Abstract
Purpose
To clarify the association between the 4G/5G polymorphism of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL).
Methods
A systematic literature search of related studies up to August 30, 2019 in the PubMed and Embase databases was performed, and the results were displayed by odds ratios (ORs), and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were assessed using the STATA12.0 software using an allele model and a recessive model.
Results
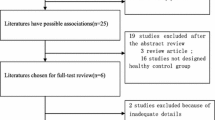
Three eligible studies covering 519 subjects (241 cases, 278 controls) were identified. No statistically significant association was detected between the 4G/5G polymorphism and SSNHL in any model (allele model: 5G vs. 4G, OR = 0.952, 95% CI = 0.765–1.185, P = 0.662; recessive model: 5G/5G vs. 4G/5G + 4G/4G, OR = 0.841, 95% CI = 0.415–1.704, P = 0.631).
Conclusions
There is no statistically significant association between the 4G/5G polymorphism of PAI-1 gene and SSNHL in the Caucasian population, and well-designed studies covering more patients and institutions should be conducted.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data are fully available without restriction.
References
Stachler RJ, Chandrasekhar SS, Archer SM, Rosenfeld RM, Schwartz SR, Barrs DM, Brown SR, Fife TD, Ford P, Ganiats TG, Hollingsworth DB, Lewandowski CA, Montano JJ, Saunders JE, Tucci DL, Valente M, Warren BE, Yaremchuk KL, Robertson PJ, American Academy of O-H, Neck S (2012) Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146(3 Suppl):S1–35. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599812436449
Alexander TH, Harris JP (2013) Incidence of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J Otol Neurotol 34(9):1586–1589
Shaia FT, Sheehy JL (2010) Sudden sensorineural hearing impairment: a report of 1,220 cases. The Laryngoscope 86(3):389–398
Chiossoine-Kerdel JA, Baguley DM, Stoddart RL, Moffat DA (2000) An investigation of the audiologic handicap associated with unilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am J Otol 21(5):645–651
Chau JK, Lin JRJ, Atashband S, Irvine RA, Westerberg BD (2010) Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. The Laryngoscope 120(5):1011–1021. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.20873
Einer H, Tengborn L, Axelsson A, Edstrom S (1994) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss and hemostatic mechanisms. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 120(5):536–540. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1994.01880290046008
Penido NDO, Ramos HVL, Barros FA, Cruz OLM, Toledo RN (2005) Clinical, etiological and progression factors of hearing in sudden deafness. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 71(5):633–638
Salahaldin AH, Bener A, ElHakeem AA, Abdulhadi K (2004) Management of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: experience in newly developing Qatar. Int Tinnitus J 10(2):165–169
Ramesh NZ, Stig A, Elisabeth H (2007) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: results drawn from the Swedish national database. Acta Otolaryngol 127(11):1168
Fetterman BL, Luxford WM, Saunders JE (2010) Sudden bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. The Laryngoscope 106(11):1347–1350
Pasquale C, Francesco O, Valeria C, Alessandro B, Antonio S, Bruno Mario C, Salvatore C, Lorenzo P (2010) Genetic and acquired prothrombotic risk factors and sudden hearing loss. The Laryngoscope 117(3):547–551
Gabriella C, Stefania A, Simona S, Silvia I, Andrea C, Raffaella M, Gaetano P (2005) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: our experience in diagnosis, treatment, and outcome. Otolaryngology 34(6):395–401
Jaffe BF (1973) Clinical studies in sudden deafness. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 20:221–228
Capaccio P, Ottaviani F, Cuccarini V, Ambrosetti U, Fagnani E, Bottero A, Cenzuales S, Cesana BM, Pignataro L (2005) Sudden hearing loss and MTHFR 677C>T/1298A>C gene polymorphisms. Genet Med 7(3):206–208. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.gim.0000157817.92509.45
Capaccio P, Ottaviani FV, Ambrosetti U, Fagnani E, Bottero A, Cenzuales S, Cesana BM, Pignataro L (2005) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene mutations as risk factors for sudden hearing loss. Am J Otolaryngol 26(6):383–387
Claudia R, Claus L, Wolfgang S, Stephan R, Michael W (2006) Vascular risk factors in sudden hearing loss. Thromb Haemost 95(03):454–461
Görür K, Tuncer U, Eskandari G, Ozcan C, Unal M, Ozsahinoglu C (2005) The role of factor V Leiden and prothrombin G20210A mutations in sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 26(4):599–601
Nam SI, Ha E, Jung KH, Baik HH, Yoon SH, Park HJ, Choe BK, Chung JH, Seo JC, Mi YL (2006) IL4 receptor polymorphism is associated with increased risk of sudden deafness in Korean population. Life Sci 78(6):664–667
Um JY, Jang CH, Kim KY, Kim SJ, Kim NH, Moon PD, Choi IY, Myung NY, Jeong HJ, Hong SH, Kim HM (2010) Candidate genes of cerebrovascular disease and sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Clin Appl Thrombosis/hemostasis 16(5):559–562. https://doi.org/10.1177/1076029609348313
Jun-Ichi S, Masahito O, Susumu M, Akiko I, Yasunobu H, Mitsuaki I, Ryozo NJEOID (2011) Effects of specific chemical suppressors of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cardiovascular diseases. Expert Opin Investig Drug 20(2):255–264
Vaughan DE, Rai R, Khan SS, Eren M, Ghosh AK (2017) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is a marker and a mediator of senescence. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 37(8):1446–1452. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309451
Marcucci R, Liotta AA, Cellai AP, Rogolino A, Berloco P, Leprini E, Pagnini P, Abbate R, Prisco D (2005) Cardiovascular and thrombophilic risk factors for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J Thromb Haemost 3(5):929–934. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01310.x
Tsantes AE, Nikolopoulos GK, Bagos PG, Bonovas S, Kopterides P, Vaiopoulos G (2008) The effect of the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 4G/5G polymorphism on the thrombotic risk. Thromb Res 122(6):736–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2007.09.005
Vaughan DE, Rai R, Khan SS, Eren M, Ghosh AK (2017) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is a marker and a mediator of senescence. Arteriosclerosis Thromb Vasc Biol 37(8):51
Belal A (1979) The effects of vascular occlusion on the human inner ear. J Laryngol Otol 93:955–968
Belal A (1980) Pathology of vascular sensorineural hearing impairment. J laryngoscope 90(11):1831–1839
Rudack C, Langer C, Junker R (2004) Platelet GPIaC807T polymorphism is associated with negative outcome of sudden hearing loss. Hear Res 191(1–2):41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2004.01.002
Akar N, Yilmaz E, Akar E, Avcu F, Yalçin A, Cin Ş (2000) Effect of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 4G/5G polymorphism in Turkish deep vein thrombotic patients with and without FV1691 G-A. Turk J Haematol 97(4):227–230
Santoso S, Kunicki TJ, Kroll H, Haberbosch W, Gardemann A (1999) Association of the platelet glycoprotein Ia C807T gene polymorphism with nonfatal myocardial infarction in younger patients. Blood 93(8):2449–2453
Akar N, Yilmaz E, Akar E, Avcu F, Yalin A (2000) Effect of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 4G/5G polymorphism in Turkish deep vein thrombotic patients with and without FV1691 G-A. Thromb Res 97:227–230
Cho SH, Chen H, Kim IS, Yokose C, Kang J, Cho D, Cai C, Palma S, Busi M, Martini A, Yoo TJ (2012) Association of the 4 g/5 g polymorphism of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. A case control study. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord 12:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6815-12-5
Yildiz Z, Ulu A, Incesulu A, Ozkaptan Y, Akar N (2008) The importance of thrombotic risk factors in the development of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 14(3):356–359. https://doi.org/10.1177/1076029607306399
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Z., Chang, K. & Fan, C. Association between the 4G/5G polymorphism of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) gene and sudden sensorineural hearing loss in Caucasian population: a meta-analysis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 278, 2203–2208 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06305-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-06305-z