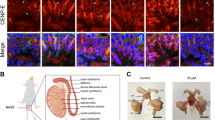
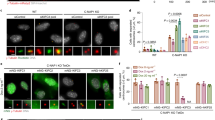
Abstract
Timely and accurate centrosome separation is critical for bipolar spindle organization and faithful chromosome segregation during cell division. Kinesin-5 Eg5 is essential for centrosome separation and spindle organization in somatic cells; however, the detailed functions and mechanisms of Eg5 in spermatocytes remain unclear. In this study, we show that Eg5 proteins are located at spindle microtubules and centrosomes in spermatocytes both in vivo and in vitro. We reveal that the spermatocytes are arrested at metaphase I in seminiferous tubules after Eg5 inhibition. Eg5 ablation results in cell cycle arrest, the formation of monopolar spindle, and chromosome misalignment in cultured GC-2 spd cells. Importantly, we find that the long-term inhibition of Eg5 results in an increased number of centrosomes and chromosomal instability in spermatocytes. Our findings indicate that Eg5 mediates centrosome separation to control spindle assembly and chromosome alignment in spermatocytes, which finally contribute to chromosome stability and faithful cell division of the spermatocytes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Agircan FG, Schiebel E, Mardin BR (2014) Separate to operate: control of centrosome positioning and separation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 369:20130461
Asraf H, Avunie-Masala R, Hershfinkel M, Gheber L (2015) Mitotic slippage and expression of survivin are linked to differential sensitivity of human cancer cell-lines to the Kinesin-5 inhibitor monastrol. PLoS One 10:e0129255
Blackwell R, Edelmaier C, Sweezy-Schindler O, Lamson A, Gergely ZR, O’Toole E, Crapo A, Hough LE, McIntosh JR, Glaser MA et al (2017) Physical determinants of bipolar mitotic spindle assembly and stability in fission yeast. Sci Adv 3:e1601603
Blangy A, Lane HA, d’Hérin P, Harper M, Kress M, Nigg EA (1995) Phosphorylation by p34cdc2 regulates spindle association of human Eg5, a kinesin-related motor essential for bipolar spindle formation in vivo. Cell 83:1159–1169
Bornens M (2002) Centrosome composition and microtubule anchoring mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol 14:25–34
Brier S, Lemaire D, Debonis S, Forest E, Kozielski F (2004) Identification of the protein binding region of S-trityl-L-cysteine, a new potent inhibitor of the mitotic kinesin Eg5. Biochemistry 43:13072–13082
Brust-Mascher I, Sommi P, Cheerambathur DK, Scholey JM (2009) Kinesin-5-dependent poleward flux and spindle length control in Drosophila embryo mitosis. Mol Biol Cell 20:1749–1762
Cameron LA, Yang G, Cimini D, Canman JC, Kisurina-Evgenieva O, Khodjakov A, Danuser G, Salmon ED (2006) Kinesin 5-independent poleward flux of kinetochore microtubules in PtK1 cells. J Cell Biol 173:173–179
Castillo A, Justice MJ (2007) The kinesin related motor protein, Eg5, is essential for maintenance of pre-implantation embryogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357:694–699
Chauvière M, Kress C, Kress M (2008) Disruption of the mitotic kinesin Eg5 gene (Knsl1) results in early embryonic lethality. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 372:513–519
Chen H, Connell M, Mei L, Reid GSD, Maxwell CA (2018) The nonmotor adaptor HMMR dampens Eg5-mediated forces to preserve the kinetics and integrity of chromosome segregation. Mol Biol Cell 29:786–796
Chen H, Fok KL, Jiang X, Jiang J, Chen Z, Gui Y, Chan HC, Cai Z (2012) CD147 regulates apoptosis in mouse spermatocytes but not spermatogonia. Hum Reprod 27:1568–1576
Chimento A, Sirianni R, Casaburi I, Ruggiero C, Maggiolini M, Andò S, Pezzi V (2012) 17β-Estradiol activates GPER- and ESR1-dependent pathways inducing apoptosis in GC-2 cells, a mouse spermatocyte-derived cell line. Mol Cell Endocrinol 355:49–59
Collins E, Mann BJ, Wadsworth P (2014) Eg5 restricts anaphase B spindle elongation in mammalian cells. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 71:136–144
Costa MFA, Ohkura H (2019) The molecular architecture of the meiotic spindle is remodeled during metaphase arrest in oocytes. J Cell Biol 218:2854–2864
DeBonis S, Skoufias DA, Lebeau L, Lopez R, Robin G, Margolis RL, Wade RH, Kozielski F (2004) In vitro screening for inhibitors of the human mitotic kinesin Eg5 with antimitotic and antitumor activities. Mol Cancer Ther 3:1079–1090
Ferenz NP, Gable A, Wadsworth P (2010) Mitotic functions of kinesin-5. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21:255–259
Ferenz NP, Paul R, Fagerstrom C, Mogilner A, Wadsworth P (2009) Dynein antagonizes eg5 by crosslinking and sliding antiparallel microtubules. Curr Biol 19:1833–1838
Fink G, Hajdo L, Skowronek KJ, Reuther C, Kasprzak AA, Diez S (2009) The mitotic kinesin-14 Ncd drives directional microtubule-microtubule sliding. Nat Cell Biol 11:717–723
Fridman V, Gerson-Gurwitz A, Shapira O, Movshovich N, Lakämper S, Schmidt CF, Gheber L (2013) Kinesin-5 Kip1 is a bi-directional motor that stabilizes microtubules and tracks their plus-ends in vivo. J Cell Sci 126:4147–4159
Ganem NJ, Storchova Z, Pellman D (2007) Tetraploidy, aneuploidy and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17:157–162
Gardner MK, Bouck DC, Paliulis LV, Meehl JB, O’Toole ET, Haase J, Soubry A, Joglekar AP, Winey M, Salmon ED et al (2008) Chromosome congression by Kinesin-5 motor-mediated disassembly of longer kinetochore microtubules. Cell 135:894–906
Gartner M, Sunder-Plassmann N, Seiler J, Utz M, Vernos I, Surrey T, Giannis A (2005) Development and biological evaluation of potent and specific inhibitors of mitotic Kinesin Eg5. ChemBioChem 6:1173–1177
Gayek AS, Ohi R (2014) Kinetochore-microtubule stability governs the metaphase requirement for Eg5. Mol Biol Cell 25:2051–2060
Gerson-Gurwitz A, Movshovich N, Avunie R, Fridman V, Moyal K, Katz B, Hoyt MA, Gheber L (2009) Mid-anaphase arrest in S. cerevisiae cells eliminated for the function of Cin8 and dynein. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:301–313
Godinho SA (2014) Centrosome amplification and cancer: branching out. Mol Cell Oncol 2:e993252
Hara-Yokoyama M, Kurihara H, Ichinose S, Matsuda H, Ichinose S, Kurosawa M, Tada N, Iwahara C, Terasawa K, Podyma-Inoue KA et al (2019) KIF11 as a potential marker of spermatogenesis within mouse seminiferous tubule cross-sections. J Histochem Cytochem 67:813–824
Hashimoto K, Chinen T, Kitagawa D (2020) Mechanisms of spindle bipolarity establishment in acentrosomal human cells. Mol Cell Oncol 7:1743899
Heck MM, Pereira A, Pesavento P, Yannoni Y, Spradling AC, Goldstein LS (1993) The kinesin-like protein KLP61F is essential for mitosis in Drosophila. J Cell Biol 123:665–679
Hentrich C, Surrey T (2010) Microtubule organization by the antagonistic mitotic motors kinesin-5 and kinesin-14. J Cell Biol 189:465–480
Hofmann MC, Abramian D, Millán JL (1995) A haploid and a diploid cell coexist in an in vitro immortalized spermatogenic cell line. Dev Genet 16:119–127
Hofmann MC, Hess RA, Goldberg E, Millán JL (1994) Immortalized germ cells undergo meiosis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:5533–5537
Iwakiri Y, Kamakura S, Hayase J, Sumimoto H (2013) Interaction of NuMA protein with the kinesin Eg5: its possible role in bipolar spindle assembly and chromosome alignment. Biochem J 451:195–204
Kaan HY, Ulaganathan V, Hackney DD, Kozielski F (2009) An allosteric transition trapped in an intermediate state of a new kinesin-inhibitor complex. Biochem J 425:55–60
Kapitein LC, Peterman EJ, Kwok BH, Kim JH, Kapoor TM, Schmidt CF (2005) The bipolar mitotic kinesin Eg5 moves on both microtubules that it crosslinks. Nature 435:114–118
Kapoor TM, Mayer TU, Coughlin ML, Mitchison TJ (2000) Probing spindle assembly mechanisms with monastrol, a small molecule inhibitor of the mitotic kinesin, Eg5. J Cell Biol 150:975–988
Kashina AS, Rogers GC, Scholey JM (1997) The bimC family of kinesins: essential bipolar mitotic motors driving centrosome separation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1357:257–271
Kashina AS, Scholey JM, Leszyk JD, Saxton WM (1996) An essential bipolar mitotic motor. Nature 384:225
Kovacovicova K, Awadova T, Mikel P, Anger M (2016) In vitro maturation of mouse oocytes increases the level of Kif11/Eg5 on meiosis II spindles. Biol Reprod 95:18
Leblond CP, Clermont Y (1952a) Definition of the stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium in the rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci 55:548–573
Leblond CP, Clermont Y (1952b) Spermiogenesis of rat, mouse, hamster and guinea pig as revealed by the periodic acid-fuchsin sulfurous acid technique. Am J Anat 90:167–215
Liu M, Li D, Sun L, Chen J, Sun X, Zhang L, Huo L, Zhou J (2014) Modulation of Eg5 activity contributes to mitotic spindle checkpoint activation and Tat-mediated apoptosis in CD4-positive T-lymphocytes. J Pathol 233:138–147
Ma N, Titus J, Gable A, Ross JL, Wadsworth P (2011) TPX2 regulates the localization and activity of Eg5 in the mammalian mitotic spindle. J Cell Biol 195:87–98
Mann BJ, Wadsworth P (2019) Kinesin-5 regulation and function in mitosis. Trends Cell Biol 29:66–79
Mayer TU, Kapoor TM, Haggarty SJ, King RW, Schreiber SL, Mitchison TJ (1999) Small molecule inhibitor of mitotic spindle bipolarity identified in a phenotype-based screen. Science 286:971–974
McCoy KM, Tubman ES, Claas A, Tank D, Clancy SA, O’Toole ET, Berman J, Odde DJ (2015) Physical limits on kinesin-5-mediated chromosome congression in the smallest mitotic spindles. Mol Biol Cell 26:3999–4014
Movshovich N, Fridman V, Gerson-Gurwitz A, Shumacher I, Gertsberg I, Fich A, Hoyt MA, Katz B, Gheber L (2008) Slk19-dependent mid-anaphase pause in kinesin-5-mutated cells. J Cell Sci 121:2529–2539
Novak M, Polak B, Simunić J, Boban Z, Kuzmić B, Thomae AW, Tolić IM, Pavin N (2018) The mitotic spindle is chiral due to torques within microtubule bundles. Nat Commun 9:3571
Ohashi A (2015) Different cell fates after mitotic slippage: from aneuploidy to polyploidy. Mol Cell Oncol 3:e1088503
Raaijmakers JA, van Heesbeen RG, Meaders JL, Geers EF, Fernandez-Garcia B, Medema RH, Tanenbaum ME (2012) Nuclear envelope-associated dynein drives prophase centrosome separation and enables Eg5-independent bipolar spindle formation. EMBO J 31:4179–4190
Rincon SA, Lamson A, Blackwell R, Syrovatkina V, Fraisier V, Paoletti A, Betterton MD, Tran PT (2017) Kinesin-5-independent mitotic spindle assembly requires the antiparallel microtubule crosslinker Ase1 in fission yeast. Nat Commu 8:15286
Roostalu J, Hentrich C, Bieling P, Telley IA, Schiebel E, Surrey T (2011) Directional switching of the kinesin Cin8 through motor coupling. Science 332:94–99
Rozelle DK, Hansen SD, Kaplan KB (2011) Chromosome passenger complexes control anaphase duration and spindle elongation via a kinesin-5 brake. J Cell Biol 193:285–294
Russell LD, Ettlin RA, Hikim APS, Clegg ED (1990) Histological and histopathological evaluation of the testis. Cache River Press, Florida, pp 119–162
Saunders AM, Powers J, Strome S, Saxton WM (2007) Kinesin-5 acts as a brake in anaphase spindle elongation. Curr Biol 17:R453–R454
Saunders WS, Hoyt MA (1992) Kinesin-related proteins required for structural integrity of the mitotic spindle. Cell 70:451–458
Sawin KE, LeGuellec K, Philippe M, Mitchison TJ (1992) Mitotic spindle organization by a plus-end-directed microtubule motor. Nature 359:540–543
Scholey JE, Nithianantham S, Scholey JM, Al-Bassam J (2014) Structural basis for the assembly of the mitotic motor Kinesin-5 into bipolar tetramers. Elife 3:e02217
Scholey JM, Civelekoglu-Scholey G, Brust-Mascher I (2016) Anaphase B. Biology (Basel) 5:51
Shapira O, Goldstein A, Al-Bassam J, Gheber L (2017) A potential physiological role for bi-directional motility and motor clustering of mitotic kinesin-5 Cin8 in yeast mitosis. J Cell Sci 130:725–734
Sharp DJ, McDonald KL, Brown HM, Matthies HJ, Walczak C, Vale RD, Mitchison TJ, Scholey JM (1999) The bipolar kinesin, KLP61F, cross-links microtubules within interpolar microtubule bundles of Drosophila embryonic mitotic spindles. J Cell Biol 144:125–138
She ZY, Yang WX (2017) Molecular mechanisms of kinesin-14 motors in spindle assembly and chromosome segregation. J Cell Sci 130:2097–2110
She ZY, Zhong N, Yu KW, Xiao Y, Wei YL, Lin Y, Li YL, Lu MH (2020) Kinesin-5 Eg5 is essential for spindle assembly and chromosome alignment of mouse spermatocytes. Cell Div 15:6
Shimamoto Y, Forth S, Kapoor TM (2015) Measuring pushing and braking forces generated by ensembles of Kinesin-5 crosslinking two microtubules. Dev Cell 34:669–681
Shimizu M, Ishii H, Ogo N, Matsuno K, Asai A (2010) Biochemical analysis of cellular target of S-trityl-L-cysteine derivatives using affinity matrix. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:1578–1580
Shu S, Iimori M, Wakasa T, Ando K, Saeki H, Oda Y, Oki E, Maehara Y (2019) The balance of forces generated by kinesins controls spindle polarity and chromosomal heterogeneity in tetraploid cells. J Cell Sci 132:jcs231530
Singh SK, Pandey H, Al-Bassam J, Gheber L (2018) Bidirectional motility of kinesin-5 motor proteins: structural determinants, cumulative functions and physiological roles. Cell Mol Life Sci 75:1757–1771
Skoufias DA, DeBonis S, Saoudi Y, Lebeau L, Crevel I, Cross R, Wade RH, Hackney D, Kozielski F (2006) S-trityl-L-cysteine is a reversible, tight binding inhibitor of the human kinesin Eg5 that specifically blocks mitotic progression. J Biol Chem 281:17559–17569
Stiff T, Echegaray-Iturra FR, Pink HJ, Herbert A, Reyes-Aldasoro CC, Hochegger H (2020) Prophase-specific perinuclear actin coordinates centrosome separation and positioning to ensure accurate chromosome segregation. Cell Rep 31:107681
Sturgill EG, Norris SR, Guo Y, Ohi R (2016) Kinesin-5 inhibitor resistance is driven by kinesin-12. J Cell Biol 213:213–227
Sturgill EG, Ohi R (2013) Kinesin-12 differentially affects spindle assembly depending on its microtubule substrate. Curr Biol 23:1280–1290
Takagi J, Sakamoto R, Shiratsuchi G, Maeda YT, Shimamoto Y (2019) Mechanically distinct microtubule arrays determine the length and force response of the meiotic spindle. Dev Cell 49:267-278.e5
Tan R, Foster PJ, Needleman DJ, McKenney RJ (2018) Cooperative accumulation of dynein-dynactin at microtubule minus-ends drives microtubule network reorganization. Dev Cell 44:233-247.e4
Tanenbaum ME, Macůrek L, Janssen A, Geers EF, Alvarez-Fernández M, Medema RH (2009) Kif15 cooperates with eg5 to promote bipolar spindle assembly. Curr Biol 19:1703–1711
Tanenbaum ME, Medema RH (2010) Mechanisms of centrosome separation and bipolar spindle assembly. Dev Cell 19:797–806
Tikhonenko I, Nag DK, Martin N, Koonce MP (2008) Kinesin-5 is not essential for mitotic spindle elongation in Dictyostelium. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 65:853–862
Tubman E, He Y, Hays TS, Odde DJ (2018) Kinesin-5 mediated chromosome congression in insect spindles. Cell Mol Bioeng 11:25–36
van Heesbeen RG, Tanenbaum ME, Medema RH (2014) Balanced activity of three mitotic motors is required for bipolar spindle assembly and chromosome segregation. Cell Rep 8:948–956
Vanneste D, Takagi M, Imamoto N, Vernos I (2009) The role of Hklp2 in the stabilization and maintenance of spindle bipolarity. Curr Biol 19:1712–1717
Vladimirou E, Mchedlishvili N, Gasic I, Armond JW, Samora CP, Meraldi P, McAinsh AD (2013) Nonautonomous movement of chromosomes in mitosis. Dev Cell 27:60–71
Wan X, Zhang Y, Lan M, Pan MH, Tang F, Zhang HL, Ou XH, Sun SC (2018) Meiotic arrest and spindle defects are associated with altered KIF11 expression in porcine oocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen 59:805–812
Wilson PG, Simmons R, Saighal S (2004) Novel nuclear defects in KLP61F-deficient mutants in Drosophila are partially suppressed by loss of Ncd function. J Cell Sci 117:4921–4933
Xie Y, Cheng M, Lu S, Yuan Q, Yang D, Chen Y, Pan C, Qiu Y, Xiong B (2018) Eg5 orchestrates porcine oocyte maturational progression by maintaining meiotic organelle arrangement. Cell Div 13:4
Yount AL, Zong H, Walczak CE (2015) Regulatory mechanisms that control mitotic kinesins. Exp Cell Res 334:70–77
Yukawa M, Yamada Y, Toda T (2019) Suppressor analysis uncovers that MAPs and microtubule dynamics balance with the Cut7/Kinesin-5 motor for mitotic spindle assembly in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. G3 (Bethesda) 9:269–280
Zhang J, Liu J, Ren L, Wei J, Zhang F, Li Y, Guo C, Duan J, Sun Z, Zhou X (2018) Silica nanoparticles induce abnormal mitosis and apoptosis via PKC-δ mediated negative signaling pathway in GC-2 cells of mice. Chemosphere 208:942–950
Acknowledgements
We thank all the members of the Cytoskeleton Laboratory at Fujian Medical University for helpful discussions. We thank Jun-Jin Lin, Ming-Xia Wu, and Lin-Ying Zhou at Public Technology Service Center, Fujian Medical University, for their technical assistance.
Funding
This study was supported by the following grants: National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 82001608), Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, China (grant number 2019J05071), Fujian Provincial Health Technology Project (grant number 2018–1-69 and 2020QNB009), Startup Fund for scientific research, Fujian Medical University (grant number 2017XQ1001), Fujian Medical University high-level talents scientific research start-up funding project (grant number XRCZX2017025), and Research project of online education and teaching of Chinese medicine graduate students (grant number B-YXC20200202-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZYS: conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; funding acquisition; investigation; methodology; project administration; resources; software; supervision; validation; visualization; roles/writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. NZ: data curation; formal analysis; software; validation; visualization; roles/writing—original draft. YLW: formal analysis; visualization; roles/writing—original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving animals were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee at Fujian Medical University, China (permit number SYXK2016-0007).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
She, ZY., Zhong, N. & Wei, YL. Kinesin-5 Eg5 mediates centrosome separation to control spindle assembly in spermatocytes. Chromosoma 131, 87–105 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-022-00772-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-022-00772-5