Abstract
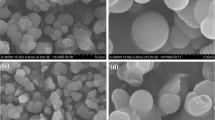
A hybrid material was prepared from a metal-organic framework (MOF) and core-shell silica by using a kinetic controlling approach. The nanocrystalline MOF (HKUST-1) was prepared from 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylate and copper(II) by tuning the reaction rate via the fraction of ethanol in the solvent. After the reaction rate was reduced to a certain degree, the pore surface would be well covered with Cu(II), which initiated the formation of a nanocrystalline HKUST-1. The resulting hybrid material was packed into a stainless-steel column (4.6 × 150 mm) and used as a stationary phase in high performance liquid chromatography. SiO2@dSiO2-HKUST-1 combined the merits of the high separation performance of the core-shell particles and the unique selectivity of the HKUST-1 nanocrystals. A separation efficiency as high as almost 140,000 plates per meter was achieved for the model analyte styrene. The material was stable and exhibited a highly reproductivity. The relative standard deviations of column-to-column, intra-day, and inter-day reproducibility of the SiO2@dSiO2-HKUST-1 packed columns for the retention time of styrene were 4.7%, 0.3%, and 0.4%, respectively.

HKUST-1 nanocrystals were coated onto the porous surface of core-shell silica spheres under careful kinetic control. The resulting particles were packed into the column, and a separation performance of up to 140,000 plates per meter was achieved.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Furukawa H, Cordova KE, O'Keeffe M, Yaghi OM (2013) The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science 341(6149):1230444. doi:10.1126/science.1230444
Zhang XQ, Han Q, Ding MY (2015) One-pot synthesis of UiO-66@SiO2 shell-core microspheres as stationary phase for high performance liquid chromatography. RSC Adv 5:1043–1050. doi:10.1039/c4ra12263a
Zhao WW, Zhang CY, Yan ZG, Bai LP, Wang X, Huang H, Zhou YY, Xie Y, Li FS, Li JR (2014) Separations of substituted benzenes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons using normal- and reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography with UiO-66 as the stationary phase. J Chromatogr A 1370:121–128. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2014.10.036
Yan ZM, Zheng JN, Chen JF, Tong P, Lu MH, Lin ZA, Zhang L (2014) Preparation and evaluation of silica-UIO-66 composite as liquid chromatographic stationary phase for fast and efficient separation. J Chromatogr A 1366:45–53. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2014.08.077
Van der Perre S, Duerinck T, Valvekens P, De Vos DE, Baron GV, Denayer JFM (2014) Chromatographic separation through confinement in nanocages. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 189:216–221. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.08.010
Yusuf K, Badjah-Hadj-Ahmed AY, Aqel A, ALOthman ZA (2015) Fabrication of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8-methacrylate monolith composite capillary columns for fast gas chromatographic separation of small molecules. J Chromatogr A 1406:299–306. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2015.06.026
Ahmed A, Forster M, Jin JS, Myers P, Zhang HF (2015) Tuning morphology of nanostructured ZIF-8 on silica microspheres and applications in liquid chromatography and dye degradation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(32):18054–18063. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b04979
Jiang JQ, Yang CX, Yan XP (2013) Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 for fast adsorption and removal of benzotriazoles from aqueous solution. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(19):9837–9842. doi:10.1021/am403079n
Fu YY, Yang CX, Yan XP (2013) Fabrication of ZIF-8@SiO2 core-shell microspheres as the stationary phase for high-performance liquid chromatography. Chem Eur J 19(40):13484–13491. doi:10.1002/chem.201301461
Li LM, Wang HF, Yan XP (2012) Metal-organic framework ZIF-8 nanocrystals as pseudostationary phase for capillary electrokinetic chromatography. Electrophoresis 33(18):2896–2902. doi:10.1002/elps.201200269
Wu YY, Yang CX, Yan XP (2015) An in situ growth approach to the fabrication of zeolite imidazolate framework-90 bonded capillary column for gas chromatography separation. Analyst 140(9):3107–3112. doi:10.1039/c5an00077g
Yu LQ, Yang CX, Yan XP (2014) Room temperature fabrication of post-modified zeolitic imidazolate framework-90 as stationary phase for open-tubular capillary electrochromatography. J Chromatogr A 1343:188–194. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2014.04.003
Yang SC, Ye FG, Zhang C, Shen SF, Zhao SL (2015) In situ synthesis of metal-organic frameworks in a porous polymer monolith as the stationary phase for capillary liquid chromatography. Analyst 140(8):2755–2761. doi:10.1039/c5an00079c
Bao T, Zhang J, Zhang WP, Chen ZL (2015) Growth of metal-organic framework HKUST-1 in capillary using liquid-phase epitaxy for open-tubular capillary electrochromatography and capillary liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1381:239–246. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2015.01.005
Yang SC, Ye FG, Lv QH, Zhang C, Shen SF, Zhao SL (2014) Incorporation of metal-organic framework HKUST-1 into porous polymer monolithic capillary columns to enhance the chromatographic separation of small molecules. J Chromatogr A 1360:143–149. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2014.07.067
El-Hankari S, Huo J, Ahmed A, Zhang HF, Bradshaw D (2014) Surface etching of HKUST-1 promoted via supramolecular interactions for chromatography. J Mater Chem A 2:13479–13485. doi:10.1039/c4ta02568g
Ahmed A, Forster M, Clowes R, Bradshaw D, Myers P, Zhang HF (2013) Silica SOS@HKUST-1 composite microspheres as easily packed stationary phases for fast separation. J Mater Chem A 1:3276–3286. doi:10.1039/c2ta01125e
Ameloot R, Liekens A, Alaerts L, Maes M, Galarneau A, Coq B, Desmet G, Sels BF, Denayer JFM, De Vos DE (2010) Silica-MOF composites as a stationary phase in liquid chromatography. Eur J Inorg Chem 2010(24):3735–3738. doi:10.1002/ejic.201000494
Yan ZM, Zhang WM, Gao J, Lin YF, Li JR, Lin ZA, Zhang L (2015) Reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography separation of positional isomers on a MIL-53(Fe) packed column. RSC Adv 5:40094–40102. doi:10.1039/c5ra02262b
Kim P-J, You Y-W, Park H, Chang J-S, Bae Y-S, Lee C-H, Suh J-K (2015) Separation of SF6 from SF6/N2 mixture using metal–organic framework MIL-100(Fe) granule. Chem Eng J 262:683–690. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.123
Yang CX, Liu SS, Wang HF, Wang SW, Yan XP (2012) High-performance liquid chromatographic separation of position isomers using metal-organic framework MIL-53(Al) as the stationary phase. Analyst 137(1):133–139. doi:10.1039/c1an15600d
Liu SS, Yang CX, Wang SW, Yan XP (2012) Metal-organic frameworks for reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Analyst 137:816–818. doi:10.1039/c2an15925b
De Malsche W, Van der Perre S, Silverans S, Maes M, De Vos DE, Lynen F, Denayer JFM (2012) Unusual pressure-temperature dependency in the capillary liquid chromatographic separation of C8 alkylaromatics on the MIL-53(Al) metal–organic framework. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 162:1–5. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2012.06.002
Maes M, Vermoortele F, Alaerts L, Couck S, Kirschhock CEA, Denayer JF, De Vos DE (2010) Separation of styrene and ethylbenzene on metal-organic frameworks: analogous structures with different adsorption mechanisms. J Am Chem Soc 132:15277–15285. doi:10.1021/ja106142x
Xu YY, Xu LF, Qi SD, Dong YL, ur Rahman Z, Chen HL, Chen XG (2013) In situ synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) in the capillary column for capillary electrochromatographic separation of small organic molecules. Anal Chem 85(23):11369–11375. doi:10.1021/ac402254u
Fu YY, Yang CX, Yan XP (2013) Metal-organic framework MIL-100(Fe) as the stationary phase for both normal-phase and reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1274:137–144. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.12.015
Yang F, Yang CX, Yan XP (2015) Post-synthetic modification of MIL-101(Cr) with pyridine for high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of tocopherols. Talanta 137:136–142. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.01.022
Yang CX, Chen YJ, Wang HF, Yan XP (2011) High-performance separation of fullerenes on metal-organic framework MIL-101(Cr). Chem Eur J 17(42):11734–11737. doi:10.1002/chem.201101593
Gu ZY, Yan XP (2010) Metal-organic framework MIL-101 for high-resolution gas-chromatographic separation of xylene isomers and ethylbenzene. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(8):1477–1480. doi:10.1002/anie.200906560
Abolghasemi MM, Yousefi V, Piryaei M (2015) Synthesis of a metal-organic framework confined in periodic mesoporous silica with enhanced hydrostability as a novel fiber coating for solid-phase microextraction. J Sep Sci 38:1187–1193. doi:10.1002/jssc.201400916
Munch AS, Seidel J, Obst A, Weber E, Mertens FO (2011) High-separation performance of chromatographic capillaries coated with MOF-5 by the controlled SBU approach. Chem Eur J 17(39):10958–10964. doi:10.1002/chem.201100642
Kong DY, Bao T, Chen ZL (2017) In situ synthesis of the imine-based covalent organic framework LZU1 on the inner walls of capillaries for electrochromatographic separation of nonsteroidal drugs and amino acids. Microchim Acta 184(4):1169–1176. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2095-5
Ahmed A, Hodgson N, Barrow M, Clowes R, Robertson CM, Steiner A, McKeown P, Bradshaw D, Myers P, Zhang HF (2014) Macroporous metal-organic framework microparticles with improved liquid phase separation. J Mater Chem A 2:9085–9090. doi:10.1039/c4ta00138a
Ameloot R, Gobechiya E, Uji-i H, Martens JA, Hofkens J, Alaerts L, Sels BF, De Vos DE (2010) Direct patterning of oriented metal-organic framework crystals via control over crystallization kinetics in clear precursor solutions. Adv Mater 22(24):2685–2688. doi:10.1002/adma.200903867
Qu QS, Min Y, Zhang LH, Xu Q, Yin YD (2015) Silica microspheres with fibrous shells: Synthesis and application in HPLC. Anal Chem 87(19):9631–9638. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02511
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Educational Committee (KJ2016SD12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1747 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Q., Si, Y., Xuan, H. et al. A nanocrystalline metal organic framework confined in the fibrous pores of core-shell silica particles for improved HPLC separation. Microchim Acta 184, 4099–4106 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2439-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2439-1