Abstract
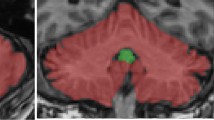
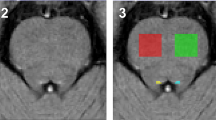
The pilot study aimed at examining the neural glutamatergic activity in autism. Seven adolescent males (mean age: 14 ± 1.8; age range: 12–17 years) with intact intellectual capacity (mean IQ: 108 ± 14.26; IQ range: 85–127) suffering from autistic disorder and an equal number of age- and sex-matched healthy controls underwent a two-dimensional magnetic resonance spectroscopy scan at 4T. Results indicated significantly high glutamate (Glu) levels in the anterior cingulate cortex of autistic disorder versus control subjects (paired t test p = 0.01) and a trend for lower Glu in the right medial temporal lobe, which was not statistically different between the groups (paired t test p = 0.06). These preliminary findings support the glutamatergic dysregulation hypothesis in autism and need to be replicated in a larger sample.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aylward EH, Minshew NJ, Goldstein G, Honeycutt NA, Augustine AM, Yates KO, Barta PE, Pearlson GD (1999) MRI volumes of amygdala and hippocampus in non-mentally retarded autistic adolescents and adults. Neurology 53:2145–2150
Bernardi S, Anagnostou E, Shen J, Kolevzon A, Buxbaum JD, Hollander E, Hof PR, Fan J (2011) In vivo 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of the attentional networks in autism. Brain Res 1380:198–205
Block W, Traber F, von Widdern O, Metten M, Schild H, Maier W, Zobel A, Jessen F (2009) Proton MR spectroscopy of the hippocampus at 3 T in patients with unipolar major depressive disorder: correlates and predictors of treatment response. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:415–422
Boddaert N, Chabane N, Gervais H, Good CD, Bourgeois M, Plumet MH, Barthelemy C, Mouren MC, Artiges E, Samson Y, Brunelle F, Frackowiak RS, Zilbovicius M (2004) Superior temporal sulcus anatomical abnormalities in childhood autism: a voxel-based morphometry MRI study. Neuroimage 23:364–369
Constantino JN (2002) The social responsiveness scale. Western Psychological Services, Los Angeles
DeVito TJ, Drost DJ, Neufeld RW, Rajakumar N, Pavlosky W, Williamson P, Nicolson R (2007) Evidence for cortical dysfunction in autism: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging study. Biol Psychiatry 61:465–473
Fatemi SH, Halt AR, Stary JM, Kanodia R, Schulz SC, Realmuto GR (2002) Glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 and 67 kDa proteins are reduced in autistic parietal and cerebellar cortices. Biol Psychiatry 52:805–810
Friedman SD, Shaw DW, Artru AA, Dawson G, Petropoulos H, Dager SR (2006) Gray and white matter brain chemistry in young children with autism. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:786–794
Friedman SD, Shaw DW, Artru AA, Richards TL, Gardner J, Dawson G, Posse S, Dager SR (2003) Regional brain chemical alterations in young children with autism spectrum disorder. Neurology 60:100–107
Golembiowska K, Zylewska A (1999) Effect of antidepressant drugs on veratridine-evoked glutamate and aspartate release in rat prefrontal cortex. Pol J Pharmacol 51:63–70
Golembiowska K, Dziubina A (2000) Effect of acute and chronic administration of citalopram on glutamate and aspartate release in the rat prefrontal cortex. Pol J Pharmacol 52:441–448
Gonenc A, Govind V, Sheriff S, Maudsley AA (2010) Comparison of spectral fitting methods for overlapping J-coupled metabolite resonances. Magn Reson Med 64:623–628
Goto N, Yoshimura R, Kakeda S, Nishimura J, Moriya J, Hayashi K, Katsuki A, Hori H, Umene-Nakano W, Ikenouchi-Sugita A, Korgoi Y, Nakamura J (2012) Six-month treatment with atypical antipsychotic drugs decreased frontal-lobe levels of glutamate plus glutamine in early-stage first-episode schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 8:119–122
Govindaraju V, Young K, Maudsley AA (2000) Proton NMR chemical shifts and coupling constants for brain metabolites. NMR Biomed 13:129–153
Gruber O, Hasan A, Scherk H, Wobrock T, Schneider-Axmann T, Ekawardhani S et al (2012) Association of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor val66met polymorphism with magnetic resonance spectroscopic markers in the human hippocampus: in vivo evidence for effects on the glutamate system. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 262:23–31
Harada M, Taki MM, Nose A, Kubo H, Mori K, Nishitani H, Matsuda T (2011) Non-invasive evaluation of the GABAergic/glutamatergic system in autistic patients observed by MEGA-editing proton MR spectroscopy using a clinical 3 tesla instrument. J Autism Dev Disord 41:447–454
Haznedar MM, Buchsbaum MS, Metyger M, Solimando A, Spiegel-Cohen J, Hollander E (1997) Anterior cingulate gyrus volume and glucose metabolism in autistic disorder. Am J Psychiatry 154:158
Henry ME, Lauriat TL, Shanahan M, Renshaw PF, Jensen JE (2010) Accuracy and stability of measuring GABA, glutamate, and glutamine by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a phantom study at 4Tesla. J Magn Reson 208:210–218
Jamain S, Betancur C, Quach H, Philippe A, Fellous M, Giros B, Gillberg C, Leboyer M, Bourgeron T (2002) Linkage and association of the glutamate receptor 6 gene with autism. Mol Psychiatry 7:302–310
Jensen JE, Licata SC, Ongur D, Friedman SD, Prescot AP, Henry ME, Renshaw PF (2009) Quantification of J-resolved proton spectra in two-dimensions with LCModel using GAMMA-simulated basis sets at 4 Tesla. NMR Biomed 22:762–769
Kemper TL, Bauman M (1998) Neuropathology of infantile autism. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57:645–652
Lappalainen R, Riikonen RS (1996) High levels of cerebrospinal fluid glutamate in Rett syndrome. Pediatr Neurol 15:213–216
McDougle CJ (2002) Current and emerging therapeutics of autistic disorder and related pervasive developmental disorders. In: Davis KL, Charney D, Coyle JT et al (eds) Psychopharmacology: the fifth generation of progress. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Moore CM, Frazier JA, Glod CA, Breeze JL, Dieterich M, Finn CT, Frederick B, Renshaw PF (2007) Glutamine and glutamate levels in children and adolescents with bipolar disorder: a 4.0-T proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of the anterior cingulate cortex. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 46:524–534
Musazzi L, Milanese M, Farisello P, Zappettini S, Tardito D, Barbiero VS, Bonifacino T, Mallei A, Baldelli P, Racagni G, Raiteri M, Benfenati F, Bonanno G, Popoli M (2010) Acute stress increases depolarization-evoked glutamate release in the rat prefrontal/frontal cortex: the dampening action of antidepressants. PLoS ONE 5:e8566
Ohnishi T, Matsuda H, Hashimoto T, Kunihiro T, Nishikawa M, Uema T, Sasaki M (2000) Abnormal regional cerebral blood flow in childhood autism. Brain 123(Pt 9):1838–1844
Page LA, Daly E, Schmitz N, Simmons A, Toal F, Deeley Q, Ambery F, McAlonan GM, Murphy KC, Murphy DG (2006) In vivo 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of amygdala-hippocampal and parietal regions in autism. Am J Psychiatry 163:2189–2192
Purcell S, Sham P (2002) Variance components models for gene-environment interaction in quantitative trait locus linkage analysis. Twin Res 5:572–576
Schultz RT, Gauthier I, Klin A, Fulbright RK, Anderson AW, Volkmar F, Skudlarski P, Lacadie C, Cohen DJ, Gore JC (2000) Abnormal ventral temporal cortical activity during face discrimination among individuals with autism and Asperger syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:331–340
Serajee FJ, Zhong H, Nabi R, Huq AH (2003) The metabotropic glutamate receptor 8 gene at 7q31: partial duplication and possible association with autism. J Med Genet 40:e42
Silk TJ, Rinehart N, Bradshaw JL, Tonge B, Egan G, O’Boyle MW, Cunnington R (2006) Visuospatial processing and the function of prefrontal-parietal networks in autism spectrum disorders: a functional MRI study. Am J Psychiatry 163:1440–1443
Smith SA, Levante TO, Meier BH, Ernst RR (1994) Computer simulations in magnetic resonance. An object-oriented programming approach. J Magn Reson A 106:75–105
Sweeten TL, Posey DJ, Shekhar A, McDougle CJ (2002) The amygdala and related structures in the pathophysiology of autism. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:449–455
Tarazi FI, Baldessarini RJ, Kula NS, Zhang K (2003) Long-term effects of olanzapine, risperidone, and quetiapine on ionotropic glutamate receptor types: implications for antipsychotic drug treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:1145–1151
Wechsler D (1999) Wechsler abbreviated scale of intelligence (WASI). The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Pediatric Psychopharmacology Council Fund and the Norma Fine Pediatric Psychopharmacology Fellowship Fund.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshi, G., Biederman, J., Wozniak, J. et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of the glutamatergic system in adolescent males with high-functioning autistic disorder: a pilot study at 4T. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 263, 379–384 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-012-0369-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-012-0369-9