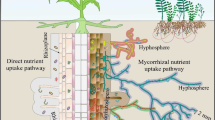
Abstract
A topic of confusion over the interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi and plants is the mycorrhizal status of some plant families such as Cyperaceae, which is generally considered to be non-mycorrhizal. Here, we conducted experiments to explore how the abiotic environmental conditions and AM network influence the interactions between AM fungi and Carex capillacea. We grew Carex capillacea alone or together with a mycorrhizal host species Medicago sativa in the presence or absence of AM fungi (soil inoculum from Mount Segrila and Rhizophagus intraradices from the Chinese Bank of the Glomeromycota, BGC). Plants were grown in a growth chamber and at two elevational sites of Mount Segrila, respectively. The results indicate that mycorrhizal host plants ensured the presence of an active AM fungal network whether under growth chamber or alpine conditions. The AM fungal network significantly depressed the growth of C. capillacea, especially when native inocula were used and the plants grew under alpine site conditions, although root colonization of C. capillacea increased in most cases. Moreover, the colonization level of C. capillacea was much higher (≤ 30%) when growing under alpine conditions compared with growth chamber conditions (< 8.5%). Up to 20% root colonization by Rhizophagus intraradices was observed in monocultures under alpine conditions. A significant negative relationship was found between shoot phosphorus concentrations in M. sativa and shoot dry mass of C. capillacea. These results indicate that growing conditions, AM network, and inoculum source are all important factors affecting the susceptibility of C. capillacea to AM fungi, and growing conditions might be a key driver of the interactions between AM fungi and C. capillacea.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MF, Allen EB (1990) Carbon source of VA mycorrhizal fungi associated with Chenopodiaceae from a semiarid shrub-steppe. Ecology 71:2019–2021. https://doi.org/10.2307/1937610
Allen MF, Allen EB, Friese CF (1989) Responses of the non-mycotrophic plant Salsola kali to invasion by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 111:45–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1989.tb04216.x
Augé RM (2001) Water relations, drought and vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Mycorrhiza 11:3–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720100097
Barrett G, Campbell CD, Hodge A (2014) The direct response of the external mycelium of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to temperature and the implications for nutrient transfer. Soil Biol Biochem 78:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.07.025
Bever JD, Richardson SC, Lawrence BM, Holmes J, Watson M (2009) Preferential allocation to beneficial symbiont with spatial structure maintains mycorrhizal mutualism. Ecol Lett 12:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01254.x
Brundrett MC (2009) Mycorrhizal associations and other means of nutrition of vascular plants: understanding the global diversity of host plants by resolving conflicting information and developing reliable means of diagnosis. Plant Soil 320:37–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9877-9
Brundrett MC, Kendrick WB (1988) The mycorrhizal status, root anatomy, and phenology of plants in a sugar maple forest. Can J Bot 66:1153–1173. https://doi.org/10.1139/b88-166
Bueno CG, Moora M, Gerz M, Davison J, Öpik M, Pärtel M, Helm A, Ronk A, Kühn I, Zobel M (2017) Plant mycorrhizal status, but not type, shifts with latitude and elevation in Europe. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 26:690–699. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12582
Cooke JC, Lefor MW (1998) The mycorrhizal status of selected plant species from Connecticut wetlands and transition zones. Restor Ecol 6:214–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-100X.1998.00628.x
Cosme M, Fernández I, van der Heijden MGA, Pieterse CMJ (2018) Non-mycorrhizal plants: the exceptions that prove the rule. Trends Plant Sci 23:577–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2018.04.004
Eason WR, Newman EI, Chuba PN (1991) Specificity of interplant cycling of phosphorus: the role of mycorrhizas. Plant Soil 137:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011205
Fitter AH, Graves JD, Watkins NK, Robinson D, Scrimgeour C (1998) Carbon transfer between plants and its control in networks of arbuscular mycorrhizas. Funct Ecol 12:406–412. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2435.1998.00206.x
Francis R, Read DJ (1994) The contributions of mycorrhizal fungi to the determination of plant community structure. Plant Soil 159:11–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00000091
Francis R, Read DJ (1995) Mutualism and antagonism in the mycorrhizal symbiosis, with special reference to impacts on plant community structure. Can J Bot 73:S1301–S1309. https://doi.org/10.1139/b95-391
Gai JP, Cai XB, Feng G, Christie R, Li XL (2006) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with sedges on the Tibetan plateau. Mycorrhiza 16:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-005-0031-8
García-Garrido JM, Ocampo JA (2002) Regulation of the plant defence response in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. J Exp Bot 53:1377–1386. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.373.1377
Genre A, Chabaud M, Balzergue C, Puech-Pagès V, Novero M, Rey T, Fournier J, Rochange S, Bécard G, Bonfante P, Barker DG (2013) Short-chain chitin oligomers from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi trigger nuclear Ca2+ spiking in Medicago truncatula roots and their production is enhanced by strigolactone. New Phytol 198:190–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12146
Govaerts R, Simpson DA (2007) World checklist of Cyperaceae. The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew
Grime JP, Mackey JML, Hillier SH, Read DJ (1987) Floristic diversity in a model system using experimental microcosms. Nature 328:420–422. https://doi.org/10.1038/328420a0
Harley JL, Harley EL (1987) A check-list of mycorrhiza in the British flora-addenda, errata and index. New Phytol 107:741–749. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1987.tb00912.x
Hirrel MC, Mehravaran H, Gerdemann JW (1978) Vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae in the Chenopodiaceae and Cruciferae: do they occur? Can J Bot 56:2813–2817. https://doi.org/10.1139/b78-336
Hodge A (1996) Impact of elevated CO2 on mycorrhizal associations and implications for plant growth. Biol Fert Soils 23:388–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00335912
Janos DP (2007) Plant responsiveness to mycorrhizas differs from dependence upon mycorrhizas. Mycorrhiza 17:75–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-006-0094-1
Ji BM, Gehring CA, Wilson GWT, Miller RM, Flores-Renteria L, Johnson NC (2013) Patterns of diversity and adaptation in Glomeromycota from three prairie grasslands. Mol Ecol 22:2573–2587. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.12268
Jiang SJ, Liu YJ, Luo JJ, Qin M, Johnson NC, Öpik M, Vasar M, Chai Y, Zhou X, Mao L, du G, An L, Feng H (2018) Dynamics of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community structure and functioning along a nitrogen enrichment gradient in an alpine meadow ecosystem. New Phytol 220:1222–1235. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15112
Johnson NC (1998) Responses of Salsola kali and Panicum virgatum to mycorrhizal fungi, phosphorus and soil organic matter: implications for reclamation. J Appl Ecol 35:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2664.1998.00277.x
Johnson D, Leake JR, Read DJ (2002) Transfer of recent photosynthate into mycorrhizal mycelium of an upland grassland: short-term respiratory losses and accumulation of 14C. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1521–1524. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00126-8
Johnson D, Booth RE, Whiteley AS, Bailey MJ, Read DJ, Grime JP, Leake JR (2003a) Plant community composition affects the biomass, activity and diversity of microorganisms in limestone grassland soil. Eur J Soil Sci 54:671–677. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1351-0754.2003.0562.x
Johnson D, Vandenkoornhuyse PJ, Leake JR, Gilbert L, Booth RE, Grime JP, Young JPW, Read DJ (2003b) Plant communities affect arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal diversity and community composition in grassland microcosms. New Phytol 161:503–515. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00938.x
Kiers ET, Duhamel M, Beesetty Y, Mensah JA, Franken O, Verbruggen E, Fellbaum CR, Kowalchuk GA, Hart MM, Bago A, Palmer TM, West SA, Vandenkoornhuyse P, Jansa J, Bucking H (2011) Reciprocal rewards stabilize cooperation in the mycorrhizal symbiosis. Science 333:880–882. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1208473
Konoplenko MA, Güsewell S, Veselkin DV (2017) Taxonomic and ecological patterns in root traits of Carex (Cyperaceae). Plant Soil 420:37–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3292-z
Lambers H, Teste FP (2013) Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal plants: do non-mycorrhizal species at both extremes of nutrient availability play the same game? Plant Cell Environ 36:1911–1915. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12117
Lambers H, Shane MW, Cramer MD, Pearse SJ, Veneklaas EJ (2006) Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits. Ann Bot 98:693–713. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcl114
Lekberg Y, Rosendahl S, Olsson PA (2015) The fungal perspective of arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization in ‘nonmycorrhizal’ plants. New Phytol 205:1399–1403. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13118
Li XL, Zhang JL, Gai JP, Cai XB, Christie P, Li XL (2015) Contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi of sedges to soil aggregation along an altitudinal alpine grassland gradient on the Tibetan Plateau. Environ Microbiol 17:2841–2857. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12792
McGonigle TP, Miller MH, Evans DG, Fairchild GL, Swan JA (1990) A new method which gives an objective measure of colonization of roots by vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 115:495–501. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1990.tb00476.x
Menzel A, Hempel S, Manceur AM, Götzenberger L, Moora M, Rillig MC, Zobel M, Kühn I (2016) Distribution patterns of arbuscular mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal plant species in Germany. Perspect Plant Ecol 21:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ppees.2016.06.002
Mikkelsen BL, Rosendahl S, Jakobsen I (2008) Underground resource allocation between individual networks of mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol 180:890–898. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02623.x
Miller RM (2005) The nonmycorrhizal root a strategy for survival in nutrient-improverished soils. New Phytol 165:655–658. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01331.x
Miller RM, Reinhardt DR, Jastrow JD (1995) External hyphal production of vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in pasture and tallgrass prairie communities. Oecologia 103:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00328420
Miller RM, Smith CR, Jastrow JD, Bever JD (1999) Mycorrhizal status of the genus Carex (Cyperaceae). Am J Bot 86:547–553. https://doi.org/10.2307/2656816
Muthukumar T, Udaiyan K (2002) Seasonality of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae in sedges in a semi-arid tropical grassland. Acta Oecol 23:337–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1146-609X(02)01165-7
Muthukumar T, Udaiyan K, Shanmughavel P (2004) Mycorrhiza in sedges - an overview. Mycorrhiza 14:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-004-0296-3
Navazio L, Moscatiello R, Genre A, Novero M, Baldan B, Bonfante P, Mariani P (2007) A diffusible signal from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi elicits a transient cytosolic calcium elevation in host plant cells. Plant Physiol 144:673–681. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.086959
Newman EI, Reddell P (1987) The distribution of mycorrhizas among families of vascular plants. New Phytol 106:745–751. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1987.tb00175.x
Ocampo JA (1986) Vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infection of “host” and “non-host” plants: effect on the growth responses of the plants and competition between them. Soil Biol Biochem 18:607–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(86)90083-0
Ocampo JA, Martin J, Hayman DS (1980) Influence of plant interactions on vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal infections. I. Host and non-host plants grown together. New Phytol 84:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1980.tb00746.x
Phillips JM, Hayman DS (1970) Improved procedure for clearing roots and staining parasitic and vesicular-arbuscular fungi for rapid assessment of infection. Trans Br Mycol Soc 55:158–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1536(70)80110-3
Playsted CWS, Johnston ME, Ramage CM, Edwards DG, Cawthray GR, Lambers H (2006) Functional significance of dauciform roots: exudation of carboxylates and acid phosphatase under phosphorus deficiency in Caustis blakei (Cyperaceae). New Phytol 170:491–500. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01697.x
Powell CL (1975) Rushes and sedges are non-mycotrophic. Plant Soil 42:481–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010023
Powell JR, Rillig MC (2018) Biodiversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and ecosystem function. New Phytol 220:1059–1075. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15119
Raven JA, Lambers H, Smith SE, Westoby M (2018) Costs of acquiring phosphorus by vascular land plants: patterns and implications for plant coexistence. New Phytol 217:1420–1427. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14967
Rinaudo V, Barberi P, Giovannetti M, van der Heijden MGA (2010) Mycorrhizal fungi suppress aggressive agricultural weeds. Plant Soil 333:7–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0202-z
Ruotsalainen AL, Aikio S (2004) Mycorrhizal inoculum and performance of nonmycorrhizal Carex bigelowii and mycorrhizal Trientalis europaea. Can J Bot 82:443–449. https://doi.org/10.1139/b04-011
Sanders IR, Koide RT (1994) Nutrient acquisition and community structure in co-occurring mycotrophic and non-mycotrophic old-field annuals. Funct Ecol 8:77–84. https://doi.org/10.2307/2390114
Shi LJ, Yang R, Zhang JL, Cai XB, Christie P, Li XL, Gai JP (2015) Evidence for functional divergence in AM fungal communities from different montane altitudes. Fungal Ecol 16:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2015.03.009
Smith SE, Read DJ (2008) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic Press, Cambridge
Spalink D, Drew BT, Pace MC, Zaborsky JG, Starr JR, Cameron KM, Givnish TJ, Sytsma KJ (2016) Biogeography of the cosmopolitan sedges (Cyperaceae) and the area-richness correlation in plants. J Biogeogr 43:1893–1904. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12802
Tester M, Smith SE, Smith FA (1987) The phenomenon of “nonmycorrhizal” plants. Can J Bot 65:419–431. https://doi.org/10.1139/b87-051
Thomas RL, Sheard RW, Moyer JR (1967) Comparison of conventional and automated procedures for nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium analysis of plant material using a single digestion. Agron J 59:240–243. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1967.00021962005900030010x
van der Heijden MGA, Klironomos JN, Ursic M, Moutoglis P, Streitwolf-Engel R, Boller T, Wiemken A, Sanders IR (1998) Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability and productivity. Nature 396:69–72. https://doi.org/10.1038/23932
Veiga RSL, Howard K, van der Heijden MGA (2012) No evidence for allelopathic effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the non-host plant Stellaria media. Plant Soil 360:319–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1256-x
Veiga RSL, Faccio A, Genre A, Pieterse CM, Bonfante P, van der Heijden MGA (2013) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi reduce growth and infect roots of the non-host plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 36:1926–1937. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12102
Veselkin DV, Konoplenko MA, Betekhtina AA (2014) The ability to form mycorrhiza in the genus Carex L. (Cyperaceae): the published data analysis. Plant Life Asian Russia 16:26–35
Waterway MJ, Bruhl JJ, Wilson KL et al (2015) Making Carex monophyletic (Cyperaceae, tribe Cariceae): a new broader circumscription. Bot J Linn Soc 179:1–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/boj.12298
Yang R, Cai XB, Li XL, Christie P, Zhang JL, Gai JP (2017) Temperature-mediated local adaptation alters the symbiotic function in arbuscular mycorrhiza. Environ Microbiol 19:2616–2628. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13737
Yang R, Li SM, Qin ZF, Cai X, Li X, Christie P, Zhang J, Feng G, Gai J (2018) Importance of AM fungi and local adaptation in plant response to environmental change: field evidence at contrasting elevations. Fungal Ecol 34:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2018.04.006
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0200200/2017YFD0200203) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Projects 41877049 and 41271269).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Qin, Z., Chu, Y. et al. Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and non-host Carex capillacea. Mycorrhiza 29, 149–157 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-019-00882-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-019-00882-6