Absrtact
Background/Objectives
Solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms (SPNs) are rare pancreatic tumors, which occur most frequently in young women and are associated with an excellent prognosis. Computed tomography (CT) is used most commonly to identify these lesions, but there are few studies evaluating the role of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) in the assessment of SPN. The aim of the study was to determine the incremental diagnostic yield of EUS-FNA compared with CT or EUS in the evaluation of patients with SPN.
Methods
A retrospective chart review of consecutive patients diagnosed with SPN who underwent CT, EUS, and EUS-FNA at five centers from three countries from 1998 to 2013. Patient demographics, imaging, endoscopic studies, cytopathology, and histology were reviewed.
Results
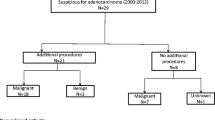
Thirty-four patients were identified with SPN. There were 31 (91.2 %) females, with a mean age at diagnosis of 37 years (range 16-81). The most common presenting symptom was abdominal pain which was present in 59 %. SPNs were incidentally detected in 14 (41.2 %) of the patients. The median tumor size was 4.2 cm (range 1.9–9.4). No patient had evidence of local or distant metastases. The most common appearance on EUS was of a mixed solid-cystic lesion (67.6 %). The diagnostic yield of CT and EUS alone was 23.5 and 41.2 %, respectively. CT and EUS combined had a diagnostic yield of 52.9 %. The addition of EUS-FNA significantly increased the diagnostic yield to 82.4 % compared with either CT or CT and EUS (p < 0.005). There were no reported adverse events reported.
Conclusions
SPNs are rare pancreatic tumors primarily affecting young women. The addition of EUS-FNA significantly increased the pre-operative diagnostic yield of SPN to 82.4 %.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- EUS:
-
Endoscopic ultrasound
- EUS-FNA:
-
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration
- SPN:
-
Solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms
References
Law JK, Ahmed A, Singh VK, Akshintala VS, Olson MT, Raman SP, Ali SZ, Fishman EK, Kamel I, Canto MI, Dal Molin M, Moran RA, Khashab MA, Ahuja N, Goggins M, Hruban RH, Wolfgang CL, Lennon AM (2014) A systematic review of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms: are these rare lesions? Pancreas 43:331–337
Reddy S, Cameron JL, Scudiere J, Hruban RH, Fishman EK, Ahuja N, Pawlik TM, Edil BH, Schulick RD, Wolfgang CL (2009) Surgical management of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas (Franz or Hamoudi tumors): a large single-institutional series. J Am Coll Surg 208:950–957 discussion 957–959
Khashab MA, Kim K, Lennon AM, Shin EJ, Tignor AS, Amateau SK, Singh VK, Wolfgang CL, Hruban RH, Canto MI (2013) Should we do EUS/FNA on patients with pancreatic cysts? The incremental diagnostic yield of EUS over CT/MRI for prediction of cystic neoplasms. Pancreas 42:717–721
Salla C, Chatzipantelis P, Konstantinou P, Karoumpalis I, Pantazopoulou A, Dappola V (2007) Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology diagnosis of solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 13:5158–5163
Cisco R, Jeffrey RB, Norton JA (2010) Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: an unexpected finding after minor abdominal trauma. Dig Dis Sci 55:240–241
Nadler EP, Novikov A, Landzberg BR, Pochapin MB, Centeno B, Fahey TJ, Spigland N (2002) The use of endoscopic ultrasound in the diagnosis of solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas in children. J Pediatr Surg 37:1370–1373
Mergener K, Detweiler SE, Traverso LW (2003) Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: diagnosis by EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration. Endoscopy 35:1083–1084
Song JS, Yoo CW, Kwon Y, Hong EK (2012) Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology diagnosis of solid pseudopapillary neoplasm: three case reports with review of literature. Korean J Pathol 46:399–406
Chatzipantelis P, Salla C, Apostolou G, Christodoulou L, Kakiopoulos G, Patralexis C (2010) Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology diagnosis of solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a report of 3 cases. Acta Cytol 54:701–706
Jani N, Dewitt J, Eloubeidi M, Varadarajulu S, Appalaneni V, Hoffman B, Brugge W, Lee K, Khalid A, McGrath K (2008) Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for diagnosis of solid pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas: a multicenter experience. Endoscopy 40:200–203
Stoita A, Earls P, Williams D (2010) Pancreatic solid pseudopapillary tumours—EUS FNA is the ideal tool for diagnosis. ANZ J Surg 80:615–618
Bardales RH, Centeno B, Mallery JS, Lai R, Pochapin M, Guiter G, Stanley MW (2004) Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology diagnosis of solid-pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a rare neoplasm of elusive origin but characteristic cytomorphologic features. Am J Clin Pathol 121:654–662
Master SS, Savides TJ (2003) Diagnosis of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas by EUS-guided FNA. Gastrointest Endosc 57:965–968
Jhala N, Siegal GP, Jhala D (2008) Large, clear cytoplasmic vacuolation: an under-recognized cytologic clue to distinguish solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas from pancreatic endocrine neoplasms on fine-needle aspiration. Cancer 114:249–254
Kang CM, Kim KS, Choi JS, Kim H, Lee WJ, Kim BR (2006) Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas suggesting malignant potential. Pancreas 32:276–280
Huang HL, Shih SC, Chang WH, Wang TE, Chen MJ, Chan YJ (2005) Solid-pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: clinical experience and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 11:1403–1409
Yu PF, Hu ZH, Wang XB, Guo JM, Cheng XD, Zhang YL, Xu Q (2010) Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: a review of 553 cases in Chinese literature. World J Gastroenterol 16:1209–1214
Triantopoulou C, Touloumis Z, Apessou D, Scotiniotis I, Rodogianni D, Papailiou J, Dervenis C (2008) Solid pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas: an enigmatic tumor. Case Rep Gastroenterol 2:486–493
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Ralph Hruban for reviewing the manuscript. We would like to acknowledge Dr. Siva Raman from the Department of Radiology, and Dr. Matthew Olson from the Department of Pathology at Johns Hopkins Hospital, for the radiology and cytopathology images respectively. This work was supported by the National Cancer Institute Grant P30CA006973. Dr. Joanna Law is the Volker Dolch Fellow in Gastroenterology at Johns Hopkins Hospital.
Disclosures
Mouen A. Khashab is a consultant for Boston Scientific and Olympus America and has received research support from Cook Medical. Vikesh K. Singh is a consultant for Abbvie, Santarus, D-Pharm, and Boston Scientific. Anne Marie Lennon is a consultant for Boston Scientific. Joanna K. Law, Alina Stoita, Wallia Weaver, Ferga C. Gleeson, Andrew M. Dries, Amanda Blackford, Vandhana Kiswani, Eun Ji Shin, Marcia I. Canto have nothing to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MPG 8642 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Law, J.K., Stoita, A., Weaver, W. et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration improves the pre-operative diagnostic yield of solid-pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas: an international multicenter case series (with video). Surg Endosc 28, 2592–2598 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3508-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3508-8