Abstract
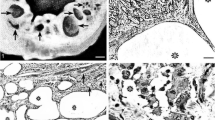
Inflammatory forestomach disorders other than those of viral, bacterial, mycotic, parasitic, chemical, or plant poisoning origin are uncommon in the bovine species. Spontaneous focal emphysematous lesions were grossly identified in the reticulum—the second part of the forestomach—of two adult Holstein-Friesian cattle (one 2-year-old steer, the other 3-year-old dairy cow). Both cattle, which appeared to be clinically normal without evidence of apparent forestomach dysfunction or other significant abnormalities on physical examination, were slaughtered conventionally for human consumption. At postmortem inspection of these two cattle, the reticulum wall showed focal spongy areas due to the occurrence of numerous minute gas bubbles (<1.0 mm in diameter). On histopathology, this emphysematous lesion was characterized by the presence of multicystic emphysematous lymphangiectasis in the submucosa. Affected lymphatics were prominently inflamed, being infiltrated to a significant degree with eosinophils and granulomas consisting of macrophages and multinucleated foreign-body giant cells in the lumen. Submucosal connective tissues surrounding the areas of lesional lymphatics exhibited varying degrees of cellular infiltrates, including eosinophils, mast cells, macrophages, plasma cells, and lymphocytes. Additionally, edema, hemorrhage, fibrin-clot formation, or collagen fiber deposition was observed throughout the lesional submucosa. There was no evidence of bacterial, mycotic, protozoal, or parasitic infection elsewhere in the lesions. Although the precise cause and pathogenesis of this emphysematous reticulitis remain unknown, there was the likelihood that a hypersensitivity reaction might have played a certain role in the development and progression of the lesions. Histopathological features of the reticulum were consistent in many respects with those documented previously in a bovine condition referred to as emphysematous eosinophilic lymphangitis in the ruminal submucosa. From the viewpoint of comparative pathology, this article provides a brief overview of similar or identical conditions involving other organs, which have previously been described in human beings and animals.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antosz Z, Zaniewski M (2004) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis-a report of two cases. Pol J Pathol 55:177–180
Azzaroli F, Turco L, Ceroni L et al (2011) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. World J Gastroenterol 17:4932–4936
Baker IK, van Dreumel AA, Palmer N (1993) The alimentary system. In: Jubb KVF, Kennedy PC, Palmer N (eds) Pathology of domestic animals, 4th edn. Academic, San Diego, pp 1–318
Biester HE, Eveleth DF, Yamashiro Y (1936) Intestinal emphysema in swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc 88:714–731
Bizimenyera ES (2003) Acute poisoning of friesian heifers by Solanum macrocarpon L. ssp dasyphyllum. Vet Hum Toxicol 45:222–223
Cebra ML, Cebra CK, Garry FB et al (1998) Idiopathic eosinophilic enteritis in four cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc 212:258–261
Choi JY, Cho SB, Kim HH et al (2014) Pneumatosis intestinalis complicated by pneumoperitoneum in a patient with asthma. Tuberc Respir 77:219–222
Cianferoni A, Spergel JM (2015) Eosinophilic esophagitis and gastroenteritis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 15:558
Cohrs P (1966) Textbook of the special pathological anatomy of domestic animals. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 416–417
Danese CA, Georgalas-Penesis M, Kark AE et al (1972) Studies of the effects of blockage of intestinal lymphatics. Am J Gastroenterol 57:541–546
Daneshjoo MD, Talley NJ (2002) Eosinophilic gastroenteritis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 4:366–372
D’Arienzo A, Manguso F, Astarita C et al (2000) Allergy and mucosal eosinophil infiltrate in ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 35:624–631
Da Silva EZM, Jamur MC, Oliver C (2014) Mast cell function: a new vision of an old cell. J Histochem Cytochem 62:698–738
Degner DA (1992) Pneumatosis coli in a dog. Can Vet J 33:609–611
Delesalle C, Deprez P, Vanbrantegem L et al (2003) Emphysematous gastritis associated with Clostridium septicum in a horse. J Vet Int Med 17:115–118
Dubucquoi S, Capran M (2000) Structure and function of polynuclear eosinophils. Rev Prat 50:597–601
Egerton JR, Murrell TGC (1965) Intestinal emphysema in pigs in the western highlands of New Guinea. J Comp Pathol 75:35–38
Enerback L, Pipkorn U, Olofsson A (1986) Intraepithelial migration of mucosal mast cells in hay fever: ultrastructural observations. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 81:289–297
Ellis TM, Rowe JB, Lloid JM (1983) Acute abomasitis due to Clostridium septicum infection in experimental sheep. Aust Vet J 60:308–309
Eveleth DF, Biester HE (1938) Further studies on intestinal emphysema of swine. Am J Epidemiol 27:364–369
Fushimi Y, Takagi M, Kawaguchi H et al (2015) Three cases of idiopathic eosinophilic enteritis with chronic obstinate diarrhea in Japanese Black fattening cattle. J Vet Med Sci 77:337–340
Galandiuk S, Fazio VW (1986) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Dis Colon Rectum 29:358–363
Gangwar RS, Levi-Schaffer FL (2014) Eosinophils interaction with mast cells: the allergic effector unit. Methods Mol Biol 1178:231–249
Gaqliardi G, Thompson IW, Hershman MJ et al (1996) Pneumatosis coli: a proposed pathogenesis based on study of 25 cases and review of the literature. Int Colorectal Dis 11:111–118
Garry FB (1996) Indigestion in ruminants. In: Smith EP (ed) Large animal internal medicine, 2nd edn. Mosby, Saint Louis, pp 824–858
Grimm JC, Berger JC, Lipsett PA et al (2015) A case of profound pneumatosis intestinalis in a patient with recent polytrauma. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 78:209–210
Gyrany J, Kopacova M, Hornychova H et al (2005) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Folia Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:68–73
Hanna P, Kassir R, Tarek D et al (2016) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis presenting as bowel perforation, a rare case. Int J Surg Case Rep 20:7–9
Horn RC, Fine G (1977) Alimentary tract. In: Anderson WAD, Kissane JM (eds) Pathology. 7 th ed. Mosby, Saint Louis, pp 1277–1320
Hughes DT, Gordon KC, Swann JC et al (1966) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Gut 7:553–557
Kancherla D, Vattikuti S, Vipperla K (2015) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: is surgery always indicated? Cleve Clin J Med 82:151–152
Kinjo M (2016) Lurking in the wall: pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis with scleroderma. Am J Med 129:382–383
Klimova K, Perez Valderas MD, Merino Rodriquez B et al (2014) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis as an infrequent cause of chronic abdominal pain. Rev Gastroenterol Mex 79:302–303
Kumar S (2012) Hypersensitivity reactions. In: Textbook of microbiology, 1st edn. Jaypee, New Delhi, pp 198–208
Lucak BK, Sansaricq C, Snyderman SE et al (1982) Disseminated ulcerations in allergic eosinophilic gastroenterocolitis. Am J Gastroenterol 77:248–252
Mäkinen PE, Archer DC, Baptiste KE et al (2008) Characterisation of the inflammatory reaction in equine idiopathic focal eosinophilic enteritis and diffuse eosinophilic enteritis. Equine Vet J 40:386–392
Méndez-Sánchez N, Chávez-Tapia NC, Vazquez E et al (2007) Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: a review. Dig Dis Sci 52:2904–2911
Mendoza FJ, Perez-Ecija RA, Estepa JC (2011) Thoracic emphysematous lymphadenitis in a foal. J Comp Pathol 145:77–79
Meyer RC, Simon J (1977) Intestinal emphysema (pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis) in a gnotobiotic pig. Can J Comp Med 41:302–305
Minai-Fleminger Y, Levi-Schaffer F (2009) Mast cells and eosinophils in the two key effector cells in allergic inflammation. Inflamm Res 58:631–638
Ohfuji S (1993) Granulomatous lymphangitis associated with interstitial pulmonary emphysema in adult cows. Vet Pathol 30:378–381
Ohfuji S (1994) Emphysematous-granulomatous lymphadenitis in cows. Vet Pathol 31:708–710
Ohfuji S (2015) Emphysematous eosinophilic lymphangitis in the ruminal submucosa of cattle. Vet Pathol 52:1163–1166
Panchiera RJ, Johnson L, Osburn BI (1966) A disease of cattle grazing hairy vetch pasture. J Am Vet Med Assoc 148:804–808
Pass DA, Bolton JR (1982) Chronic eosinophilic gastroenteritis in the horse. Vet Pathol 19:486–496
Peris B, Garca V, Blas E et al (2005) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis in a rabbit doe (Oryctolagus cuniculus). J Vet Diagn Invest 17:256–258
Read NW, Al-Janabi MN, Cann PA (1984) Is raised breath hydrogen related to the pathogenesis of pneumatosis coli? Gut 25:839–845
Rothenberg ME (2004) Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID). J Allergy Clin Immunol 113:11–28
Shen HH, Ochkur SI, McGarry MP et al (2003) A causative relationship exists between eosinophils and the development of allergic pulmonary pathologies in the mouse. J Immunol 170:3296–3305
Songer JG, Miskimins DW (2005) Clostridial abomasitis in calves: case report and review of the literature. Anaerobe 11:290–294
Suter MM, Palmer DG, Schenk H (1985) Primary intestinal lymphangiectasia in three dogs: a morphological and immunopathological investigation. Vet Pathol 22:123–130
Sweeney RW, Divers TJ, Gillette DM et al (1989) Mycotic omasitis and rumenitis as sequelae to sepsis in dairy cattle: six cases (1979–1986). J Am Vet Med Assoc 194:552–553
Takahashi K, Maita K, Shirasu Y (1984) Two cases of murine intestinal emphysema. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi 46:933–936
Van Kruiningen HJ (1995) Gastrointestinal system. In: Carlton WW, McGavin MD (eds) Thomson’s special veterinary pathology. Mosby, Saint Louis, pp 1–80
Van Mook WN, van der Geest S, Goessens ML et al (2002) Gas within the wall of the stomach due to emphysematous gastritis: case report and review. Eur J Gatroenterol Hepatol 14:1155–1160
Walsh GM, Sexton DW, Blaylock MG (2003) Corticosteroids, eosinophils and bronchial epithelial cells: new insights into the resolution of inflammation in asthma. J Endocrinol 178:37–43
Wardlaw AJ, Brightling C, Green R et al (2000) Eosinophils in asthma and other allergic diseases. Br Med Bull 56:985–1003
Weldon AD, Rowland PH, Rebhun WC (1991) Emphysematous gastritis in a horse. Cornell Vet 81:51–58
Wo LL, Yang YS, Dou Y, Liu QS (2013) A systemic analysis of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. World J Gastroenterol 14:4973–4978
Wyatt AP (1972) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Proc R Soc Med 65:780–782
Yager JA, Scott DW (1993) The skin and appendages. In: Jubb KVF, Kennedy PC, Palmer N (eds) Pathology of domestic animals, 4th edn. Academic, San Diego, pp 531–73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was not funded.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohfuji, S. Pathology of emphysematous reticulitis in cattle: report of two cases and comparative overview of similar or identical conditions. Comp Clin Pathol 25, 805–813 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-016-2267-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-016-2267-4