Abstract
There is still a debate on the extent to which Notch3 signaling is involved in lung carcinogenesis and whether such function is dependent on cancer type or not.
Purpose
To evaluate Notch3 expression in different types of human lung cancer cells.
Methods
Notch3 was detected in human lung cancer cell lines and in tissues. Then, small interfering RNA (siRNA) was used to down-regulate the expression of Notch3 in H69AR small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) cells; two non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) cells; A549 adenocarcinoma (ADC); and H2170 squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). In addition, Notch3 intracellular domain (N3ICD) plasmid was transfected into H1688 human SCLC cells. We observed the effect of deregulating Notch3 signaling on the following cell properties: Notch-related proteins, cell morphology, adhesion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), motility, proliferation and neuroendocrine (NE) features of SCLC.
Results
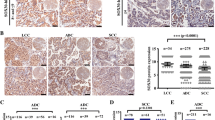
Notch3 is mainly expressed in NSCLC, and the expression of Notch1, Hes1 and Jagged1 is affected by Notch3. Notch3 has opposite functions in SCLC and NSCLC, being a tumor suppressor in the former and tumor promoting in the latter, in the context of cell adhesion, EMT and motility. Regarding cell proliferation, we found that inhibiting Notch3 in NSCLC decreases cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in NSCLC. Notch3 has no effect on cell proliferation or NE features of SCLC.
Conclusion
Notch3 signaling in lung carcinoma is dependent on cell type. In SCLC, Notch3 behaves as a tumor suppressor pathway, while in NSCLC it acts as a tumor-promoting pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arasada RR, Amann JM, Rahman MA, Huppert SS, Carbone DP (2014) EGFR blockade enriches for lung cancer stem-like cells through Notch3-dependent signaling. Cancer Res 74(19):5572–5584
Bunn PA Jr (2012) Worldwide overview of the current status of lung cancer diagnosis and treatment. Arch Pathol Lab Med 136:1478–1481
Chen X, Stoeck A, Lee SJ, IeM Shih, Wang MM, Wang TL (2010) Jagged1 expression regulated by Notch3 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 3:210–218
Collins BJ, Kleeberger W, Ball DW (2004) Notch in lung development and lung cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 14(5):357–364
Dang TP, Gazdar AF, Virmani AK, Sepetavec T, Hande KR, Minna JD, Roberts JR, Carbone DP (2000) Chromosome 19 translocation, overexpression of Notch3, and human lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:1355–1357
Ertel A, Verghese A, Byers SW, Ochs M, Tozeren A (2006) Pathway-specific differences between tumor cell lines and normal and tumor tissue cells. Mol Cancer 5(1):55
Gadgeel SM, Ramalingam SS, Kalemkerian GP (2012) Treatment of lung cancer. Radiol Clin North Am 50(5):961–974
Haruki N, Kawaguchi KS, Eichenberger S, Massion PP, Olson S, Gonzalez A, Carbone DP, Dang TP (2005) Dominant-negative Notch3 receptor inhibits mitogen activated protein kinase pathway and the growth of human lung cancers. Cancer Res 65(9):3555–3561
Hassan KA, Wang L, Korkaya H, Chen G, Maillard I, Beer DG, Kalemkerian GP, Wicha MS (2013) Notch pathway activity identifies cells with cancer stem cell-like properties and correlates with worse survival in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 19(8):1972–1980
Hassan WA, Yoshida R, Kudoh S, Hasegawa K, Niimori-Kita K, Ito T (2014) Notch1 controls cell invasion and metastasis in small cell lung carcinoma cell lines. Lung Cancer 86(3):304–310
Hassan WA, Udaka N, Ueda A, Ando Y, Ito T (2015) Neoplastic lesions in CADASIL syndrome—report of an autopsied Japanese case. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(6):7533–7539
Hintermann E, Quaranta V (2004) Epithelial cell motility on laminin-5: regulation by matrix assembly, proteolysis, integrins and erbB receptors. Matrix Biol 23:75–85
Ito T, Udaka N, Yazawa T, Okudela K, Hayashi H, Sudo T, Guillemot F, Kageyama R, Kitamura H (2000) Basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors regulate the neuroendocrine differentiation of fetal mouse pulmonary epithelium. Development 127:3913–3921
Konishi J, Kawaguchi KS, Vo H, Haruki N, Gonzalez A, Carbone DP, Dang TP (2007) Gamma-secretase inhibitor prevents Notch3 activation and reduces proliferation in human lung cancers. Cancer Res 67(17):8051–8057
Lee S, Jung C, Ko Y, Choi J, Lee K, Kang C (2008) Expression of Notch 1 and 3 is related to inhibition of lymph node metastasis and progression in non-small lung carcinoma. Basic Appl Pathol 1(2):93–97
Li C, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Cui Z, Yu M, Zhang S, Xue X (2011) Evidence of the cross talk between Wnt and Notch signaling pathways in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Notch3-siRNA weakens the effect of LiCl on the cell cycle of NSCLC cell lines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137(5):771–778
Lin L, Mernaugh R, Yi F, Blum D, Carbone DP, Dang TP (2010) Targeting specific regions of the Notch3 ligand-binding domain induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth in lung cancer. Cancer Res 70(2):632–638
Liu L, Chen X, Wang Y, Qu Z, Lu Q, Zhao J, Yan X, Zhang H, Zhou Y (2014) Notch3 is important for TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer bone metastasis by regulating ZEB-1. Cancer Gene Ther 21(9):364–372
Lu KH, Patterson AP, Wang L, Marquez RT, Atkinson EN, Baggerly KA, Ramoth LR, Rosen DG, Liu J, Hellstrom I, Smith D, Hartmann L, Fishman D, Berchuck A, Schmandt R, Whitaker R, Gershenson DM, Mills GB, Bast RC Jr (2004) Selection of potential markers for epithelial ovarian cancer with gene expression arrays and recursive descent partition analysis. Clin Cancer Res 10:3291–3300
Miyamoto Y, Maitra A, Ghosh B, Zechner U, Argani P, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Sriuranpong V, Iso T, Meszoely IM, Wolfe MS, Hruban RH, Ball DW, Schmid RM, Leach SD (2003) Notch mediates TGF alpha-induced changes in epithelial differentiation during pancreatic tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 3(6):565–576
Morimoto M, Nishinakamura R, Saga Y, Kopan R (2012) Different assemblies of Notch receptors coordinate the distribution of the major bronchial Clara, ciliated and neuroendocrine cells. Development 139(23):4365–4373
Osanyingbemi-Obidi J, Dobromilskaya I, Illei PB, Hann CL, Rudin CM (2011) Notch signaling contributes to lung cancer clonogenic capacity in vitro but may be circumvented in tumorigenesis in vivo. Mol Cancer Res 9(12):1746–1754
Pietanza MC, Spira A, Jotte R, Gadgeel S, Mita A, Liu S, Gluck WL, Kalemkerian GP, Chiang A, Hart L, Kapoun A, Xu L, Hill D, Zhou L, Dupont J, Spige DR (2014) Phase 1b trial of tarextumab (OMP 59R5) (anti-Notch 2/3 antibody) in combination with etoposide and cisplatin (EP) in patients (pts) with untreated extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC): PINNACLE study. Ann Oncol 25(4):iv511–iv516. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdu355
Platta CS, Greenblatt DY, Kunnimalaiyaan M, Chen H (2008) Valproic acid induces Notch1 signaling in small cell lung cancer cells. J Surg Res 148(1):31–37
Rizzo P, Osipo C, Foreman K, Golde T, Osborne B, Miele L (2008) Rational targeting of Notch signaling in cancer. Oncogene 27:5124–5131
Roy M, Pear WS, Aster JC (2007) The multifaceted role of Notch in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17(1):52–59
Scheel C, Weinberg RA (2012) Cancer stem cells and epithelial mesenchymal transition: concepts and molecular links. Semin Cancer Biol 22:396–403
Shan L, Aster JC, Sklar J, Sunday ME (2007) Notch-1 regulates pulmonary neuroendocrine cell differentiation in cell lines and in transgenic mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292(2):L500–L509
Shimizu K, Chiba S, Saito T, Kumano K, Hamada Y, Hirai H (2002) Functional diversity among Notch1, Notch2, and Notch3 receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 291(4):775–779
Sriuranpong V, Borges MW, Ravi RK, Arnold DR, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB, Ball DW (2001) Notch signaling induces cell cycle arrest in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 61:3200–3205
Sriuranpong V, Borges MW, Strock CL, Nakakura EK, Watkins DN, Blaumueller CM, Nelkin BD, Ball DW (2002) Notch signaling induces rapid degradation of achaete-scute homolog 1. Mol Cell Biol 22:3129–3139
Sullivan JP, Spinola M, Dodge M, Raso MG, Behrens C, Gao B, Schuster K, Shao C, Larsen JE, Sullivan LA, Honorio S, Xie Y, Scaglioni PP, DiMaio JM, Gazdar AF, Shay JW, Wistuba II, Minna JD (2010) Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity selects for lung adenocarcinoma stem cells dependent on notch signaling. Cancer Res 70(23):9937–9948
Travis W, Brambilla E, Burke AP, Marx A, Nicholson AG (2015) WHO classification of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. World Health organization Classification of Tumours. IARC Press, Lyon, France
Vo K, Amarasinghe B, Washington K, Gonzalez A, Berlin J, Dang TP (2011) Targeting notch pathway enhances rapamycin antitumor activity in pancreas cancers through PTEN phosphorylation. Mol Cancer 10:138
Wael H, Yoshida R, Kudoh S, Hasegawa K, Niimori-Kita K, Ito T (2014) Notch1 signaling controls cell proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation in lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer 85(2):131–140
Yeasmin S, Nakayama K, Rahman MT, Rahman M, Ishikawa M, Iida K, Otsuki Y, Kobayashi H, Nakayama S, Miyazaki K (2010) Expression of nuclear Notch3 in cervical squamous cell carcinomas and its association with adverse clinical outcomes. Gynecol Oncol 117(3):409–416
Yoshida R, Nagata M, Nakayama H, Niimori-Kita K, Hassan W, Tanaka T, Shinohara M, Ito T (2013) The pathological significance of Notch1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Lab Invest 93:1068–1081
Zhou M, Jin WY, Fan ZW, Han RC (2013) Analysis of the expression of the Notch3 receptor protein in adult lung cancer. Oncol Lett 5(2):499–504
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Mitsuru Morimoto (Laboratory of Lung Development and Regeneration, RIKEN Center for Development Biology, Kobe, Japan), Dr. Koki Hasegawa and Prof. Kanako Niimori-Kita for their comments. We would like to thank Mrs. Motoko Kagayama, Mrs. Yuko Fukuchi-Nakaishi and Mrs. Takako Maeda for their technical assistance.
Funding
This study was partially funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C; No. 25460439) from Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Regarding the usage of human samples (formalin-fixed paraffin sections), the study followed the guidelines of the Ethics Committee of Kumamoto University (approval number 342).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, W.A., Yoshida, R., Kudoh, S. et al. Evaluation of role of Notch3 signaling pathway in human lung cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142, 981–993 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2117-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2117-4