Abstract
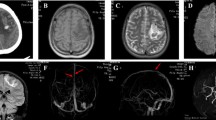
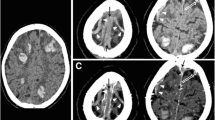
We report the clinico-radiological characteristics of SE in the patients with cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), and compare the relative risk of SE in determining death and disability compared with those patients with and without self-limiting seizures. Consecutive patients with magnetic resonance venography (MRV) confirmed CVT, admitted during 2006–2017, were included. Their clinical details, risk factors, and magnetic resonance imaging and MRV findings were noted. Duration of SE, Status Epilepticus Severity Score (STESS), Glasgow Coma Scale score, and response to antiepileptic drugs were noted. 6-month outcomes were noted using the modified Rankin Scale. Of 153 CVT patients, 28 (18.3%) had SE, 62 (40.5%) self-limiting seizures, and 63 (41.2%) did not have seizures or SE. The SE group had a higher incidence of focal motor deficit (71.4% vs. 33%, P = 0.006) and supratentorial lesions (93% vs 55.5%, P = 0.003) than the no-seizure group. Multivariate analysis of SE and no-SE group (includes self-limiting and no seizure) did not indicate any significant predictor, but multivariate analysis of SE and no-seizure group indicated that supratentorial lesion only predicted SE (odds ratio 5.65, 95% confidence interval 1.11–28.76; P = 0.03). Patients with SE and self-limiting seizure had similar clinical and MRI findings. In total, 17.8% had refractory SE; refractoriness was related to the pretreatment duration of SE (P < 0.001). The death and disability were not significantly different between the three groups. At 6 months, 84% patients with SE, 92.3% with self-limiting seizure, and 94.8% in no-seizure group had good recovery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferro JM, Canha˜o P, Stam J, Bousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F, ISCVT I (2004) Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: results of the international study on cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke 35:664–670
Misra UK, Kalita J, Nair PP (2008) Status epilepticus in central nervous system infections: an experience from a developing country. Am J Med 121:618–623
Kalita J, Chandra S, Misra UK (2012) Significance of seizure in cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Seizure 21:639–642
Kalita J, Nair PP, Misra UK (2010) A clinical, radiological and outcome study of status epilepticus from India. J Neurol 257:224–229
Knake S, Rosenow F, Vescovi M, Oertel WH, Mueller HH, Wirbatz A, Katsarou N, Hamer HM, Status Epilepticus Study Group Hessen (SESGH) (2001) Status epilepticus study group hessen (SESGH) incidence of status epilepticus in adults in Germany: a prospective, population-based study. Epilepsia 42:714–718
Aminoff MJ, Simon RP (1989) Status epilepticus: causes, clinical features and consequences in 98 patients. Am J Med 69:657–666
Stam J (2005) Thrombosis of the cerebral veins and sinuses. N Engl J Med 352:17911798
Kalita J, Goyal G, Kumar P, Misra UK (2014) Intracerebral hemorrhage in young patients from a tertiary neurology center in North India. J Neurol Sci 336:42–47
Zohair NA, Mansoor I, Uzma J, Sumaira N, Mughal Shahzad (2015) Etiology of stroke in young Pakistani adults; results of a single center study. Pakistan J Neurol Sci (PJNS) 10
Ferro JM, Canha˜o P, Bousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F, ISCVT, Investigators (2008) Early seizures in cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: risk factors and role of antiepileptic. Stroke 39:1152–1158
Bousser MG, Russell RR (1997) Cerebral venous thrombosis. In: Warlow CP, Van Gijn J (eds) Major problems in neurology. WB Saunders, London, pp 25–140
Mehvari Habibabadi J, Saadatnia M, Tabrizi N (2018) Seizure in cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis. Epilepsia Open 3(3):316–322
Beghi E, D’Alessandro R, Beretta S, Consoli D, Crespi V, Delaj L, Gandolfo C, Greco G, La Neve A, Manfredi M, Mattana F, Musolino R, Provinciali L, Santangelo M, Specchio LM, Zaccara G, Epistroke Group (2011) Incidence and predictors of acute symptomatic seizures after stroke. Neurology 77:1785–1793
Willmore LJ (1993) Post-traumatic seizures. Neurol Clin 11:823–834
Kucukkaya B, Aker R, Yuksel M, Onat F, Yalcin A (1998) Low dose MK-801 protects against iron-induced oxidative changes in a rat model of focal epilepsy. Brain Res 788:133–136
Trinka E, Cock H, Hesdorffer D, Rossetti AO, Scheffer IE, Shinnar S, Shinnar S, Shorvon S, Lowenstein DH (2015) A definition and classification of status epilepticus-report of the ILAE task force on classification of status epilepticus. Epilepsia 56:1515–1523
Beghi E, Carpio A, Forsgren L, Hesdorffer DC, Malmgren K, Sander JW, Tomson T, Hauser WA (2010) Recommendation for a definition of acute symptomatic seizure. Epilepsia 51(4):671–675
Misra UK, Kalita J, Maurya PK (2012) Levetiracetam versus lorazepam in status epilepticus: a randomized, open labeled pilot study. J Neurol 259(4):645–648
Misra UK, Dubey D, Kalita J (2017) Comparison of lacosamide versus sodium valproate in status epilepticus: a pilot study. Epilepsy Behav 76:110–113
Ylikotila P, Ketola RA, Timonen S, Malm H, Ruuskanen JO (2015) Early pregnancy cerebral venous thrombosis and status epilepticus treated with levetiracetam and lacosamide throughout pregnancy. Reprod Toxicol 57:204–206
Finkel L, Piantino J, Goldstein J, Wainwright MS (2015) Venous stroke and status epilepticus due to milk-induced anemia in a child. Pediatr Emerg Care 31:129–131
Zis P, Tavernarakis A (2013) Headache and status epilepticus in the postpartum period; posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome or cerebral venous thrombosis? Case Rep Emerg Med 2013:680327
Demir CF, Inci MF, Özkan F, Yıldız M, Özdemir H (2013) Clinical and radiological management and outcome of pregnancies complicated by cerebral venous thrombosis: a review of 19 cases. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 22:1252–1257
Costa P, Biscoito L, Vieira M, Marçal M, Camilo C, Neto L, Abecasis F, Almeida M, Correia M (2010) Endovascular thrombolysis for massive cerebral venous thrombosis in a teenager with nephrotic syndrome. Acta Med Port 23:1141–1146
Wang TY, Yen HJ, Hung GY, Hsieh MY, Tang RB (2011) A rare complication in a child undergoing chemotherapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: superior sagittal sinus thrombosis. J Chin Med Assoc 74:183–187
Kozic D, Zarkov M, Semnic RR, Ostojic J, Radovanovic B, Ivanovski D (2010) Overlooked early CT signs of cerebral venous thrombosis with lethal outcome. Acta Neurol Belg 110:345–348
Sinha S, Satishchandra P (2007) Epilepsia partialis continua over last 14 years: experience from a tertiary care center from south India. Epilepsy Res 74:55–59
Masuhr F, Busch M, Amberger N, Ortwein H, Weih M, Neumann K, Einhäupl K, Mehraein S (2006) Risk and predictors of early epileptic seizures in acute cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis. Eur J Neurol 13:852–856
Bateman BT, Claassen J, Willey JZ, Hirsch LJ, Mayer SA, Sacco RL, Schumacher HC (2007) Convulsive status epilepticus after ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage: frequency, predictors, and impact on outcome in a large administrative dataset. Neurocrit Care 7:187–193
Traenka C, De Marchis GM, Hert L, Seiffge DJ, Polymeris A, Peters N, Bonati LH, Engelter S, Lyrer P, Rüegg S, Sutter R (2017) Acute ischemic stroke in nonconvulsive status epilepticus–underestimated? Results from an 8-year cohort study. J Stroke 19(2):236–238
Assis TM, Bacellar A, Costa G, Nascimento OJ (2015) Mortality predictors of epilepsy and epileptic seizures among hospitalized elderly. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 73:510–515
Benninger F, Holtkamp M (2017) Epileptic seizures and epilepsy after a stroke: Incidence, prevention and treatment. Nervenarzt 88(10):1197–1207
Alme KN, Engelsen BA, Naik M, Naess H (2017) Identifying patients at risk of acute symptomatic seizure after ischemic stroke. Acta Neurol Scand 136(3):265–271
Kharatishvili I, Pitkänen A (2010) Association of the severity of cortical damage with the occurrence of spontaneous seizures and hyperexcitability in an animal model of posttraumatic epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 90(1–2):47–59
Misra UK, Kalita J, Dubey D (2017) A study of super refractory status epilepticus from India. Front Neurol 8:636
Kalita J, Nair P, Misra UK (2008) Status epilepticus in encephalitis: a study of clinical findings, magnetic resonance imaging, and response to antiepileptic drugs. J Neurovirol 14:412–417
Hesdorffer DC, Benn EK, Cascino GD, Hauser WA (2009) Is a first acute symptomatic seizure epilepsy? Mortality and risk for recurrent seizure. Epilepsia 50(5):1102–1108
Srivastava R, Kalita J, Khan MY, Misra UK (2009) Free radical generation by neurons in rat model of Japanese encephalitis. Neurochem Res 34:2141–2146
Kumar S, Misra UK, Kalita J, Khanna VK, Khan MY (2009) Imbalance in oxidant/antioxidant system in different brain regions of rat after the infection of Japanese encephalitis virus. Neurochem Int 55(7):648–654
Tiwari HS, Tripathi AK, Misra DP, Kalita J, Misra UK (2015) A study of ER stress in rat model of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Neurosci Lett 589:121–125
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. SK Mandal for statistical analysis and Mr. Shakti Kumar for secretarial help. We are grateful to Elenka Rodrigues for language editing which was supported by Sanofi. The authors individually and collectively are responsible for all contents and editorial decisions and received no payment from any agency directly or indirectly (through a third party) related to the development/presentation of this publication.
Funding
This research is investigator initiated and did not receive any grant from the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sector funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JK: planning, writing & analysis. UKM: planning & work management. VKS and DD: data collection & statistical analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None of the authors has any conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
We confirm that we have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines. Statistical analysis conducted by Dr. SK Mandal (Statistician of Centre for Biomedical Research at SGPGIMS, Lucknow, India).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalita, J., Misra, U.K., Singh, V.K. et al. Predictors and outcome of status epilepticus in cerebral venous thrombosis. J Neurol 266, 417–425 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-018-9145-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-018-9145-8