Abstract
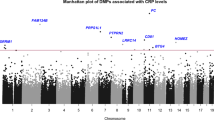
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a heritable biomarker of systemic inflammation and a predictor of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Large-scale genetic association studies for CRP have largely focused on individuals of European descent. We sought to uncover novel genetic variants for CRP in a multiethnic sample using the ITMAT Broad-CARe (IBC) array, a custom 50,000 SNP gene-centric array having dense coverage of over 2,000 candidate CVD genes. We performed analyses on 7,570 African Americans (AA) from the Candidate gene Association Resource (CARe) study and race-combined meta-analyses that included 29,939 additional individuals of European descent from CARe, the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) and KORA studies. We observed array-wide significance (p < 2.2 × 10−6) for four loci in AA, three of which have been reported previously in individuals of European descent (IL6R, p = 2.0 × 10−6; CRP, p = 4.2 × 10−71; APOE, p = 1.6 × 10−6). The fourth significant locus, CD36 (p = 1.6 × 10−6), was observed at a functional variant (rs3211938) that is extremely rare in individuals of European descent. We replicated the CD36 finding (p = 1.8 × 10−5) in an independent sample of 8,041 AA women from WHI; a meta-analysis combining the CARe and WHI AA results at rs3211938 reached genome-wide significance (p = 1.5 × 10−10). In the race-combined meta-analyses, 13 loci reached significance, including ten (CRP, TOMM40/APOE/APOC1, HNF1A, LEPR, GCKR, IL6R, IL1RN, NLRP3, HNF4A and BAZ1B/BCL7B) previously associated with CRP, and one (ARNTL) previously reported to be nominally associated with CRP. Two novel loci were also detected (RPS6KB1, p = 2.0 × 10−6; CD36, p = 1.4 × 10−6). These results highlight both shared and unique genetic risk factors for CRP in AA compared to populations of European descent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitman TJ, Cooper LD, Norsworthy PJ, Wahid FN, Gray JK et al (2000) Malaria susceptibility and CD36 mutation. Nature 405:1015–1016
Anderson CA, Zhu G, Falchi M, van den Berg SM, Treloar SA et al (2008) A genome-wide linkage scan for age at menarche in three populations of European descent. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:3965–3970
Auer PL, Srivastava S, Doerge RW (2012a) Differential expression––the next generation and beyond. Brief Funct Genomics 11:57–62
Auer PL, Johnsen JM, Johnson AD, Logsdon BA, Lange LA et al (2012b) Imputation of exome sequence variants into population-based samples and blood-cell-trait-associated loci in African Americans: NHLBI GO exome sequencing project. Am J Hum Genet 91:794–808
Buijs RM, Scheer FA, Kreier F, Yi C, Bos N et al (2006) Organization of circadian functions: interaction with the body. Prog Brain Res 153:341–360
Bunger MK, Wilsbacher LD, Moran SM, Clendenin C, Radcliffe LA et al (2000) Mop3 is an essential component of the master circadian pacemaker in mammals. Cell 103:1009–1017
Chen MH, Yang Q (2010) GWAF: an R package for genome-wide association analyses with family data. Bioinformatics 26:580–581
Coburn CT, Knapp FF Jr, Febbraio M, Beets AL, Silverstein RL et al (2000) Defective uptake and utilization of long chain fatty acids in muscle and adipose tissues of CD36 knockout mice. J Biol Chem 275:32523–32529
Coon H, Leppert MF, Eckfeldt JH, Oberman A, Myers RH et al (2001) Genome-wide linkage analysis of lipids in the hypertension genetic epidemiology network (HyperGEN) Blood Pressure Study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:1969–1976
Curtis AM, Cheng Y, Kapoor S, Reilly D, Price TS et al (2007) Circadian variation of blood pressure and the vascular response to asynchronous stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3450–3455
Dehghan A, Dupuis J, Barbalic M, Bis JC, Eiriksdottir G et al (2011) Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies in >80,000 subjects identifies multiple loci for C-reactive protein levels. Circulation 123:731–738
Doumatey AP, Chen G, Tekola AF, Zhou J, Erdos M et al (2012) C-reactive protein (CRP) promoter polymorphisms influence circulating CRP levels in a genome-wide association study of African Americans. Hum Mol Genet 21:3063–3072
Fry AE, Ghansa A, Small KS, Palma A, Auburn S et al (2009) Positive selection of a CD36 nonsense variant in sub-Saharan Africa, but no association with severe malaria phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet 18:2683–2692
Ghosh A, Murugesan G, Chen K, Zhang L, Wang Q et al (2011) Platelet CD36 surface expression levels affect functional responses to oxidized LDL and are associated with inheritance of specific genetic polymorphisms. Blood 117:6355–6366
Goyal T, Mitra S, Khaidakov M, Wang X, Singla S et al (2012) Current concepts of the role of oxidized LDL receptors in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep 14:150–159
Guo Y, Shen H, Xiao P, Xiong DH, Yang TL et al (2006) Genomewide linkage scan for quantitative trait loci underlying variation in age at menarche. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:1009–1014
Handberg A, Levin K, Hojlund K, Beck-Nielsen H (2006) Identification of the oxidized low-density lipoprotein scavenger receptor CD36 in plasma: a novel marker of insulin resistance. Circulation 114:1169–1176
Harris TB, Ferrucci L, Tracy RP, Corti MC, Wacholder S et al (1999) Associations of elevated interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein levels with mortality in the elderly. Am J Med 106:506–512
Honma S, Ikeda M, Abe H, Tanahashi Y, Namihira M et al (1998) Circadian oscillation of BMAL1, a partner of a mammalian clock gene clock, in rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 250:83–87
Howie BN, Donnelly P, Marchini J (2009) A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet 5:e1000529
Ji SR, Wu Y, Potempa LA, Qiu Q, Zhao J (2006) Interactions of C-reactive protein with low-density lipoproteins: implications for an active role of modified C-reactive protein in atherosclerosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38:648–661
Jones CI, Bray S, Garner SF, Stephens J, de Bono B et al (2009) A functional genomics approach reveals novel quantitative trait loci associated with platelet signaling pathways. Blood 114:1405–1416
Karlsson B, Knutsson A, Lindahl B (2001) Is there an association between shift work and having a metabolic syndrome? Results from a population based study of 27,485 people. Occup Environ Med 58:747–752
Keating BJ, Tischfield S, Murray SS, Bhangale T, Price TS et al (2008) Concept, design and implementation of a cardiovascular gene-centric 50 k SNP array for large-scale genomic association studies. PLoS One 3:e3583
Knutsson A, Akerstedt T, Jonsson BG, Orth-Gomer K (1986) Increased risk of ischaemic heart disease in shift workers. Lancet 2:89–92
Koenig W, Sund M, Frohlich M, Fischer HG, Lowel H et al (1999) C-reactive protein, a sensitive marker of inflammation, predicts future risk of coronary heart disease in initially healthy middle-aged men: results from the MONICA (monitoring trends and determinants in cardiovascular disease) Augsburg Cohort Study, 1984 to 1992. Circulation 99:237–242
Larkin EK, Rosen CL, Kirchner HL, Storfer-Isser A, Emancipator JL et al (2005) Variation of C-reactive protein levels in adolescents: association with sleep-disordered breathing and sleep duration. Circulation 111:1978–1984
Li Y, Willer CJ, Ding J, Scheet P, Abecasis GR (2010) MaCH: using sequence and genotype data to estimate haplotypes and unobserved genotypes. Genet Epidemiol 34:816–834
Lo KS, Wilson JG, Lange LA, Folsom AR, Galarneau G et al (2011) Genetic association analysis highlights new loci that modulate hematological trait variation in Caucasians and African Americans. Hum Genet 129:307–317
Love-Gregory L, Sherva R, Sun L, Wasson J, Schappe T et al (2008) Variants in the CD36 gene associate with the metabolic syndrome and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Hum Mol Genet 17:1695–1704
Love-Gregory L, Sherva R, Schappe T, Qi JS, McCrea J et al (2011) Common CD36 SNPs reduce protein expression and may contribute to a protective atherogenic profile. Hum Mol Genet 20:193–201
Lowel H, Doring A, Schneider A, Heier M, Thorand B et al (2005) The MONICA Augsburg surveys-basis for prospective cohort studies. Gesundheitswesen 67(Suppl 1):S13–S18
Maemura K, Layne MD, Watanabe M, Perrell MA, Nagai R et al (2001) Molecular mechanisms of morning onset of myocardial infarction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 947:398–402
Manning-Tobin JJ, Moore KJ, Seimon TA, Bell SA, Sharuk M et al (2009) Loss of SR-A and CD36 activity reduces atherosclerotic lesion complexity without abrogating foam cell formation in hyperlipidemic mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:19–26
Mendall MA, Patel P, Ballam L, Strachan D, Northfield TC (1996) C reactive protein and its relation to cardiovascular risk factors: a population based cross sectional study. BMJ 312:1061–1065
Miyaoka K, Kuwasako T, Hirano K, Nozaki S, Yamashita S et al (2001) CD36 deficiency associated with insulin resistance. Lancet 357:686–687
Musunuru K, Romaine SP, Lettre G, Wilson JG, Volcik KA et al (2012) Multi-ethnic analysis of lipid-associated loci: the NHLBI CARe project. PLoS One 7:e36473
Naito Y, Tsujino T, Kawasaki D, Okumura T, Morimoto S et al (2003) Circadian gene expression of clock genes and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in heart and aorta of spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar-Kyoto rats. J Hypertens 21:1107–1115
Nappo A, Iacoviello L, Fraterman A, Gonzalez-Gil EM, Hadjigeorgiou C, Marild S, Molnar D, Moreno LA, Peplies J, Sioen I, Veidebaum T, Siani A, Russo P (2013) High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is a predictive factor of adiposity in children: results of the identification and prevention of dietary- and lifestyle-induced health effects in children and infants (IDEFICS) study. J Am Heart Assoc 2(3):e000101
Omi K, Ohashi J, Patarapotikul J, Hananantachai H, Naka I et al (2003) CD36 polymorphism is associated with protection from cerebral malaria. Am J Hum Genet 72:364–374
Pankow JS, Folsom AR, Cushman M, Borecki IB, Hopkins PN et al (2001) Familial and genetic determinants of systemic markers of inflammation: the NHLBI family heart study. Atherosclerosis 154:681–689
Portman MA (2001) Molecular clock mechanisms and circadian rhythms intrinsic to the heart. Circ Res 89:1084–1086
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA et al (2006) Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 38:904–909
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA et al (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Qayyum R, Snively BM, Ziv E, Nalls MA, Liu Y et al (2012) A meta-analysis and genome-wide association study of platelet count and mean platelet volume in African Americans. PLoS Genet 8:e1002491
Reiner AP, Barber MJ, Guan Y, Ridker PM, Lange LA et al (2008) Polymorphisms of the HNF1A gene encoding hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha are associated with C-reactive protein. Am J Hum Genet 82:1193–1201
Reiner AP, Beleza S, Franceschini N, Auer PL, Robinson JG et al (2012) Genome-wide association and population genetic analysis of C-reactive protein in African American and Hispanic American women. Am J Hum Genet 91:502–512
Ridker PM (2010) Inflammation, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and vascular protection. Tex Heart Inst J 37:40–41
Robbie L, Libby P (2001) Inflammation and atherothrombosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 947:167–179
Rothenbuhler A, Fradin D, Heath S, Lefevre H, Bouvattier C et al (2006) Weight-adjusted genome scan analysis for mapping quantitative trait loci for menarchal age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:3534–3537
Rudic RD, McNamara P, Curtis AM, Boston RC, Panda S et al (2004) BMAL1 and CLOCK, two essential components of the circadian clock, are involved in glucose homeostasis. PLoS Biol 2:e377
Sabeti PC, Schaffner SF, Fry B, Lohmueller J, Varilly P et al (2006) Positive natural selection in the human lineage. Science 312:1614–1620
Scheer FA, Hilton MF, Mantzoros CS, Shea SA (2009) Adverse metabolic and cardiovascular consequences of circadian misalignment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:4453–4458
Schnabel RB, Lunetta KL, Larson MG, Dupuis J, Lipinska I et al (2009) The relation of genetic and environmental factors to systemic inflammatory biomarker concentrations. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2:229–237
Shimba S, Ishii N, Ohta Y, Ohno T, Watabe Y et al (2005) Brain and muscle Arnt-like protein-1 (BMAL1), a component of the molecular clock, regulates adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:12071–12076
Silverstein RL (2009) Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and arterial thrombosis: role of the scavenger receptor CD36. Cleve Clin J Med 76(Suppl 2):S27–S30
Slade GD, Offenbacher S, Beck JD, Heiss G, Pankow JS (2000) Acute-phase inflammatory response to periodontal disease in the US population. J Dent Res 79:49–57
Sun Y, Scavini M, Orlando RA, Murata GH, Servilla KS et al (2010) Increased CD36 expression signals monocyte activation among patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 33:2065–2067
Tanaka T, Nakata T, Oka T, Ogawa T, Okamoto F et al (2001) Defect in human myocardial long-chain fatty acid uptake is caused by FAT/CD36 mutations. J Lipid Res 42:751–759
The Women’s Health Initiative Study Group (1998) Design of the Women’s Health Initiative clinical trial and observational study. Control Clin Trials 19:61–109
Tracy RP, Psaty BM, Macy E, Bovill EG, Cushman M et al (1997) Lifetime smoking exposure affects the association of C-reactive protein with cardiovascular disease risk factors and subclinical disease in healthy elderly subjects. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17:2167–2176
van Leeuwen WM, Lehto M, Karisola P, Lindholm H, Luukkonen R et al (2009) Sleep restriction increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases by augmenting proinflammatory responses through IL-17 and CRP. PLoS One 4:e4589
Willer CJ, Li Y, Abecasis GR (2010) METAL: fast and efficient meta-analysis of genome wide association scans. Bioinformatics 26:2190–2191
Acknowledgments
CARe is supported by contract number HHSN268200625226C from the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI). Sources of funding for individual CARe cohorts: Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC): NHLBI (N01 HC-55015, N01 HC-55016, N01HC-55017, N01 HC-55018, N01 HC-55019, N01 HC-55020, N01 HC-55021); Cardiovascular Health Study (CHS): NHLBI (N01-HC-85239, N01-HC-85079 through N01-HC-85086, N01-HC-35129, N01 HC-15103, N01 HC-55222, N01-HC-75150, N01-HC-45133, grant HL080295 and contract HHSN268201200036C), with additional support from NINDS and from NIA (AG-023629, AG-15928, AG-20098, and AG-027058); Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA): NHLBI (N01-HC95095 & N01-HC48047, N01-HC48048, N01-HC48049, and N01-HC48050); Framingham Heart Study (FHS): NHLBI (N01-HC-25195 and grant R01 NS17950) with additional support from NIA (AG08122 and AG033193); Jackson Heart Study (JHS): NHLBI and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities (N01 HC-95170, N01 HC-95171 and N01 HC-95172); MultiEthnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA): N01 HC-95159, N01-HC-95160, N01-HC-95161, N01-HC-95162, N01-HC-95163, N01-HC-95164, N01-HC-95165, N01-HC-95166, N01-HC-95167, N01-HC-95168, N01-HC-95169 and RR-024156. Funding for CARe genotyping was provided by NHLBI Contract N01-HC-65226. Additional financial support was provided by NHLBI grant R01 HL071862. The MONICA/KORA Augsburg studies were financed by the Helmholtz Zentrum München, German Research Center for Environmental Health, Neuherberg, Germany and supported by grants from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Part of this work was financed by the German National Genome Research Network (project number 01GS0834), by the German Research Foundation (TH-784/2-1 and TH-784/2-2), by the European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes and through additional funds from the Helmholtz Zentrum München, the German Diabetes Center and the University of Ulm. Furthermore, the research was supported within the Munich Center of Health Sciences as part of the Ludwig Maximilians University innovative. The authors wish to thank the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Exome Sequencing Project for providing a reference panel for CD36 rs3211938 imputation. Funding for GO ESP was provided by NHLBI grants RC2 HL-103010 (HeartGO), RC2 HL-102923 (LungGO) and RC2 HL-102924 (WHISP). The exome sequencing was performed through NHLBI grants RC2 HL-102925 (BroadGO) and RC2 HL-102926 (SeattleGO).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellis, J., Lange, E.M., Li, J. et al. Large multiethnic Candidate Gene Study for C-reactive protein levels: identification of a novel association at CD36 in African Americans. Hum Genet 133, 985–995 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-014-1439-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-014-1439-z