Abstract
Purpose
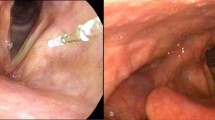
Reinke’s edema is a benign laryngeal condition characterized by swelling of the superficial layer of the lamina propria of the vocal fold. The aim of this work is to propose a new classification of Reinke’s edema based on its morphological characteristics.
Methods
Our classification is a synthesis of the classifications available in the literature and is based on morphological characteristics such as the involvement of one or two vocal folds and the presence or absence of polypoid lesions regardless of the observation method.
Results
We indicate four types of Reinke’s edema: type 1: Reinke’s edema of one vocal fold; type 2: Reinke’s edema of both vocal folds; type 3: Reinke’s edema of one vocal fold with associated polypoid lesion, not necessarily the same fold of the edema; type 4: Reinke’s edema of both vocal folds with associated polypoid lesion on one or both folds.
Conclusion
Our proposed classification for Reinke’s edema represents a synthesis of the classifications available in the literature and is characterized by a simple categorization based on morphological characteristics commonly visible through laryngoscopy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tavaluc R, Tan-Geller M (2019) Reinke’s Edema. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 52(4):627–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2019.03.006
Senior A (2015) Friedrich Berthold Reinke (1862–1919): brilliant yet troubled anatomist of the vocal fold. J Laryngol Otol 129(11):1053–1057. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215115002522
Mayet A (1961) Morphological principles of Reinke's edema of the vocal cords. Arch Ohren Nasen Kehlkopfheilkd 177:160–173
Marcotullio D, Magliulo G, Pezone T (2002) Reinke’s edema and risk factors: clinical and histopathologic aspects. Am J Otolaryngol 23(2):81–84. https://doi.org/10.1053/ajot.2002.30961
Wang JS, Li JR (2016) The role of laryngopharyngeal reflux in the pathogenesis of Reinke's edema. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 30(24):1931–1934. https://doi.org/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2016.24.007
Lechien JR, Saussez S, Nacci A, Barillari MR, Rodriguez A, Le Bon SD, Crevier-Buchman L, Harmegnies B, Finck C, Akst LM (2019) Association between laryngopharyngeal reflux and benign vocal folds lesions: a systematic review. Laryngoscope 129(9):E329–E341. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.27932
Lumpkin SM, Bennett S, Bishop SG (1990) Postsurgical follow-up study of patients with severe polypoid degeneration. Laryngoscope 100(4):399–402. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-199004000-00013
Kravos A, Zupevc A, Cizmarevic B, Hocevar-Boltezar I (2010) The role of allergy in the etiology of Reinke's edema on vocal folds. Wien Klin Wochenschr 122(Suppl 2):44–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-010-1349-6
Lim JY, Choi JN, Kim KM, Choi HS (2006) Voice analysis of patients with diverse types of Reinke's edema and clinical use of electroglottographic measurements. Acta Otolaryngol 126(1):62–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016480510043927
Hantzakos A, Remacle M, Dikkers FG, Degols JC, Delos M, Friedrich G, Giovanni A, Rasmussen N (2009) Exudative lesions of Reinke's space: a terminology proposal. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266(6):869–878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-008-0863-x
Bykova VP, Kochesokova EA, Ivanchenko GF, Rotova ID (2015) The morphology of vocal fold polyps and mucosa in Reinke's edema. Arkh Patol 77(1):30–37. https://doi.org/10.17116/patol201577130-
Vasconcelos D, Gomes AOC, Araujo CMT (2019) Vocal Fold Polyps: Literature Review. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 23(1):116–124. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1675391
Arruda Henry MA, Martins RH, Lerco MM, Carvalho LR, Lamonica-Garcia VC (2011) Gastroesophageal reflux disease and vocal disturbances. Arq Gastroenterol 48(2):98–103. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0004-28032011000200003
Sulica L (2005) Polyps and Reinke's edema: distinct laryngeal pathologies with different potential for glottic airway obstruction. Anesth Analg 100(6):1863–1864. https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ANE.0000156696.28573.FF
Yonekawa H (1988) A clinical study of Reinke's edema. Auris Nasus Larynx 15(1):57–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0385-8146(88)80010-5
Kraft M, Glanz H, Gerlach S, Wisweh H, Lubatschowski H, Arens C (2010) Morphologic classification of Reinke's edema through optical coherence tomography. Laryngorhinootologie 89(4):224–227. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1243169
Tan M, Bryson PC, Pitts C, Woo P, Benninger MS (2017) Clinical grading of Reinke's edema. Laryngoscope 127(10):2310–2313. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.26647
Burduk PK, Wierzchowska M, Orzechowska M, Kazmierczak W, Pawlak-Osinska K (2015) Assessment of voice quality after carbon dioxide laser and microdebrider surgery for Reinke edema. J Voice 29(2):256–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2014.07.016
Salmen T, Ermakova T, Schindler A, Ko SR, Goktas O, Gross M, Nawka T, Caffier PP (2018) Efficacy of microsurgery in Reinke's oedema evaluated by traditional voice assessment integrated with the Vocal Extent Measure (VEM). Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 38(3):194–203. https://doi.org/10.14639/0392-100X-1544
Hirano S (1982) Microsurgery of the larynx. Voice Found 1:1–3
Liang F, Chen R, Lin P, Han P, Cai Q, Huang X (2019) Two-handed tying technique in vocal fold mucosa microsuture for the treatment of Reinke's edema. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276(7):2015–2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05480-y
Yan Y, Olszewski AE, Hoffman MR, Zhuang P, Ford CN, Dailey SH, Jiang JJ (2010) Use of lasers in laryngeal surgery. J Voice 24(1):102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2008.09.006
Khodeir MS, Hassan SM, El Shoubary AM, Saad MNA (2019) Surgical and nonsurgical lines of treatment of Reinke's edema: a systematic literature review. J Voice. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2019.10.016
Hu HC, Lin SY, Hung YT, Chang SY (2017) Feasibility and associated limitations of office-based laryngeal surgery using carbon dioxide lasers. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 143(5):485–491. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2016.4129
Sridharan S, Achlatis S, Ruiz R, Jeswani S, Fang Y, Branski RC, Amin MR (2014) Patient-based outcomes of in-office KTP ablation of vocal fold polyps. Laryngoscope 124(5):1176–1179. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24442
Hess MM, Fleischer S, Ernstberger M (2018) New 445 nm blue laser for laryngeal surgery combines photoangiolytic and cutting properties. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 275(6):1557–1567. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-018-4974-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Vincentiis, M., Ralli, M., Cialente, F. et al. Reinke’s edema: a proposal for a classification based on morphological characteristics. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 277, 2279–2283 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-05934-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-05934-8