Abstract
Background
The relationship between percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) insertion and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is widely disputed in the current literature. The aim of this systematic review is to examine the available evidence documenting the association between PEG and GERD.
Methods
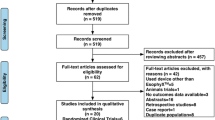
The following databases were searched: MEDLINE (1950 to week 2, January 2011), PubMed, ISI Web of Knowledge (1898 to week 2, January, 2011), EMBASE (1980 to week 2, January 2011) and The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) using the terms “gastroesophageal reflux”, “gastroesophageal disease”, “GERD”, “GERD”, “GER”, “GER” and “percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy”, “PEG”, “gastrostomy”. In addition, the reference lists of all included studies were reviewed for relevant citations. Studies examining children pre and post insertion of PEG for GERD and written in English language were included. Data extraction was performed by two authors, and the methodology and statistical analysis of each study were assessed.
Results
Eight studies were included in this systematic review. Two reported increased incidence of GERD after PEG. However, neither was of high methodological quality. The remaining six reported no change or decreased GERD. Nonetheless, few demonstrated rigorous methodology.
Conclusions
The current evidence examining the effect of PEG insertion on GERD has been inconsistent and is not of high quality and therefore is unconvincing, preventing a definitive conclusion. Overall, the available literature on this topic does not demonstrate a causal effect of PEG insertion on GERD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gauderer MWL, Ponksy JL, Izzat RJ (1980) Gastrostomy without laparotomy: a percutaneous endoscopic technique. J Pediatr Surg 15:872–875
El-Matary W (2008) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children. Can J Gastroenterol 22:993–998
Heine RG, Reddihough DS, Catto-Smith AG (1995) Gastro-oesophageal reflux and feeding problems after gastrostomy in children with severe neurological impairment. Dev Med Child Neurol 34:320–329
Razeghi S, Lang T, Behrens R (2002) Influence of Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy on gastroesophageal reflux: a prospective study in 68 children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 35:27–30
Sherman PH, Hassall E, Fagundes-Neto U, Gold BD, Kato S, Koletzko S, Orenstein S, Rudolph C, Vakil N, Vandenplas Y (2009) A global, evidence-based consensus on the definition of gastroesophageal reflux disease in the pediatric population. Am J Gastroenterol 104:1278–1295
Salvatore S, Hauser B, Vandemaele K, Novario R, Vandenplas Y (2005) Gastroesophageal reflux disease in infants: how much is predictable with questionnaires, pH-metry, endoscopy and histology? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 40:210–215
Skopnik H, Silny J, Heiber O, Schulz J, Rau G, Heimann G (1996) Gastroesophageal reflux in infants: evaluation of a new intraluminal impedance technique. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 23:591–598
Vandenplas Y, Rudolph CD, Di Lorenzo C, Andenplas Y, Rudolph CDD, Lorenzo C, Hassall E, Liptak G, Mazur L, Sondheimer J, Staiano A, Thomson M, Veereman-Wauters G, Wenzl TG (2009) Pediatric gastroesophageal reflux clinical practice guidelines: joint recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (NASPGHAN) and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 49:498–547
Launay V, Gottrand F, Turck D, Michaud L, Ategbo S, Farriaux JP (1996) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children: influence on gastroesophageal reflux. Pediatrics 97:726–728
Hament JM, Bax NMA, van der Zee DC, De Schryver JE, Nesselaar C (2001) Complications of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy with or without concomitant antireflux surgery in 96 children. J Pediatr Surg 36:1412–1415
Davidson PM, Catto-Smith AG, Beasley SW (1995) Technique and complications of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children. Aust N Z J Surg 65:194–196
Khattak IU, Kimber C, Kiely EM, Spitz L (1998) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in paediatric practice: complications and outcome. J Pediatr Surg 33:67–72
Wheatley MJ, Wesley JR, Tkach DM, Coran AG (1991) Long-term follow-up of brain-damaged children requiring feeding gastrostomy: should an antireflux procedure always be performed? J Pediatr Surg 26:301–304
van der Merwe WG, Brown RA, Ireland JD (2003) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children—a 5-year experience. S Afr Med J 93:781–785
Gebora-Kowalska B, Wasowska-Krolikowska K, Toporowska-Kowalska E (2010) The influence of PEG on GER exponents by means of MII/Ph monitoring in neurologically impaired children preliminary study results. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 50:E133–E143
Bosman DK, Hulsbergen MH, Aronson DC (1999) The effects of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: a prospective study in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 28:549
van der Zee DC, Bax NMA, Ure BM (2000) Laparoscopic secondary antireflux procedure after PEG placement in children. Surg Endosc 14:1105–1106
Langer JC, Wesson DE, Ein SH, Filler RM, Shandling B, Superina RA, Papa M (1988) Feeding gastrostomy in neurologically impaired children: is an antireflux procedure necessary? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 6:837–841
Borowitz SM, Sutphen JL, Hutcheson RL (1997) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy without an antireflux procedure in neurologically disabled children. Clin Pediatr 3:25–29
Jolley SG, Smith EI, Tunell WP (1985) Protective antireflux operation with feeding gastrostomy. Experience with children. Ann Surg 201:736–740
Sathesh-Kumar T, Rollins H, Cheslyn-Curtis S (2009) General paediatric surgical provision of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in a district general hospital—a 12-year experience. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 91:404–409
Oliver MR, Heine RG, Ng CH, Volders E, Olinsky A (2004) Factors affecting clinical outcome in gastrostomy-fed children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 37:324–329
Gottrand F, Michaud L (2002) Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy and gastro-esophageal reflux: are we correctly addressing the question? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 35:22–24
Kimber C, Beasley S (1999) Limitations of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in facilitating enteral nutrition in children: review of the shortcomings of a new technique. J Paediatr Child Health 35:427–431
Sulaeman E, Udall JN, Brown RF, Mannick EE, Loe WA, Hill CB, Schmidt-Sommerfeld E (1998) Gastroesophageal reflux and Nissen fundoplication following percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 26:269–273
Davis J, Skaff P (1993) Gastroesophageal reflux secondary to percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube placement in a pediatric population. Clin Res 41:A112–A122
Seekri IK, Rescorla FJ, Canal DF, Zollinger TW, Saywell R Jr, Grosfeld JL (1991) Lesser curvature gastrostomy reduces the incidence of postoperative gastroesophageal reflux. J Pediatr Surg 26:982–985
Wesley JR, Coran AG, Sarahan TM, Klein MD, White SJ (1981) The need for evaluation of gastro-esophageal reflux in brain-damaged children referred for feeding gastrostomy. J Pediatr Surg 16:866–871
Peters RT, Balduyck B, Nour S (2010) Gastrostomy complications in infants and children: a comparative study. Pediatr Surg Int 26:707–709
Vernon-Roberts A, Sullivan PB (2007) Fundoplication versus post-operative medication for gastro-oesophageal reflux in children with neurological impairment undergoing gastrostomy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD006151
Cheung KM, Tse HW, Tse PW (2006) Nissen fundoplication and gastrostomy in severely neurologically impaired children with gastroesophageal reflux. Hong Kong Med J 12:282–288
Plantin I, Arnbjornsson E, Larsson LT (2006) No increase in gastroesophageal reflux after laparoscopic gastrostomy in children. Pediatr Surg Int 22:581–584
Kutiyanawala MA, Hussain A, Johnstone JM, Everson NW, Nour S (1998) Gastrostomy complications in infants and children. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 80:240–243
Berezin S, Schwarz SM, Halata MS, Newman LJ (1986) Gastroesophageal reflux secondary to gastrostomy tube placement. Am J Dis Child 140:699–701
Mollitt DL, Golladay ES, Seibert JJ (1985) Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux following gastrostomy in neurologically impaired patients. Pediatrics 75:1124–1126
Grunow JE, Al-Hafidh A, Tunell PT (1989) Gastroesophageal reflux following percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. J Pediatr Surg 24:42–45
Samuel M, Holmes K (2002) Quantitative and qualitative analysis of gastroesophageal reflux after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. J Pediatr Surg 2:256–261
Isch JA, Rescorla FJ, Tres Scherer LR III, West KW, Grosfeld JL (1997) The development of gastroesophageal reflux after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. J Pediatr Surg 32(2):321–323
Puntis JWL (2000) Children with neurological disorders do not always need fundoplication concomitant with percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Dev Med Child Neurol 42:97–99
Wilson GJP, van der Zee DC, Bax NMA (2006) Endoscopic gastrostomy placement in the child with gastroesophageal reflux: is concomitant antireflux surgery indicated? J Pediatr Surg 41:1441–1445
Halpern LM, Jolley SG, Johnson DG (1985) Gastroesophageal reflux: a significant association with central nervous disease. J pediatr surg 26:171–173
Malfroot DL, Golladay ES, Seibert JJ (1991) New insights on gastro-oesophageal reflux in cystic fibrosis by longitudinal follow-up. Arch Dis Child 66:1339–1345
Disclosure
Authors Louise Noble, A Mark Dalzell and Wael El-Matary have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noble, L.J., Dalzell, A.M. & El-Matary, W. The relationship between percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in children: a systematic review. Surg Endosc 26, 2504–2512 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2221-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-012-2221-8