Abstract
Background
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is characterized by chronic inflammation in the colon and epigenetic factors underlying the occurrence. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been under intensive focus due to the circular construct and gene-regulating functions. However, the changes and roles of circRNAs in UC remain unknown.
Methods
Microarrays were used to detect the differentially expressed genes, and quantitative real-time PCR was used to identify the changes in UC. In silico analyses were performed to predict the functions of circRNAs and mRNAs. In vitro, epithelial cell lines were stimulated by pro-inflammation effectors to test the alterations in circRNAs. CircRNAs–microRNAs–mRNAs network clarified the potential mechanisms underlying circRNAs in UC. The binding site between hsa_circ_0007919 and miR-138 or let-7a was verified using dual-luciferase assay.
Results
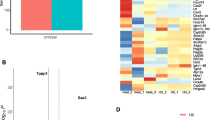
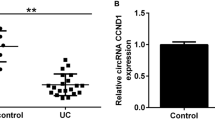
A total of 264 significantly dysregulated circRNAs and 1869 differentially expressed mRNAs in inflamed mucosa were compared with the non-inflamed mucosa in UC. Hsa_circ_0004662 and hsa_circ_0007919 were altered largely in UC tissues. Hsa_circ_0007919 was reduced persistently after inflammatory treatments, and it was relevant to Mayo endoscopic subscores and the expression of tight junction molecules. Finally, hsa_circ_0007919 could harbor miR-138, and let-7a to regulate the targeted mRNAs EPC1 and VIPR1.
Conclusions
Several circRNAs were differentially expressed in UC. Hsa_circ_0007919 is related to clinical characteristics and epithelial integrity by binding to hsa-let-7a, hsa-miR-138 to regulate the target genes. CircRNAs, especially hsa_circ_0007919, are associated with the pathogenesis and development of UC, with potential diagnostic and therapeutic implications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- UC:
-
Ulcerative colitis
- circRNAs:
-
Circular RNAs
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genome
- BP:
-
Biological process
- CC:
-
Cellular component
- MF:
-
Molecular function
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- IL1-β:
-
Interleukin 1β
References
Magro F, Gionchetti P, Eliakim R, et al. Third European evidence-based consensus on diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. Part 1: definitions, diagnosis, extra-intestinal manifestations, pregnancy, cancer surveillance, surgery, and ileo-anal pouch disorders. J Crohn's Colitis. 2017;11:649–70.
Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet. 2017;390:2769–78.
Costello CM, Mah N, Hasler R, et al. Dissection of the inflammatory bowel disease transcriptome using genome-wide cDNA microarrays. PLoS Med. 2005;2:e199.
Ventham NT, Kennedy NA, Nimmo ER, et al. Beyond gene discovery in inflammatory bowel disease: the emerging role of epigenetics. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:293–308.
Mirza AH, Berthelsen CH, Seemann SE, et al. Transcriptomic landscape of lncRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease. Genome Med. 2015;7:39.
He C, Yu T, Shi Y, et al. MicroRNA 301A promotes intestinal inflammation and colitis-associated cancer development by inhibiting BTG1. Gastroenterology. 2017;152:1434–48.e15.
Min M, Peng L, Yang Y, et al. MicroRNA-155 is involved in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis by targeting FOXO3a. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014;20:652–9.
Hsu MTC-PM. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1979;280:339–40.
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 2013;19:141–57.
Salzman JCR, Olsen MN, Wang PL, et al. Cell-type specifc features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(9):e1003777.
Militello G, Weirick T, John D, et al. Screening and validation of lncRNAs and circRNAs as miRNA sponges. Br Bioinform. 2017;18:780–8.
Piwecka M, Glazar P, Hernandez-Miranda LR, et al. Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science. 2017;357(6357):eaam8526. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aam8526.
Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22:256–64.
Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR, et al. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell. 2014;56:55–66.
Han D, Li J, Wang H, et al. Circular RNA circMTO1 acts as the sponge of microRNA-9 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Hepatology. 2017;66:1151–64.
Liu Q, Zhang X, Hu X, et al. Circular RNA related to the chondrocyte ECM regulates MMP13 expression by functioning as a MiR-136 'Sponge' in human cartilage degradation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22572.
Iparraguirre L, Munoz-Culla M, Prada-Luengo I, et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals that circular RNAs from ANXA2 can be used as new biomarkers for multiple sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26:3564–72.
Yuan G, Chen T, Zhang H, et al. Comprehensive analysis of differential circular RNA expression in a mouse model of colitis-induced colon carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2018;57:1825–34.
Zeng K, Chen X, Xu M, et al. CircHIPK3 promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by sponging miR-7. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(4):417.
Wang H, Chao K, Ng SC, et al. Pro-inflammatory miR-223 mediates the cross-talk between the IL23 pathway and the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. Genome Biol. 2016;17:58.
Qiao Y, Cai C, Shen J, et al. Circular RNA expression alterations in colon tissues of Crohn's disease patients. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19:4500–6.
Paramsothy S, Kamm MA, Kaakoush NO, et al. Multidonor intensive faecal microbiota transplantation for active ulcerative colitis: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389:1218–28.
Matsuhisa K, Watari A, Iwamoto K, et al. Lignosulfonic acid attenuates NF-kappaB activation and intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction induced by TNF-alpha/IFN-gamma in Caco-2 cells. J Nat Med. 2018;72:448–55.
Stauffer JS, Manzano LA, Balch GC, et al. Development and characterization of normal colonic epithelial cell lines derived from normal mucosa of patients with colon cancer. Am J Surg. 1995;169:190–6.
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2008;4:44.
Ravasz E, Somera AL, Mongru DA, et al. Hierarchical organization of modularity in metabolic networks. Science. 2002;297:1551.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8.
Pasquinelli AE. MicroRNAs and their targets: recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13:271.
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, et al. MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol. 2004;5:R1.
Barrett SP, Wang PL, Salzman J. Circular RNA biogenesis can proceed through an exon-containing lariat precursor. eLife. 2015;4:e07540.
Wu F, Huang Y, Dong F, et al. Ulcerative colitis-associated long noncoding RNA, BC012900, regulates intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016;22:782–95.
Sitkovsky M, Lukashev D. Regulation of immune cells by local-tissue oxygen tension: HIF1 alpha and adenosine receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:712–21.
Ishihara S, Nishikimi A, Umemoto E, et al. Dual functions of Rap1 are crucial for T-cell homeostasis and prevention of spontaneous colitis. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8982.
Mateescu RB, Bastian AE, Nichita L, Marinescu M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor—key mediator of angiogenesis and promising therapeutical target in ulcerative colitis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2017;58:1339–455.
Dieckgraefe BK, Crimmins DL, Landt V, et al. Expression of the regenerating gene family in inflammatory Bowel disease mucosa: reg Iα upregulation, processing, and antiapoptotic activity. J Investig Med. 2002;50:421–34.
LalNag M, Morin PJ. The claudins. Genome Biol. 2009;10:235.
Amasheh S, Meiri N, Gitter AH, et al. Claudin-2 expression induces cation-selective channels in tight junctions of epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:4969.
Amoozadeh Y, Dan Q, Xiao J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces a biphasic change in claudin-2 expression in tubular epithelial cells: role in barrier functions. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015;309:C38–C50.
Poritz LS, Garver KI, Green C, et al. Loss of the tight junction protein ZO-1 in dextran sulfate sodium induced colitis. J Surg Res. 2007;140:12–9.
Clark PM, Dawany N, Dampier W, et al. Bioinformatics analysis reveals transcriptome and microRNA signatures and drug repositioning targets for IBD and other autoimmune diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18:2315–33.
Shouval DS, Biswas A, Kang YH, et al. Interleukin 1β mediates intestinal inflammation in mice and patients with interleukin 10 receptor deficiency. Gastroenterology. 2016;151:1100–4.
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013;495:333–8.
Zheng Q, Bao C, Guo W, et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11215.
Valmiki S, Ahuja V, Paul J. MicroRNA exhibit altered expression in the inflamed colonic mucosa of ulcerative colitis patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23:5324–32.
Jönsson M, Norrgård Ö, Forsgren S. Epithelial expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide in ulcerative colitis: down-regulation in markedly inflamed colon. Dig Dis Sci. 2012;57:303–10.
Csaba Z, Dournaud P. Cellular biology of somatostatin receptors. Neuropeptides. 2001;35:1–23.
Geng H, Bu HF, Liu F, et al. In inflamed intestinal tissues and epithelial cells, interleukin 22 signaling increases expression of H19 long noncoding RNA which promotes mucosal regeneration. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:144–55.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Peking University People’s Hospital Research and Development Funds Project (Grant No. RDX2018-05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Consent for publication
All authors have read, edited, and approved the manuscript for publication.
Ethical considerations
This study was approved by the Human Ethics Committee of the Peking University People’s Hospital and conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was acquired from all the participants in the study prior to the collection of samples. All the work that involved RNA and DNA in this study was conducted under institutional biosafety committee (IBC)-approved protocols approved at the Peking University People’s Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Chen, N., Ren, W. et al. Integrated analysis of circRNAs and mRNAs expression profile revealed the involvement of hsa_circ_0007919 in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis. J Gastroenterol 54, 804–818 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-019-01585-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-019-01585-7