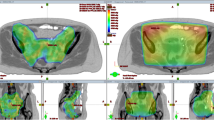
Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of a hybrid technique which results from combining intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for the treatment of cervical cancer patients. Plans made with the hybrid technique and pure IMRT and VMAT were retrospectively compared in 20 patients with cervical cancer at different stages. All plans were made using the same contours based on the original computed tomography (CT) scans. Conformity (CI) and homogeneity (HI) indices of the planning target volumes (PTVs) were calculated for each technique in order to evaluate plan quality. All techniques were compared in terms of dose to organs at risk (OARs), number of monitor units (MUs) and treatment time. It turned out that plans made with the hybrid technique had improved dose conformity and homogeneity compared to plans made only with IMRT and VMAT (p < 0.001). Regarding the OARs, the maximum dose (Dmax) delivered to the bladder, rectum and femoral heads was lower for the hybrid plans compared to the IMRT and VMAT plans (p < 0.001). The volumes irradiated to doses of 50 Gy (V50Gy) for rectum, bladder and bowel were lower for the hybrid plans (p < 0.001, p = 0.002). Furthermore, the treatment time and MU values for the hybrid plans were found to be between of the values for the IMRT and VMAT plans. It is concluded that, as compared to IMRT and VMAT plans, the hybrid plan technique allowed a better conformity and homogeneity for the dose distribution in the PTV and a dose reduction to the OARs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbas U, Koksal C, Kesen ND et al (2019) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiotherapy with hybrid technique. Med Dosim 44:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meddos.2018.09.003
Bedford JL, Smyth G, Hanson IM et al (2016) Quality of treatment plans and accuracy of in vivo portal dosimetry in hybrid intensity-modulated radiation therapy and volumetric modulated arc therapy for prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol 120:320–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2016.07.004
Berger T, Seppenwoolde Y, Pötter R et al (2019) Importance of technique, target selection, contouring, dose prescription, and dose-planning in external beam radiation therapy for cervical cancer: evolution of practice from EMBRACE-I to II. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 104:885–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.03.020
Bhatla N, Berek JS, Cuello M et al (2019) Revised FIGO staging for carcinoma of the cervix uteri. Int J Gynecol Obstet 145:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.12749
Bucci MK, Bevan A, Roach M (2005) Advances in radiation therapy: conventional to 3D, to IMRT, to 4D, and beyond. CA Cancer J Clin 55:117–134. https://doi.org/10.3322/canjclin.55.2.117
Chang Y, Yang ZY, Li GL et al (2016) Correlations between radiation dose in bone marrow and hematological toxicity in patients with cervical cancer: a comparison of 3DCRT, IMRT, and RapidARC. Int J Gynecol Cancer 26:770–776. https://doi.org/10.1097/IGC.0000000000000660
Deng X, Han C, Chen S et al (2017) Dosimetric benefits of intensity-modulated radiotherapy and volumetric-modulated arc therapy in the treatment of postoperative cervical cancer patients. J Appl Clin Med Phys 18:25–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12003
Earl M, Shepard D, Yu X (2007) United States Patent Earl et al. Patent No.: US 7162008 B2. 1–3
Fung AYC, Enke CA, Ayyangar KM et al (2005) Effects of field parameters on IMRT plan quality for gynecological cancer: a case study. J Appl Clin Med Phys 6:46–62. https://doi.org/10.1120/jacmp.v6i3.2087
Guckenberger M, Richter A, Krieger T et al (2009) Is a single arc sufficient in volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for complex-shaped target volumes? Radiother Oncol 93:259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2009.08.015
Guy JB, Falk AT, Auberdiac P et al (2016) Dosimetric study of volumetric arc modulation with RapidArc and intensity-modulated radiotherapy in patients with cervical cancer and comparison with 3-dimensional conformal technique for definitive radiotherapy in patients with cervical cancer. Med Dosim 41:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meddos.2015.06.002
Hall EJ (2006) Intensity-modulated radiation therapy, protons, and the risk of second cancers. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.01.027
Huang B, Fang Z, Huang Y et al (2014) A dosimetric analysis of volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy with jaw width restriction vs 7 field intensity-modulated radiotherapy for definitive treatment of cervical cancer. Br J Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20140183
Jin X, Ph D, Yi J et al (2013) Medical dosimetry comparison of whole-field simultaneous integrated boost VMAT and IMRT in the treatment of nasopharyngeal cancer. Med Dosim 38:418–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meddos.2013.05.004
Korreman S, Rasch C, McNair H et al (2010) The European Society of Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology-European Institute of Radiotherapy (ESTRO-EIR) report on 3D CT-based in-room image guidance systems: a practical and technical review and guide. Radiother Oncol 94:129–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2010.01.004
Laughlin JS, Mohan R, Kutcher GJ (1986) Choice of optimum megavoltage for accelerators for photon beam treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 12:1551–1557. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-3016(86)90277-4
Lesnock JL, Farris C, Beriwal S, Krivak TC (2013) Upfront treatment of locally advanced cervical cancer with intensity modulated radiation therapy compared to four-field radiation therapy: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Gynecol Oncol 129:574–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2013.02.012
Lin JF, Yeh DC, Yeh HL et al (2015) Dosimetric comparison of hybrid volumetric-modulated arc therapy, volumetric-modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiation therapy for left-sided early breast cancer. Med Dosim 40:262–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meddos.2015.05.003
Matuszak MM, Steers JM, Long T et al (2013) FusionArc optimization: a hybrid volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) and intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) planning strategy. Med Phys. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4808153
Morris M, Eifel PJ, Lu J et al (1999) Pelvic radiation with concurrent chemotherapy compared with pelvic and para-aortic radiation for high-risk cervical cancer. N Engl J Med 340:1137–1143. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199904153401501
Otto K (2008) Volumetric modulated arc therapy: IMRT in a single gantry arc. Med Phys 35:310–317. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.2818738
Pirzkall A, Mark C, Pickett B et al (2002) The effect of beam energy and number of fields on photon-based IMRT for deep-seated targets. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:434–442
Popple R, Fiveash J, Brezovich I, Bonner J (2010) RapidArc radiation therapy: first year experience at the university of Alabama at Birmingham. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:932–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.09.001
Pötter R, Tanderup K, Kirisits C et al (2018) The EMBRACE II study: the outcome and prospect of two decades of evolution within the GEC-ESTRO GYN working group and the EMBRACE studies. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol 9:48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctro.2018.01.001
Quan EM, Li X, Li Y et al (2012) A comprehensive comparison of IMRT and VMAT plan quality for prostate cancer treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:1169–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.09.015
Randall ME, Ibbott GS (2006) Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for gynecologic cancers: pitfalls, hazards, and cautions to be considered. Semin Radiat Oncol 16:138–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semradonc.2006.02.002
Robar JL, Thomas C (2012) Medical dosimetry HybridArc: a novel radiation therapy technique combining optimized dynamic arcs and intensity modulation. Med Dosim 37:358–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meddos.2012.02.001
Roeske JC, Lujan A, Rotmensch J et al (2000) Intensity-modulated whole pelvic radiation therapy in patients with gynecologic malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 48:1613–1621. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3016(00)00771-9
Sharfo AWM, Voet PWJ, Breedveld S et al (2015) Comparison of VMAT and IMRT strategies for cervical cancer patients using automated planning. Radiother Oncol 114:395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2015.02.006
Teoh M, Clark CH, Wood K et al (2011) Volumetric modulated arc therapy: a review of current literature and clinical use in practice. Br J Radiol 84:967–996. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/22373346
Ugurlu BT, Temelli O (2020) The impact of the field width on VMAT plan quality and the assessment of half field method. J Appl Clin Med Phys 21:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1002/acm2.12834
Vaccarella S, Laversanne M, Ferlay J, Bray F (2017) Cervical cancer in Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean and Asia: regional inequalities and changing trends. Int J Cancer 141:1997–2001. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.30901
Van Rij CM, Oughlane-Heemsbergen WD, Ackerstaff AH et al (2008) Parotid gland sparing IMRT for head and neck cancer improves xerostomia related quality of life. Radiat Oncol 3:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-3-41
Verbakel WFAR, Cuijpers JP, Hoffmans D et al (2009) Volumetric intensity-modulated arc therapy vs. conventional IMRT in head-and-neck cancer: a comparative planning and dosimetric study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.12.033
Wu Y, Zhu B, Han J et al (2019) A comparative dosimetric study of cervical cancer patients with para-aortic lymph node metastasis treated with volumetric modulated arc therapy vs. 9-field intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Ann Transl Med 7:675. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.10.53
Yin L, Wu H, Gong J et al (2012) Volumetric-modulated arc therapy vs c-IMRT in esophageal cancer: a treatment planning comparison. World J Gastroenterol 18:5266–5275. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i37.5266
Zhao N, Yang R, Jiang Y et al (2015a) A hybrid IMRT/VMAT technique for the treatment of nasopharyngeal cancer. Biomed Res Int 2015:1–8
Zhao N, Yang R, Wang J et al (2015b) An IMRT/VMAT technique for non-small cell lung cancer. BioMed Res Int 2015:1–8
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Radiotherapy Department (medical physicists, radiation oncologists, dosimetrists, radiation therapists, nurses and administrative personnel) of IMSS-UMAE Mérida for their work and invaluable collaboration.
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This research work complies with the considerations issued in the Nuremberg Code, the Declaration of Helsinki promulgated in 1964 and its various modifications, including the update of Fortaleza, Brazil in 2013, as well as the international guidelines for medical research with human beings adopted by WHO and the Council for International Organizations for Research with Human Beings; In Mexico, it complies with the provisions of the General Health Law and the INAI (Instituto Nacional de Transparencia, Acceso a la Información y Protección de Datos Personales) on Research for Health and Protection of Personal Data, respectively.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martín-Tovar, E.A., Badillo-Alvarado, A.H. & Cocom-Poot, L.E. Dosimetric study of a hybrid plan technique for external beam radiotherapy in patients with cervical cancer. Radiat Environ Biophys 60, 653–662 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-021-00931-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-021-00931-9