent the leakage of nanomaterials. Under optimized conditions, the method displays good analytical performance for the detection of PSA by DPV and by using hexacyanoferrate as the electrochemical probe. The peak current (typically measured at 0.16 V vs. SCE) increases linearly in the 1 pg mL−1 to 100 ng mL−1 PSA concentration range, and the detection limit is 0.15 pg mL−1 at a signal to noise ratio of 3. The method was successfully applied to the determination of PSA in serum. The assay is highly selective, sensitive, reproducible and stable. In our perception, it represents an attractive alternative to the commercially available ELISA kits for PSA.

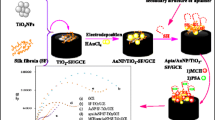
Schematic of a molecularly imprinted material obtained via electropolymerization of dopamine onto gold nanoparticles and placed, along with graphene nanoplatelets and chitosan on an electrode to detect prostate specific antigen (PSA). The sensor shows good specificity and accuracy for PSA detection in female serum.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu H, Levesque MA, Clark GM, Diamandis EP (1999) Enhanced prediction of breast cancer prognosis by evaluating expression of p53 and prostate-specific antigen in combination. Br J Cancer 81:490–495
Yu F, Persson B, Lofas S, Knoll W (2004) Surface plasmon fluorescence immunoassay of free prostate-specific antigen in human plasma at the femtomolar level. Anal Chem 76:6765–6770
Grubisha DS, Lipert RJ, Park HY, Driskell J, Porter MD (2003) Femtomolar detection of prostate-specific antigen: an immunoassay based on surface-enhanced raman scattering and immunogold labels. Anal Chem 75:5936–5943
Black MH, Giai M, Ponzone R, Sismondi P, Yu H, Diamandis EP (2000) Serum total and free prostate-specific antigen for breast cancer diagnosis in women. Clin. Cancer Res 6:467–473
Moon JM, Kim YH, Cho Y (2014) A nanowire-based label-free immunosensor: direct incorporation of a PSA antibody in electropolymerized polypyrrole. Biosens Bioelectron 57:157–161
Kim DJ, Lee NE, Park JS, Park IJ, Kim JG, Cho HJ (2010) Organic electrochemical transistor based immunosensor for prostate specific antigen (PSA) detection using gold nanoparticles for signal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 25:2477–2482
Chikkaveeraiah BV, Mani V, Patel V, Gutkind JS, Rusling JF (2011) Microfluidic electrochemical immunoarray for ultrasensitive detection of two cancer biomarker proteins in serum. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4477–4483
Wu L, Li M, Zhang M, Yan M, Ge S, Yu J (2013) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for tumor marker detection based on nanoporous sliver@carbon dots as labels. Sensors Actuators B Chem 186:761–767
Dey A, Kaushik A, Arya SK, Bhansali S (2012) Mediator free highly sensitive polyaniline–gold hybrid nanocomposite based immunosensor for prostate-specificantigen (PSA) detection. J Mater Chem 22:14763–14772
Triroj N, Jaroenapibal P, Shi H, Yeh JI, Beresford R (2011) Microfluidic chip-based nanoelectrode array as miniaturized biochemical sensing platform for prostate-specific antigen detection. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2927–2933
Liu J, Lu CY, Zhou H, Xu JJ, Wang ZH, Chen HY (2013) A dual-functional electrochemical biosensor for the detection of prostate specificantigen and telomerase activity. Chem Commun 49:6602–6604
Suaifan GARY, Esseghaier C, Ng A, Zourob M (2012) Wash-less and highly sensitive assay for prostate specific antigen detection. Analyst 137:5614–5619
Chuah K, Lai LMH, Goon IY, Parker SG, Amal R, Gooding JJ (2012) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) using gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles as dispersible electrodes. Chem Commun 48:3503–3505
Acevedo B, Perera Y, Ruiz M, Rojas G, Benítez J, Ayala M, Gavilondo J (2002) Development and validation of a quantitative ELISA for the measurement of PSA concentration. Clin Chim Acta 317:55–63
Ma Y, Shen XL, Zeng Q, Wang HS, Wang LS (2017) A multi-walled carbon nanotubes based molecularly imprinted polymers electrochemical sensor for the sensitive determination of HIV-p24. Talanta 164:121–127
Ma Y, Shen XL, Zeng Q, Wang LS (2017) MIPs-graphene nanoplatelets-MWCNTs modified glassy carbon electrode for the determination of cardiac troponin I. Anal Biochem 520:9–15
Liu Y, Liu J, Liu J, Gan W, Ye BC, Li YC (2017) Highly sensitive and selective voltammetric determination of dopamine using a gold electrode modified with a molecularly imprinted polymeric film immobilized on flaked hollow nickel nanospheres. Microchim Acta 184:1285–1294
Turner NW, Jeans CW, Brain KR, Allender CJ, Hlady V, Britt DW (2006) From 3D to 2D: a review of the molecular imprinting of proteins. Biotechnol Prog 22(6):474–1489
Moreira FTC, Sharma S, Dutra RAF, Noronha JPC, Cass AEG, Sales MGF (2013) Smart plastic antibody material (SPAM) tailored on disposable screen printed electrodes for protein recognition: application to myoglobin detection. Biosens Bioelectron 45:237–244
Chen HJ, Zhang ZH, Luo LJ, Yao SZ (2012) Surface-imprinted chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes biosensor for detection of bovine serum albumin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 163:76–83
Ramanaviciene A, Ramanavicius A (2004) Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole-based synthetic receptor for direct detection of bovine leukemia virus glycoproteins. Biosens Bioelectron 20:1076–1082
Lee MH, O’Hare D, Guo HZ, Yang CH, Lin HY (2016) Electrochemical sensing of urinary progesterone with molecularly imprinted poly(aniline-co-metanilic acid)s. J Mater Chem B 4:3782–3787
Ouyang RZ, Lei JP, Ju HX, Xue YD (2007) A molecularly imprinted copolymer designed for enantioselective recognition of glutamic acid. Adv Funct Mater 17:3223–3230
Li YC, Liu J, Liu MH, Yu F, Zhang L, Tang H, Ye BC, Lai LF (2016) Fabrication of ultra-sensitive and selective dopamine electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer modified graphene@carbon nanotube foam. Electrochem Commun 64:42–45
Erdőssy J, Horváth V, Yarman A, Scheller FW, Gyurcsányi RE (2016) Electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted polymers for protein recognition. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 79:179–190
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Rochefort A, Wuest JD (2009) Interaction of substituted aromatic compounds with graphene. Langmuir 25:210–215
Liu K, Zhang JJ, Wang C, Zhu JJ (2011) Graphene-assisted dual amplification strategy for the fabrication of sensitive amperometric immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3627–3632
Liu N, Ma Z (2014) Au–ionic liquid functionalized reduced graphene oxide immunosensing platform for simultaneous electrochemical detection of multiple analytes. Biosens Bioelectron 51:184–190
Stoller MD, Park SJ, Zhu YW, An JH, Ruoff RS (2008) Graphene-based ultracapacitors. Nano Lett 8:3498–3502
Kim H, Abdala AA, Macosko CW (2010) Graphene/polymer nanocomposites. Macromolecules 43:6515–6530
Novoselov K, Geim A, Morozov S, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos S, Grigorieva I, Firsov A (2004) Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 30:6666–6669
Sheng ZH, Zheng XQ, Xu JY, Bao WJ, Wang FB, Xia XH (2012) Electrochemical sensor based on nitrogen doped graphene: simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Biosens Bioelectron 34:125–131
Zhang LL, Zhou R, Zhao X (2010) Graphene-based materials as supercapacitor electrodes. J Mater Chem 20:5983–5992
Shan J, Ma Z (2017) A review on amperometric immunoassays for tumor markers based on the use of hybrid materials consisting of conducting polymers and noble metal nanomaterials. Microchim Acta 184(4):969–979
Chartarrayawadee W, Moulton SE, Li D, Too CO, Wallace GG (2012) Novel composite graphene/platinum electro-catalytic electrodes prepared by electrophoretic deposition from colloidal solutions. Electrochim Acta 60:213–223
Muszynski R, Seger B, Kamat PV (2008) Decorating graphene sheets with gold nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 112:5263–5266
Shanmugharaj AM, Ryu SH (2012) Excellent electrochemical performance of graphene-silver nanoparticle hybrids prepared using a microwave spark assistance process. Electrochim Acta 74:207–214
Wang XD, Dong J, Ming HM, Ai SY (2013) Sensing of glycoprotein via a biomimetic sensor based on molecularly imprintedpolymers and graphene−au nanoparticles. Analyst 138:1219–1225
Lai GS, Yan F, Wu J, Leng C, Ju HX (2011) Ultrasensitive multiplexed immunoassay with electrochemical stripping analysis of silver nanoparticles catalytically deposited by gold nanoparticles and enzymatic reaction. Anal Chem 83:2726–2732
Liang RP, Wang ZX, Zhang L, Qiu JD (2012) A label-free amperometric immunosensor for alpha-fetoprotein determination based on highly ordered porous multi-walled carbon nanotubes/silica nanoparticles array platform. Sensors Actuators B Chem 166−167:569–575
Wang D, Gan N, Zhang HR, Li TH, Qiao L, Cao YT, Su XR, Jiang S (2015) Simultaneous electrochemical immunoassay using graphene−au grafted recombinant apoferritin-encoded metallic labels as signal tags and dual-template magnetic molecular imprinted polymer as capture probes. Biosens Bioelectron 65:78–82
Bai HP, Wang CQ, Chen J, Peng J, Cao Q (2015) A novel sensitive electrochemical sensor based on in-situ polymerized molecularly imprinted membranes at graphene modified electrode for artemisinin determination. Biosens Bioelectron 64:352–358
Jolly P, Tamboli V, Harniman RL, Estrela P, Allender CJ, Bowen JL (2016) Aptamer–MIP hybrid receptor for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 75:188–195
Patra S, Roy E, Madhuri R, Sharma PK (2015) Nano-iniferter based imprinted sensor for ultra trace level detection of prostate-specific antigen in both men and women. Biosens Bioelectron 66:1–10
Rebelo TSCR, Noronha JP, Galésio M, Costa-Rodrigues J (2016) Testing the variability of PSA expression by different human prostate cancer cell lines by means of a new potentiometric device employing molecularly antibody assembled on graphene surface. Mater Sci Eng C 59:1069–1078
Biniaz Z, Mostafavi A, Shamspur T, Torkzadeh-Mahani M, Mohamadi M (2017) Electrochemical sandwich immunoassay for the prostate specific antigen using a polyclonal antibody conjugated to thionine and horseradish peroxidase. Microchim Acta 184:2731–2738
Jiao L, Mu ZG, Miao LY, Du WW, Wei Q (2017) Li H (2017) enhanced amperometric immunoassay for the prostate specific antigen using Pt-cu hierarchical trigonal bipyramid nanoframes as a label. Microchim Acta 184:423–429
Sun XC, Lei C, Guo L, Zhou Y (2016) Sandwich immunoassay for the prostate specific antigen using a micro-fluxgate and magnetic bead labels. Microchim Acta 183:2385–2393
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 21475046, 21427809, 21645004). We also acknowledge the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2015ZP028 and 2017MS094).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 10412 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y., Shen, XL., Zeng, Q. et al. A glassy carbon electrode modified with graphene nanoplatelets, gold nanoparticles and chitosan, and coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer for highly sensitive determination of prostate specific antigen. Microchim Acta 184, 4469–4476 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2458-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2458-y