Abstract
Purpose
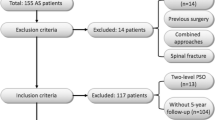
To determine the clinical- and surgical-related factors of hip joint structural changes in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients with thoracolumbar kyphosis who underwent PSO.
Methods
Hip involvement was assessed by the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Hip Index (BASRI-h) and defined by a score of at least 2. 52 patients with BASRI-h scores maintained and 78 patients with BASRI-h scores increased during follow-up were retrospectively reviewed. Clinical data were recorded. Radiological assessment was performed preoperatively, postoperatively, and at the final follow-up.
Results
No significant difference existed in age, gender and follow-up time between the groups, but earlier onset of AS, longer disease and kyphotic duration, and worse Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI) scores at the final follow-up were observed in patients with BASRI-h scores increased (P < 0.05). Besides, global kyphosis (GK), T1-pelvic angle (TPA), pelvic tilt (PT) and anterior pelvic plane angle (APPA) were always larger in patients with BASRI-h scores increased, accompanied with more sacral fixation (P < 0.05). Multivariate logistics regression showed that earlier onset of AS, longer kyphotic duration, larger preoperative GK, sacral fixation and larger APPA during follow-up were independent risk factors.
Conclusion
Earlier onset of AS and longer kyphotic duration were the clinical risk factors of hip joint structural changes in AS patients following PSO, while larger preoperative GK, sacral fixation in PSO and larger APPA during follow-up were the surgical-related factors. Surgeons should inform patients with risk factors of the possibility for severe hip joint structural changes after PSO.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braun J, Sieper J (2007) Ankylosing spondylitis. Lancet 369:1379–1390. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(07)60635-7
Dean LE, Jones GT, MacDonald AG, Downham C, Sturrock RD, Macfarlane GJ (2014) Global prevalence of ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 53:650–657. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ket387
Dougados M, Baeten D (2011) Spondyloarthritis. Lancet 377:2127–2137. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60071-8
Vander Cruyssen B, Munoz-Gomariz E, Font P, Mulero J, de Vlam K, Boonen A, Vazquez-Mellado J, Flores D, Vastesaeger N, Collantes E, Worki A-R-R (2010) Hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis: epidemiology and risk factors associated with hip replacement surgery. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kep174
Boonen A, van der Cruyssen B, de Vlam K, Steinfeld S, Ribbens C, Lenaerts J, van den Bosch F, Mielants H, Dewulf L, Vastesaeger N (2009) Spinal radiographic changes in ankylosing spondylitis: association with clinical characteristics and functional outcome. J Rheumatol 36:1249–1255. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.080831
Zhao J, Zheng W, Zhang C, Li J, Liu D, Xu W (2015) Radiographic hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis: factors associated with severe hip diseases. J Rheumatol 42:106–110. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.140428
Vander Cruyssen B, Vastesaeger N, Collantes-Estevez E (2013) Hip disease in ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 25:448–454. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283620e04
Chen HA, Chen CH, Liao HT, Lin YJ, Chen PC, Chen WS, Chou CT (2011) Factors associated with radiographic spinal involvement and hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 40:552–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2010.07.008
Mackay K, Brophy S, Mack C, Doran M, Calin A (2000) The development and validation of a radiographic grading system for the hip in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Hip Index. J Rheumatol 27:2866–2872
Qian BP, Jiang J, Qiu Y, Wang B, Yu Y, Zhu ZZ (2013) Radiographical predictors for postoperative sagittal imbalance in patients with thoracolumbar kyphosis secondary to ankylosing spondylitis after lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:E1669–E1675. https://doi.org/10.1097/brs.0000000000000021
Zhong W, Chen Z, Zeng Y, Sun C, Li W, Qi Q, Guo Z (2019) Two-Level osteotomy for the corrective surgery of severe kyphosis from ankylosing spondylitis: a retrospective series. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 44:1638–1646. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000003095
Gu M, Zhang Z, Kang Y, Sheng P, Yang Z, Zhang Z, Liao W (2015) Roles of sagittal anatomical parameters of the pelvis in primary total hip replacement for patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Arthroplasty 30:2219–2223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2015.06.027
Protopsaltis T, Schwab F, Bronsard N, Smith JS, Klineberg E, Mundis G, Ryan DJ, Hostin R, Hart R, Burton D, Ames C, Shaffrey C, Bess S, Errico T, Lafage V, Int Spine Study G (2014) The T1 pelvic angle, a novel radiographic measure of global sagittal deformity, accounts for both spinal inclination and pelvic tilt and correlates with health-related quality of life. J Bone Joint Surg Am 96A:1631–1640. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.M.01459
Loppini M, Longo UG, Ragucci P, Trenti N, Balzarini L, Grappiolo G (2017) Analysis of the pelvic functional orientation in the sagittal plane: a radiographic study with EOS 2D/3D technology. J Arthroplast 32:1027–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2016.09.015
Kawai T, Shimizu T, Goto K, Kuroda Y, Okuzu Y, Fujibayashi S, Matsuda S (2021) Number of levels of spinal fusion associated with the rate of joint-space narrowing in the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 103:953–960. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.20.01578
Kozaki T, Hashizume H, Nishiyama D, Iwasaki H, Tsutsui S, Takami M, Yukawa Y, Minamide A, Taniguchi T, Nagata K, Fukui D, Tamai H, Taiji R, Murata S, Oka H, Yamada H (2021) Adjacent segment disease on hip joint as a complication of spinal fusion surgery including sacroiliac joint fixation. Eur Spine J 30:1314–1319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-020-06700-4
Roussouly P, Pinheiro-Franco JL (2011) Biomechanical analysis of the spino-pelvic organization and adaptation in pathology. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):609–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-011-1928-x
Hu J, Qian BP, Qiu Y, Wang B, Yu Y, Zhu ZZ, Jiang J, Mao SH, Qu Z, Zhang YP (2017) Can acetabular orientation be restored by lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis patients with thoracolumbar kyphosis? Eur Spine J 26:1826–1832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4709-8
Mekhael M, Kawkabani G, Saliby RM, Skalli W, Saad E, Jaber E, Rachkidi R, Kharrat K, Kreichati G, Ghanem I, Lafage V, Assi A (2021) Toward understanding the underlying mechanisms of pelvic tilt reserve in adult spinal deformity: the role of the 3D hip orientation. Eur Spine J 30:2495–2503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-021-06778-4
Lum ZC, Klineberg EO, Danielsen B, Giordani M, Meehan JP (2019) Female sex and longer fusion constructs significantly increase the risk of total hip arthroplasty following spinal fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am 101:675–681. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.18.00667
Stefl M, Lundergan W, Heckmann N, McKnight B, Ike H, Murgai R, Dorr LD (2017) Spinopelvic mobility and acetabular component position for total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J 99B:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.99b1.Bjj-2016-0415.R1
van Weely SFE, van Denderen JC, Steultjens MPM, van der Leeden M, Nurmohamed MT, Dekker J, Dijkmans BAC, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE (2012) Moving instead of asking? Performance-based tests and BASFI-questionnaire measure different aspects of physical function in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Res Ther. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3765
Li Y, Qian BP, Qiu Y, Zhao SZ, Zhong XL, Wang B (2022) Influence of lumbar sagittal profile on pelvic orientation and pelvic motion during postural changes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis-related thoracolumbar kyphosis following pedicle subtraction osteotomy. J Neurosurg Spine 36:624–631. https://doi.org/10.3171/2021.7.SPINE21114
Bernstein J, Charette R, Sloan M, Lee GC (2019) Spinal fusion is associated with changes in acetabular orientation and reductions in pelvic mobility. Clin Orthop Relat Res 477:324–330. https://doi.org/10.1097/corr.0000000000000390
Salib CG, Reina N, Perry KI, Taunton MJ, Berry DJ, Abdel MP (2019) Lumbar fusion involving the sacrum increases dislocation risk in primary total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J 101-B:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.101B2.BJJ-2018-0754.R1
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (Bang-ping Qian) has received funding from the Jiangsu Provincial Medical Talent (RC2011147). Another author (Yong Qiu) has received 315 funding from the Jiangsu Provincial Key Medical Center (YXZXA2016009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Qian, Bp., Qiu, Y. et al. Risk factors of hip joint structural changes following pedicle subtraction osteotomy for ankylosing spondylitis-related thoracolumbar kyphosis: a minimum two-year observation. Eur Spine J 32, 2293–2302 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-07726-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-023-07726-0