Abstract
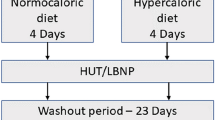
Water drinking reduces the occurrence of syncope in healthy volunteers but the effects of hyperhydration are unknown. This study assessed the effects of combined creatine (Cr) and glycerol (Gly) induced hyperhydration on the cardiovascular and haematological responses to postural change. Subjects in all trials lay supine for 30 min before being tilted head-up to 70° for a further 30 min or until the limit of their tolerance. Following 2 baseline trials, 19 subjects were matched for body mass and assigned to ingest either 20 g Cr and 2 g Gly kg−1 body mass (BM) plus 2 l of water or 2 l of water alone (Pl) each day for 6 days and once more 5 h prior to the experimental trial. Subjects ingested 500 ml of water prior to all trials to ensure euhydration. During baseline trials, 3 subjects in the Cr/Gly group and 2 in the Pl group experienced presyncope during head-up tilt. Following Cr/Gly supplementation, BM increased by (mean ± S.D.) 0.9 ± 0.3 and total body water (TBW) increased by 0.7 ± 0.2 l with no change in the Pl group. Cr/Gly supplementation resulted in a significant increase in systolic (11 mmHg) and diastolic (7 mmHg) blood pressure during head-up tilt with no change following Pl supplementation. Cr/Gly. Following Cr/Gly supplementation the number of subjects who became presyncopal was reduced from 3 to 1, with no change in the Pl group. These data suggest that hyperhydration mediated by Cr and Gly can enhance orthostatic tolerance in healthy individuals.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alegria JR, Gersh BJ, Scott CG, Hodge DO, Hammill SC, Shen WK (2003) Comparison of frequency of recurrent syncope after beta-blocker therapy versus conservative management for patients with vasovagal syncope. Am J Cardiol 92:82–84. doi:10.1016/S0002-9149(03)00475-2
Armstrong LE, Kenefick RW, Castellani JW, Riebe D, Kavouras SA, Kuznicki JT, Maresh CM (1997) Bioimpedance spectroscopy technique: intra-, extracellular, and total body water. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29:1657–1663. doi:10.1097/00005768-199712000-00017
Benditt DG, Ferguson DW, Grubb BP, Kapoor WN, Kugler J, Lerman BB, Maloney JD, Raviele A, Ross B, Sutton R, Wolk MJ, Wood DL (1996) Tilt table testing for assessing syncope. American College of Cardiology. J Am Coll Cardiol 28:263–275. doi:10.1016/0735-1097(96)00236-7
Blomqvist CG (1990) Orthostatic intolerance. In: Parmley WW, Chatterjee K (eds) Cardiology. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 1–37
Boobis LH, Maughan RJ (1983) A simple one-step enzymatic fluorometric method for the determination of glycerol in 20 microliters of plasma. Clin Chim Acta 132:173–179. doi:10.1016/0009-8981(83)90245-0
Buckey JC Jr, Gaffney FA, Lane LD, Levine BD, Watenpaugh DE, Wright SJ, Yancy CW Jr, Meyer DM, Blomqvist CG (1996) Central venous pressure in space. J Appl Physiol 81:19–25
Carter R, Cheuvront SN, Vernieuw CR, Sawka MN (2006) Hypohydration and prior heat stress exacerbates decreases in cerebral blood flow velocity during standing. J Appl Physiol 101:1744–1750. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00200.2006
Claydon VE, Schroeder C, Norcliffe LJ, Jordan J, Hainsworth R (2006) Water drinking improves orthostatic tolerance in patients with posturally related syncope. Clin Sci (Lond) 110:343–352. doi:10.1042/CS20050279
Colman N, Nahm K, Ganzeboom KS, Shen WK, Reitsma JB, Linzer M, Wieling W, Kaufmann H (2004) Epidemiology of reflex syncope. Clin Auton Res 14:9–17. doi:10.1007/s10286-004-1003-3
Convertino VA, Armstrong LE, Coyle EF, Mack GW, Sawka MN, Senay LC, Sherman WM (1996) American College of Sports Medicine position stand—exercise and fluid replacement. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:R1–R7
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red-cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
Easton C, Calder A, Kingsmore D, Pitsiladis YP (2006) The effects of a novel ‘fluid loading’ strategy combining creatine and glycerol on fluid retention and distribution in humans. In: Proceedings of the 57th meeting of the International Astronautical Congress
Easton C, Turner S, Pitsiladis YP (2007) Creatine and glycerol hyperhydration in trained subjects prior to exercise in the heat. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 17:70–91
ElSayed H, Hainsworth R (1995) Relationship between plasma-volume, carotid baroreceptor sensitivity and orthostatic tolerance. Clin Sci 88:463–470
ElSayed H, Hainsworth R (1996) Salt supplement increases plasma volume and orthostatic tolerance in patients with unexplained syncope. Heart 75:134–140. doi:10.1136/hrt.75.2.134
Freund BJ, Montain SJ, Young AJ, Sawka MN, Deluca JP, Pandolf KB, Valeri CR (1995) Glycerol hyperhydration: hormonal, renal, and vascular fluid responses. J Appl Physiol 79:2069–2077
Hainsworth R (2004) Pathophysiology of syncope. Clin Auton Res 14:18–24. doi:10.1007/s10286-004-1004-2
Hainsworth R, el Bedawi KM (1994) Orthostatic tolerance in patients with unexplained syncope. Clin Auton Res 4:239–244. doi:10.1007/BF01827428
Kaufmann H, Freeman R (2004) Pharmacological treatment of reflex syncope. Clin Auton Res 14:71–75. doi:10.1007/s10286-004-1010-4
Kaufmann H, Saadia D, Voustianiouk A (2002) Midodrine in neurally mediated syncope: a double-blind, randomized, crossover study. Ann Neurol 52:342–345. doi:10.1002/ana.10293
Kenny RA, Bayliss J, Ingram A, Sutton R (1986) Head-up tilt—a useful test for investigating unexplained syncope. Lancet 1:1352–1355
Kilduff LP, Georgiades E, James N, Minnion RH, Mitchell M, Kingsmore D, Hadjicharlambous M, Pitsiladis YP (2004) The effects of creatine supplementation on cardiovascular, metabolic, and thermoregulatory responses during exercise in the heat in endurance-trained humans. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 14:443–460
Kosinski D, Grubb BP, Temesyarmos P (1995) Pathophysiological aspects of neurocardiogenic syncope—current concepts and new perspectives. Pace-Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 18:716–724. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.1995.tb04666.x
Koulmann N, Jimenez C, Regal D, Bolliet P, Launay JC, Savourey G, Melin B (2000) Use of bioelectrical impedance analysis to estimate body fluid compartments after acute variations of the body hydration level. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:857–864. doi:10.1097/00005768-200004000-00020
Leach CS, Alfrey CP, Suki WN, Leonard JI, Rambaut PC, Inners LD, Smith SM, Lane HW, Krauhs JM (1996) Regulation of body fluid compartments during short-term spaceflight. J Appl Physiol 81:105–116
Lu CC, Diedrich A, Tung CS, Paranjape SY, Harris PA, Byrne DW, Jordan J, Robertson D (2003) Water ingestion as prophylaxis against syncope. Circulation 108:2660–2665. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000101966.24899.CB
Lurie KG, Benditt D (1996) Syncope and the autonomic nervous system. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 7:760–776. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8167.1996.tb00582.x
Mahanonda N, Bhuripanyo K, Kangkagate C, Wansanit K, Kulchot B, Nademanee K, Chaithiraphan S (1995) Randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of oral atenolol in patients with unexplained syncope and positive upright tilt-table test-results. Am Heart J 130:1250–1253. doi:10.1016/0002-8703(95)90150-7
Ogoh S, Brothers RM, Barnes Q, Eubank WL, Hawkins MN, Purkayastha S, Yurvati A, Raven PB (2005) The effect of changes in cardiac output on middle cerebral artery mean blood velocity at rest and during exercise. J Physiol Lond 569:697–704. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.095836
Oribe E, Kaufmann H, Winters S, Gomes J (1992) Fludrocortsone versus beta-adrenergic blockers in the treatment of vasovagal syncope. Neurology 42:213
Powers ME, Arnold BL, Weltman AL, Perrin DH, Mistry D, Kahler DM, Kraemer W, Volek J (2003) Creatine supplementation increases total body water without altering fluid distribution. J Athl Train 38:44–50
Rowe PC, Calkins H, DeBusk K, McKenzie R, Anand R, Sharma G, Cuccherini BA, Soto N, Hohman P, Snader S, Lucas KE, Wolff M, Straus SE (2001) Fludrocortisone acetate to treat neurally mediated hypotension in chronic fatigue syndrome—a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 285:52–59. doi:10.1001/jama.285.1.52
Schroeder C, Bush VE, Norcliffe LJ, Luft FC, Tank J, Jordan J, Hainsworth R (2002) Water drinking acutely improves orthostatic tolerance in healthy subjects. Circulation 106:2806–2811. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000038921.64575.D0
Sheldon R, Splawinski J, Killam S (1992) Reproducibility of tilt-table tests in patients with syncope. Am J Cardiol 69:1300–1305. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(92)91225-S
Sulzman FM (1996) Life sciences space missions. Overview. J Appl Physiol 81:3–6
Tenharkel ADJ, Vanlieshout JJ, Wieling W (1994) Effects of leg muscle pumping and tensing on orthostatic arterial-pressure—a study in normal subjects and patients with autonomic failure. Clin Sci 87:553–558
Vandenberghe K, Gillis N, Van Leemputte M, Van Hecke P, Vanstapel F, Hespel P (1996) Caffeine counteracts the ergogenic action of muscle creatine loading. J Appl Physiol 80:452–457
Weinberger MH (2000) Salt and blood pressure. Curr Opin Cardiol 15:254–257. doi:10.1097/00001573-200007000-00008
Wieling W, Colman N, Krediet CTP, Freeman R (2004) Nonpharmacological treatment of reflex syncope. Clin Auton Res 14:62–70. doi:10.1007/s10286-004-1009-x
Zhang R, Zuckerman JH, Iwasaki K, Wilson TE, Crandall CG, Levine BD (2002) Autonomic neural control of dynamic cerebral autoregulation in humans. Circulation 106:1814–1820. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000031798.07790.FE
Zorbas YG, Yarullin VL, Denogratov SD, Deogenov VA (2003) Fluid volume measurements in normal subjects to disclose body hydration during acute bed rest. Int Urol Nephrol 35:457–465. doi:10.1023/B:UROL.0000025636.41034.83
Acknowledgments
This study was part funded by a grant from the John Robertson Bequest, University of Glasgow. We acknowledge the invaluable assistance of Miss Laura Irwin who was recipient of a summer vacation studentship for this work from the Physiological Society (UK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Easton, C., Calder, A., Prior, F. et al. The effects of a novel “fluid loading” strategy on cardiovascular and haematological responses to orthostatic stress. Eur J Appl Physiol 105, 899–908 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0976-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0976-3