Abstract
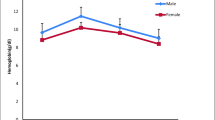
In the present study, some hematological indices were assayed after salinity challenge in smolts obtained from wild populations of Caspian brown trout. The experiment was designed into three treatments and one control group containing 90 fish per treatment. In experimental treatment, fish were exposed to salinity challenge (12 mg/l salinity) for 48 h. Fish of control group were not challenged and held in freshwater with 0.37 g/l salinity. After salinity challenge in seawater, the higher values of plasma cortisol and glucose were found in fish acclimated to seawater compared to control group (P < 0.05). No significant differences were found between control group and fish before salinity challenge in terms of plasma glucose and cortisol levels (P > 0.05). Plasma potassium and sodium concentrations were statistically similar between experimental groups and control group (P > 0.05). Also, plasma protein levels were lower in fish exposed to salinity challenge compared to control (P < 0.05). The values of red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC), and hemoglobin (Hb) increased significantly after salinity challenge (P < 0.05). In addition, there were no significant differences between control group and fish before salinity challenge in terms of plasma RBC, WBC, and Hb (P > 0.05). In conclusion, the results of the present study confirm the ability of the Caspian brown trout smolts in controlling osmoregulation by alternation of some hematological parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cataldi E, Marco PD, Mandich A et al (1998) Serum parameters of Adriatic sturgeon Acipenser naccarii (Pisces: Acipenseriformes). Effects of temperature and stress. Comp Biochem Physiol A 121:351–354
Evans DH (1993) Osmotic and ionic regulation. In: Evans DH (ed) The physiology of fishes. Harwood Academic Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 315–343
Fazio F, Faggio C, Marafioti S et al (2012) Comparative study of haematological profile on Gobius niger in two different habitat sites: Faro Lake and Tyrrhenian Sea. Cah Biol Mar 53:213–219
Fazio F, Marafioti S, Arfuso F et al (2013) Influence of different salinity on haematological and biochemical parameters of the widely cultured mullet, Mugil cephalus. Mar Freshwat Behav Physiol 46(4):211–218
Fazio F, Arfuso F, Levanti M et al (2017) High stocking density and water salinity levels influence haematological and serum protein profiles in mullet Mugil cephalus, Linnaeus, 1758. Cah Biol Mar 58:331–339
Garcia-Navarro CEK (1994) Hematologia dos animais domésticos. In: CEK G-N, Pachaly JR (eds) Manualde Hematologia veterinaria. Primeira ediçao, Sao Paulo, pp 11–119 Varela
Hajirezaee S, Amiri BM, Mirvaghefi AR et al (2010a) Evaluation of semen quality of endangered Caspian brown trout (Salmo trutta caspius) in different times of spermiation during a spawning season. Czech J Anim Sci 55(1 0):445–455
Hajirezaee S, Amiri BM, Mirvaghefi AR (2010b) Changes in sperm production, sperm motility, and composition of seminal fluid in Caspian brown trout, Salmo trutta caspius, over the course of a spawning season. J App Aquacult 22:1 57–1 70
Hoar WS (1988) The physiology of smolting salmonids. Fish Physiol XIB:275–343
Huang X, Zhang L, Zhuang P et al (2006) Hematological parameters of Amur sturgeon, Acipenser schrencki, during different salinity domestication. Mar Fish 28(177):184
Kiabi BH, Abdoli A, Naderi M (1999) Status of fish fauna in the south Caspian basin of Iran. Zool Middle East 18:57–65
Krumschnabel G, Lackner R (1993) Stress responses in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss alevins. Comp Biochem Physiol 104:777–784
Lin H (1999) The physiology of fishes. Guangdong higher education press, Guangzhou
McCormick SD (2001) Endocrine control of osmoregulation in teleost fish. Am Zool 41:781–794
Pickering AD, Pottinger TG (1995) Biochemical effects of stress. In: Hochachka PW and Mommsen TP, Eds. Biochem Molecul Biol Fish 5:349–379
Plaut I (1998) Comparison of salinity tolerance and osmoregulation in two closely related species of blennies from different habitats. Fish Physiol Biochem 19:181–188
Ranzani-Paiva MJT, Salles FA, Eiras JC et al (1999) Analise hematologica de curimbata (Prochilodus scrofa), pacu (Piractus mesopotamicus) e tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) das estaçoes de piscicultura do instituto de pesca. Bol Inst Pesca 25:77–83
Serpunin GG, Likhatchyova OA (1998) Use of the ichthyohaematological studies in ecological monitoring of the reservoirs. Acta Vet Brno 67:339–345
Shahkar E, Kim DJ, Mohseni M et al (2015) Effects of salinity changes on hematological responses in juvenile ship sturgeon Acipenser nudiventris. Fish Aquat Sci 18(1):45–50
Tseng YC, Hwang PP (2008) Some insights into energy metabolism for osmoregulation in fish. Com Biochem Physiol Part C: Toxicol Pharmacol 148(4):419–429
Toorchi M, Bani A, Alizadehsabet H (2012) Effects of salinity on osmoregulation and plasma cortisol levels of juvenile Caspian trout, Salmo trutta caspius Kessler, 1877. J Appl Ichthyol 28(1):130–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experiments were conducted under a protocol for the care and use of animals approved by the committee of ethics of the faculty of sciences of the University of Tehran (357; 8 November 2000).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkheil, M., Sorki, M.P. & Raefipour, H. Effects of acclimation to seawater salinity on some blood parameters in wild Caspian brown trout, Salmo trutta caspius . Comp Clin Pathol 26, 1315–1318 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2531-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2531-2