Abstract
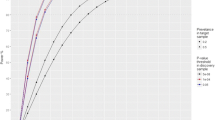
Migraine and major depressive disorder (MDD) are comorbid, moderately heritable and to some extent influenced by the same genes. In a previous paper, we suggested the possibility of causality (one trait causing the other) underlying this comorbidity. We present a new application of polygenic (genetic risk) score analysis to investigate the mechanisms underlying the genetic overlap of migraine and MDD. Genetic risk scores were constructed based on data from two discovery samples in which genome-wide association analyses (GWA) were performed for migraine and MDD, respectively. The Australian Twin Migraine GWA study (N = 6,350) included 2,825 migraine cases and 3,525 controls, 805 of whom met the diagnostic criteria for MDD. The RADIANT GWA study (N = 3,230) included 1,636 MDD cases and 1,594 controls. Genetic risk scores for migraine and for MDD were used to predict pure and comorbid forms of migraine and MDD in an independent Dutch target sample (NTR–NESDA, N = 2,966), which included 1,476 MDD cases and 1,058 migraine cases (723 of these individuals had both disorders concurrently). The observed patterns of prediction suggest that the ‘pure’ forms of migraine and MDD are genetically distinct disorders. The subgroup of individuals with comorbid MDD and migraine were genetically most similar to MDD patients. These results indicate that in at least a subset of migraine patients with MDD, migraine may be a symptom or consequence of MDD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonaci F, Nappi G, Galli F, Manzoni GC, Calabresi P, Costa A (2011) Migraine and psychiatric comorbidity: a review of clinical findings. J Headache Pain 12:115–125
Boomsma DI, de Geus EJ, Vink JM, Stubbe JH, Distel MA, Hottenga JJ, Posthuma D, van Beijsterveldt TC, Hudziak JJ, Bartels M, Willemsen G (2006) Netherlands twin register: from twins to twin families. Twin Res Hum Genet 9:849–857
Boomsma DI, Willemsen G, Sullivan PF, Heutink P, Meijer P, Sondervan D, Kluft C, Smit G, Nolen WA, Zitman FG, Smit JH, Hoogendijk WJ, van Dyck R, de Geus EJ, Penninx BW (2008) Genome-wide association of major depression: description of samples for the GAIN major depressive disorder study: NTR and NESDA biobank projects. Eur J Hum Genet 16:335–342
Breslau N, Davis GC, Andreski P (1991) Migraine, psychiatric disorders, and suicide attempts: an epidemiologic study of young adults. Psychiatry Res 37:11–23
Breslau N, Schultz LR, Stewart WF, Lipton RB, Lucia VC, Welch KM (2000) Headache and major depression: is the association specific to migraine? Neurology 54:308–313
Breslau N, Schultz LR, Welch KMA, Lipton RB, Stewart WF (2003) Comorbidity of migraine and depression: investigating potential etiology and prognosis. Neurology 60:1308–1312
Cohen-Woods S, Gaysina D, Craddock N, Farmer A, Gray J, Gunasinghe C, Hoda F, Jones L, Knight J, Korszun A (2009) Depression case control (DeCC) study fails to support involvement of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 (CHRM2) gene in recurrent major depressive disorder. Hum Mol Genet 18:1504–1509
Davies G, Tenesa A, Payton A, Yang J, Harris SE, Liewald D, Ke X, Le Hellard S, Christoforou A, Luciano M, McGhee K, Lopez L, Gow AJ, Corley J, Redmond P, Fox HC, Haggarty P, Whalley LJ, McNeill G, Goddard ME, Espeseth T, Lundervold AJ, Reinvang I, Pickles A, Steen VM, Ollier W, Porteous DJ, Horan M, Starr JM, Pendleton N, Visscher PM, Deary IJ (2011) Genome-wide association studies establish that human intelligence is highly heritable and polygenic. Mol Psychiatry 16:996–1005
De Moor MH, Boomsma DI, Stubbe JH, Willemsen G, de Geus EJ (2008) Testing causality in the association between regular exercise and symptoms of anxiety and depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65:897–905
Demirkan A, Penninx BWJH, Hek K, Wray NR, Amin N, Aulchenko YS, Van Dyck R, de Geus EJC, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG (2010) Genetic risk profiles for depression and anxiety in adult and elderly cohorts. Mol psychiatry 16:773–783
Dudbridge F (2013) Power and predictive accuracy of polygenic risk scores. PLoS Genet 9:e1003348
Farmer A, Breen G, Brewster S, Craddock N, Gill M, Korszun A, Maier W, Middleton L, Mors O, Owen M (2004) The depression network (DeNT) study: methodology and sociodemographic characteristics of the first 470 affected sibling pairs from a large multi-site linkage genetic study. BMC Psychiatry 4:42
Hazel LN (1943) The genetic basis for constructing selection indexes. Genetics 28:476
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (2004) The international classification of headache disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 24(suppl 1):9–160
Kundu S, Aulchenko YS, van Duijn CM, Janssens ACJ (2011) PredictABEL: an R package for the assessment of risk prediction models. Eur J Epidemiol 26:261–264
Lépine JP, Briley M (2004) The epidemiology of pain in depression. Hum Psychopharmacol 19(suppl 1):S3–S7
Levinson DF (2006) The genetics of depression: a review. Biol Psychiatry 60:84–92
Lewis CM, Ng MY, Butler AW, Cohen-Woods S, Uher R, Pirlo K, Weale ME, Schosser A, Paredes UM, Rivera M (2010) Genome-wide association study of major recurrent depression in the UK population. Am J Psychiatry 167:949–957
Ligthart L, Boomsma DI (2012) Causes of comorbidity: pleiotropy or causality? Shared genetic and environmental influences on migraine and neuroticism. Twin Res Hum Genet 15:158–165
Ligthart L, Boomsma DI, Martin NG, Stubbe JH, Nyholt DR (2006) Migraine with aura and migraine without aura are not distinct entities: further evidence from a large Dutch population study. Twin Res Hum Genet 9:54–63
Ligthart L, Nyholt DR, Penninx BW, Boomsma DI (2010a) The shared genetics of migraine and anxious depression. Headache 50:1549–1560
Ligthart L, Penninx BW, Nyholt DR, Distel MA, de Geus EJ, Willemsen G, Smit JH, Boomsma DI (2010b) Migraine symptomatology and major depressive disorder. Cephalalgia 30:1073–1081
Lipton R, Dodick D, Sadovsky R, Kolodner K, Endicott J, Hettiarachchi J, Harrison W (2003) A self-administered screener for migraine in primary care the ID Migraine™ validation study. Neurology 61:375–382
Marchini J, Howie B (2010) Genotype imputation for genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet 11:499–511
Medland SE, Nyholt DR, Painter JN, McEvoy BP, McRae AF, Zhu G, Gordon SD, Ferreira MA, Wright MJ, Henders AK, Campbell MJ, Duffy DL, Hansell NK, Macgregor S, Slutske WS, Heath AC, Montgomery GW, Martin NG (2009) Common variants in the trichohyalin gene are associated with straight hair in Europeans. Am J Hum Genet 85:750–755
Merikangas KR, Angst J, Isler H (1990) Migraine and psychopathology. Results of the Zurich cohort study of young adults. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:849–853
Middeldorp CM, De Moor MHM, McGrath LM, Gordon SD, Blackwood DH, Costa PT, Terracciano A, Krueger RF, De Geus EJC, Nyholt DR (2011) The genetic association between personality and major depression or bipolar disorder. A polygenic score analysis using genome-wide association data. Transl Psychiatry 1:e50
Mulder EJ, Van Baal C, Gaist D, Kallela M, Kaprio J, Svensson DA, Nyholt DR, Martin NG, MacGregor AJ, Cherkas LF, Boomsma DI, Palotie A (2003) Genetic and environmental influences on migraine: a twin study across six countries. Twin Res 6:422–431
Nyholt DR, Gillespie NG, Heath AC, Merikangas KR, Duffy DL, Martin NG (2004) Latent class and genetic analysis does not support migraine with aura and migraine without aura as separate entities. Genet Epidemiol 26:231–244
Nyholt DR, Morley KI, Ferreira MA, Medland SE, Boomsma DI, Heath AC, Merikangas KR, Montgomery GW, Martin NG (2005) Genomewide significant linkage to migrainous headache on chromosome 5q21. Am J Hum Genet 77:500–512
Penninx BW, Beekman AT, Smit JH, Zitman FG, Nolen WA, Spinhoven P, Cuijpers P, De Jong PJ, Van Marwijk HW, Assendelft WJ, Van Der Meer K, Verhaak P, Wensing M, De Graaf R, Hoogendijk WJ, Ormel J, Van Dyck R (2008) The Netherlands study of depression and anxiety (NESDA): rationale, objectives and methods. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 17:121–140
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PI, Daly MJ, Sham PC (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Purcell SM, Wray NR, Stone JL, Visscher PM, O’Donovan MC, Sullivan PF, Sklar P, Purcell Leader SM, Stone JL, Sullivan PF, Ruderfer DM, McQuillin A, Morris DW, O’Dushlaine CT, Corvin A, Holmans PA, O’Donovan MC, Sklar P, Wray NR, Macgregor S, Sklar P, Sullivan PF, O’Donovan MC, Visscher PM, Gurling H, Blackwood DH, Corvin A, Craddock NJ, Gill M, Hultman CM, Kirov GK, Lichtenstein P, McQuillin A, Muir WJ, O’Donovan MC, Owen MJ, Pato CN, Purcell SM, Scolnick EM, St Clair D, Stone JL, Sullivan PF, Sklar Leader P, O’Donovan MC, Kirov GK, Craddock NJ, Holmans PA, Williams NM, Georgieva L, Nikolov I, Norton N, Williams H, Toncheva D, Milanova V, Owen MJ, Hultman CM, Lichtenstein P, Thelander EF, Sullivan P, Morris DW, O’Dushlaine CT, Kenny E, Quinn EM, Gill M, Corvin A, McQuillin A, Choudhury K, Datta S, Pimm J, Thirumalai S, Puri V, Krasucki R, Lawrence J, Quested D, Bass N, Gurling H, Crombie C, Fraser G, Leh Kuan S, Walker N, St Clair D, Blackwood DH, Muir WJ, McGhee KA, Pickard B, Malloy P, Maclean AW, Van Beck M, Wray NR, Macgregor S, Visscher PM, Pato MT, Medeiros H, Middleton F, Carvalho C, Morley C, Fanous A, Conti D, Knowles JA, Paz Ferreira C et al (2009) Common polygenic variation contributes to risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Nature 460:748–752
Schur EA, Noonan C, Buchwald D, Goldberg J, Afari N (2009) A twin study of depression and migraine: evidence for a shared genetic vulnerability. Headache 49:1493–1502
Stahl SM (2002) Does depression hurt? J Clin Psychiatry 63:273–274
Stam AH, de Vries B, Janssens AC, Vanmolkot KR, Aulchenko YS, Henneman P, Oostra BA, Frants RR, van den Maagdenberg AM, Ferrari MD, van Duijn CM, Terwindt GM (2010) Shared genetic factors in migraine and depression. Evidence from a genetic isolate. Neurology 74:288–294
Sullivan PF, de Geus EJ, Willemsen G, James MR, Smit JH, Zandbelt T, Arolt V, Baune BT, Blackwood D, Cichon S, Coventry WL, Domschke K, Farmer A, Fava M, Gordon SD, He Q, Heath AC, Heutink P, Holsboer F, Hoogendijk WJ, Hottenga JJ, Hu Y, Kohli M, Lin D, Lucae S, Macintyre DJ, Maier W, McGhee KA, McGuffin P, Montgomery GW, Muir WJ, Nolen WA, Nothen MM, Perlis RH, Pirlo K, Posthuma D, Rietschel M, Rizzu P, Schosser A, Smit AB, Smoller JW, Tzeng JY, van Dyck R, Verhage M, Zitman FG, Martin NG, Wray NR, Boomsma DI, Penninx BW (2008) Genome-wide association for major depressive disorder: a possible role for the presynaptic protein piccolo. Mol Psychiatry 14:359–375
Swartz KL, Pratt LA, Armenian HK, Lee LC, Eaton WW (2000) Mental disorders and the incidence of migraine headaches in a community sample: results from the Baltimore epidemiologic catchment area follow-up study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:945
Uher R, Huezo-Diaz P, Perroud N, Smith R, Rietschel M, Mors O, Hauser J, Maier W, Kozel D, Henigsberg N (2009) Genetic predictors of response to antidepressants in the GENDEP project. Pharmacogenomics J 9:225–233
Von Korff M, Simon G (1996) The relationship between pain and depression. Br J Psychiatry 168:101–108
Wittchen HU (1994) Reliability and validity studies of the WHO—composite international diagnostic interview (CIDI): a critical review. J Psychiatr Res 28:57–84
Wray N, Pergadia M, Blackwood D, Penninx B, Gordon S, Nyholt D, Ripke S, Macintyre D, McGhee K, Maclean A (2010) Genome-wide association study of major depressive disorder: new results, meta-analysis, and lessons learned. Mol Psychiatry 17:36–48
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Naomi Wray for her helpful comments and suggestions. This study was supported by: the EMGO+ Institute for Health and Care Research, the European Research Council (ERC-230374 and ERC-284167), the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO 904-61-193, NWO/ZonMW 91210020). The infrastructure for the NESDA study (http://www.nesda.nl) is funded through the Geestkracht program of the Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (Zon-Mw, Grant Number 10-000-1002) and is supported by participating universities and mental health care organisations [VU University Medical Center, GGZ inGeest, Arkin, Leiden University Medical Center, GGZ Rivierduinen, University Medical Center Groningen, Lentis, GGZ Friesland, GGZ Drenthe, Scientific Institute for Quality of Healthcare (IQ healthcare), Netherlands Institute for Health Services Research (NIVEL) and Netherlands Institute of Mental Health and Addiction (Trimbos Institute)]. Genotyping in the NTR and NESDA samples was funded by the Genetic Association Information Network (GAIN) of the Foundation for the US National Institutes of Health, and analysis was supported by grants from GAIN and the US National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) (MH081802). Statistical analyses were partly carried out on the Genetic Cluster Computer (NWO 480-05-003). Funding for the Australian cohort was provided by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (241944, 339462, 389927, 389875, 389891, 389892, 389938, 442915, 442981, 443036, 496675, 496739, 552485, 552498, 613602, 613608, 613674 and 619667), the Australian Research Council (A7960034, A79906588, A79801419, DP0212016, DP0343921, FT0991022 and FT0991360), the EU FP5 GenomEUtwin Project (QLG2-CT-2002-01254) and the US National Institutes of Health (AA07535, AA10249, AA13320, AA13321, AA13326, AA14041, MH66206, DA12854, DA019951) and Center for Inherited Disease Research (Baltimore, MD, USA). We thank P.M. Visscher, D.L. Duffy, A.K. Henders, S.E. Medland, B. Usher, E. Souzeau, A. Kuot, A. McMellon, M.J. Wright, M.J. Campbell, A. Caracella, L. Bowdler, S. Smith, S.D. Gordon, B. Haddon, D. Smyth, H. Beeby, O. Zheng and B. Chapman for their input into project management, databases, phenotype collection, and sample collection, processing and genotyping. We thank the twins and their families registered at the Australian Twin Registry for their participation in the many studies that have contributed to this research. Genotyping of the RADIANT study was funded by a joint grant from the UK Medical Research Council and GlaxoSmithKline (G0701420). DeCC study collection was supported by the UK MRC (G0000647) and the GENDEP study was funded by a European Commission Framework 6 grant, EC Contract Ref.: LSHB-CT-2003-503428.
Conflict of interest
A.E. Farmer and P. McGuffin have received consultancy fees and honoraria for participating in expert panels for pharmaceutical companies including GlaxoSmithKline. The other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standard
All experiments comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
D. I. Boomsma and D. R. Nyholt contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ligthart, L., Hottenga, JJ., Lewis, C.M. et al. Genetic risk score analysis indicates migraine with and without comorbid depression are genetically different disorders. Hum Genet 133, 173–186 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-013-1370-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-013-1370-8