Abstract
Purpose
The association between the preoperative absolute neutrophil count (NC), lymphocyte count (LC), and monocyte count (MC) in the peripheral blood and the prognosis of gastric cancer (GC) patients has not been investigated widely.
Methods
We enrolled 445 patients who underwent surgery for GC between January, 2005 and April, 2013 to analyze the correlations among NC, LC, and MC and their prognoses.
Results
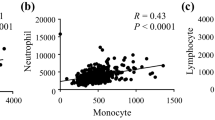
Based on cut-off values calculated by ROC analysis, patients were sub grouped as having: NC ≥ 4477 (NCHigh), NC < 4477 (NCLow); and as LC ≥ 1447 (LCHigh), LC < 1447 (LCLow); and as MC ≥ 658.5 (MCHigh), MC < 658.5 (MCLow). Each group was assigned as follows; NCHigh group = 1, NCLow group = 0, LCHigh group = 0, LCLow group = 1, MCHigh group = 1, MCLow group = 0, and the sum of each score was defined as the lymphocyte–monocyte–neutrophil score (LMN score). The overall 5-year survival rates were 89%, 74%, 57.8%, and 53.3% for LMN scores of 0, 1, 2, and 3, respectively (P = 0.0004). Multivariate analysis indicated that the LMN score was an independent prognostic indicator.
Conclusions
The combination of preoperative NC, LC, and MC appears to be a useful indicator of GC prognosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Park HJ, Ahn JY, Jung HY, Lim H, Lee JH, Choi KS, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes for gastric cancer patients aged 18–30 years. Gastric Cancer. 2014;17:649–60.
Nam DH, Lee YK, Park JC, Lee H, Shin SK, Lee SK, et al. Prognostic value of early postoperative tumor marker response in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20:3905–11.
Saito H, Kono Y, Murakami Y, Shishido Y, Kuroda H, Matsunaga T, et al. Postoperative serum albumin is a potential prognostic factor for older patients with gastric cancer. Yonago Acta Med. 2018;61:72–8.
Saito H, Kono Y, Murakami Y, Shishido Y, Kuroda H, Yamamoto M, et al. Prognostic significance of pre- and postoperative lymphocyte counts in patients with gastric cancer. Digestive Surg. 2019;36:137–43.
Saito H, Kono Y, Murakami Y, Shishido Y, Kuroda H, Matsunaga T, et al. Prognostic significance of platelet-based inflammatory indicators in patients with gastric cancer. World J Surg. 2018;42:2542–50.
Kono Y, Saito H, Murakami Y, Shishido Y, Kuroda H, Matsunaga T, et al. Postoperative ratio of the maximum C-reactive protein level to the minimum peripheral lymphocyte count as a prognostic indicator for gastric cancer patients. Surg Today 2018.
Miyatani K, Saito H, Kono Y, Murakami Y, Kuroda H, Matsunaga T, et al. Combined analysis of the pre- and postoperative neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio predicts the outcomes of patients with gastric cancer. Surg Today. 2018;48:300–7.
Murakami Y, Saito H, Kono Y, Shishido Y, Kuroda H, Matsunaga T, et al. Combined analysis of the preoperative and postoperative prognostic nutritional index offers a precise predictor of the prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. Surg Today. 2018;48:395–403.
Saito H, Kono Y, Murakami Y, Shishido Y, Kuroda H, Matsunaga T, et al. Prognostic significance of the preoperative ratio of C-reactive protein to albumin and neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio in gastric cancer patients. World J Surg. 2018;42:1819–25.
Clark EJ, Connor S, Taylor MA, Madhavan KK, Garden OJ, Parks RW. Preoperative lymphocyte count as a prognostic factor in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 2007;9:456–60.
Feng JF, Liu JS, Huang Y. Lymphopenia predicts poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Med (Baltimore). 2014;93:e257.
Saroha S, Uzzo RG, Plimack ER, Ruth K, Al-Saleem T. Lymphopenia is an independent predictor of inferior outcome in clear cell renal carcinoma. J Urol. 2013;189:454–61.
Borregaard N. Neutrophils, from marrow to microbes. Immunity. 2010;33:657–70.
Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science. 2004;303:1532–5.
Teramukai S, Kitano T, Kishida Y, Kawahara M, Kubota K, Komuta K, et al. Pretreatment neutrophil count as an independent prognostic factor in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: an analysis of Japan Multinational Trial Organisation LC00-03. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:1950–8.
Lee YY, Choi CH, Kim HJ, Kim TJ, Lee JW, Lee JH, et al. Pretreatment neutrophil:lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in cervical carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:1555–611.
Sadeghi N, Badalato GM, Hruby G, Grann V, McKiernan JM. Does absolute neutrophil count predict high tumor grade in African-American men with prostate cancer? Prostate. 2012;72:386–91.
Gondo T, Nakashima J, Ohno Y, Choichiro O, Horiguchi Y, Namiki K, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and establishment of novel preoperative risk stratification model in bladder cancer patients treated with radical cystectomy. Urology. 2012;79:1085–91.
Jiang Y, Xu H, Jiang H, Ding S, Zheng T. Pretreatment neutrophil–lymphocyte count ratio may associate with gastric cancer presence. Cancer Biomark. 2016;16:523–8.
Chen Z, Chen W, Wang J, Zhu M, Zhuang Z. Pretreated baseline neutrophil count and chemotherapy-induced neutropenia may be conveniently available as prognostic biomarkers in advanced gastric cancer. Intern Med J. 2015;45:854–9.
Kaynar M, Yildirim ME, Badem H, Cavis M, Tekinarslan E, Istanbulluoglu MO, et al. Bladder cancer invasion predictability based on preoperative neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:6601–5.
Watt DG, Martin JC, Park JH, Horgan PG, McMillan DC. Neutrophil count is the most important prognostic component of the differential white cell count in patients undergoing elective surgery for colorectal cancer. Am J Surg. 2015;210:24–30.
Mantovani A, Schioppa T, Porta C, Allavena P, Sica A. Role of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006;25:315–22.
Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002;420:860–7.
Tang X. Tumor-associated macrophages as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013;332:3–10.
Shigeoka M, Urakawa N, Nakamura T, Nishio M, Watajima T, Kuroda D, et al. Tumor associated macrophage expressing CD204 is associated with tumor aggressiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2013;104:1112–9.
Zhou K, Yan Y, Zhao S, Li B. Clinical application and prognostic assessment of serum tumor associated material (TAM) from esophageal cancer patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18:3870–6.
Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma: 3rd English edition. Gastric cancer : official journal of the International Gastric Cancer Association and the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association 2011;14:101–12.
Ray-Coquard I, Cropet C, Van Glabbeke M, Sebban C, Le Cesne A, Judson I, et al. Lymphopenia as a prognostic factor for overall survival in advanced carcinomas, sarcomas, and lymphomas. Cancer Res. 2009;69:5383–91.
Gooden MJ, de Bock GH, Leffers N, Daemen T, Nijman HW. The prognostic influence of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 2011;105:93–103.
Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pages C, et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science. 2006;313:1960–4.
Tang Y, Xu X, Guo S, Zhang C, Tang Y, Tian Y, et al. An increased abundance of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells is correlated with the progression and prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 2014;9:e91551.
Qiu H, Xiao-Jun W, Zhi-Wei Z, Gong C, Guo-Qiang W, Li-Yi Z, et al. The prognostic significance of peripheral T-lymphocyte subsets and natural killer cells in patients with colorectal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2009;56:1310–5.
Tachibana T, Onodera H, Tsuruyama T, Mori A, Nagayama S, Hiai H, et al. Increased intratumor Valpha24-positive natural killer T cells: a prognostic factor for primary colorectal carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:7322–7.
Berntsson J, Nodin B, Eberhard J, Micke P, Jirstrom K. Prognostic impact of tumour-infiltrating B cells and plasma cells in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2016;139:1129–39.
Yoshikawa T, Saito H, Osaki T, Matsumoto S, Tsujitani S, Ikeguchi M. Elevated Fas expression is related to increased apoptosis of circulating CD8+ T cell in patients with gastric cancer. J Surg Res. 2008;148:143–51.
Sionov RV, Fridlender ZG, Granot Z. The multifaceted roles neutrophils play in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron. 2015;8:125–58.
Fridlender ZG, Sun J, Kim S, Kapoor V, Cheng G, Ling L, et al. Polarization of tumor-associated neutrophil phenotype by TGF-beta: "N1" versus "N2" TAN. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:183–94.
Sun R, Luo J, Li D, Shu Y, Luo C, Wang SS, et al. Neutrophils with protumor potential could efficiently suppress tumor growth after cytokine priming and in presence of normal NK cells. Oncotarget. 2014;5:12621–344.
Ikeguchi M, Hatada T, Yamamoto M, Miyake T, Matsunaga T, Fukumoto Y, et al. Serum interleukin-6 and -10 levels in patients with gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2009;12:95–100.
Gordon SR, Maute RL, Dulken BW, Hutter G, George BM, McCracken MN, et al. PD-1 expression by tumour-associated macrophages inhibits phagocytosis and tumour immunity. Nature. 2017;545:495–9.
Matsunaga T, Saito H, Ikeguchi M. Increased B7–H1 and B7–H4 expressions on circulating monocytes and tumor-associated macrophages are involved in immune evasion in patients with gastric cancer. Yonago Acta Med. 2011;54:1–10.
Bozzetti F, Bonfanti G, Morabito A, Bufalino R, Menotti V, Andreola S, et al. A multifactorial approach for the prognosis of patients with carcinoma of the stomach after curative resection. Surg Gynecol Obst. 1986;162:229–34.
Maruyama K. The most important prognostic factors for gastric cancer patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987;22:63–8.
Shimada H, Noie T, Ohashi M, Oba K, Takahashi Y. Clinical significance of serum tumor markers for gastric cancer: a systematic review of literature by the Task Force of the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Gastric Cancer. 2014;17:26–33.
Lin JX, Wang W, Lin JP, Xie JW, Wang JB, Lu J, et al. Preoperative tumor markers independently predict survival in stage III gastric cancer patients: should we include tumor markers in AJCC staging? Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25:2703–12.
Uda H, Kanda M, Tanaka C, Kobayashi D, Inaoka K, Tanaka Y, et al. Perioperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen levels predict recurrence and survival of patients with pathological T2–4 gastric cancer treated with curative gastrectomy. Digestive Surg. 2018;35:55–63.
Fujiya K, Tokunaga M, Makuuchi R, Nishiwaki N, Omori H, Takagi W, et al. Early detection of nonperitoneal recurrence may contribute to survival benefit after curative gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2017;20:141–9.
Park CH, Park JC, Chung H, Shin SK, Lee SK, Cheong JH, et al. Impact of the surveillance interval on the survival of patients who undergo curative surgery for gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23:539–45.
Saito T, Nishikawa H, Wada H, Nagano Y, Sugiyama D, Atarashi K, et al. Two FOXP3(+)CD4(+) T cell subpopulations distinctly control the prognosis of colorectal cancers. Nat Med. 2016;22:679–84.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were carried out in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or with comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, H., Shimizu, S., Kono, Y. et al. Score of the preoperative absolute number of lymphocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils as a prognostic indicator for patients with gastric cancer. Surg Today 49, 850–858 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-019-01817-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-019-01817-6