Abstract
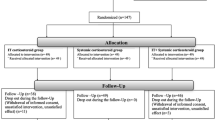
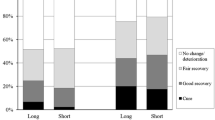
Corticosteroid treatment has been considered the most effective treatment modality for sudden sensorineural hearing loss so far. Application route of corticosteroids may vary. We have designed a prospective randomized case-controlled clinical trial to evaluate the effectivenesses of the different application routes of steroids in the treatment of SSHL. Thirty-five patients were distributed randomly to two groups which were treated with either ‘oral’ or ‘intratympanic’ corticosteroids. Intratympanic steroid administration was performed three times every other day transtympanically. At the end of third month, recovery rate in the ‘intratympanic’ group was 84.2%, whereas in the ‘oral’ group, it was 87.5%. The difference between the recovery rates was not statistically significant. There were no major complications related to transtympanic steroid administration. These findings support that intratympanic steroid therapy is an alternative to systemic steroid therapy in the initial treatment of sudden hearing loss. In addition, transtympanic technique is an easy to perform and safe method for delivering steroids into the inner ear.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fetterman BL, Saunders JE, Luxford WM (1996) Prognosis and treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Am J Otol 17:529–536
Süslü N, Yilmaz T, Gürsel B (2009) Utility of anti-HSP 70, TNF-alpha, ESR, antinuclear antibody, and antiphospholipid antibodies in the diagnosis and treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 119:341–346
Mattox DE, Simmons FB (1997) Natural history of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 86:463–480
Wilson WR, Byl FM, Laird N (1980) The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss: a double-blind clinical study. Arch Otolaryngol 106:772–776
Chen CY, Halpin C, Rauch SD (2003) Oral steroid treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a ten year retrospective analysis. Otol Neurotol 24:728–733
Conlin AE, Parnes LS (2007) Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss, II: a meta-analysis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:582–586
Chandrasekhar SS (2001) Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: clinical and laboratory evaluation. Otol Neurotol 22:18–23
Sennaroglu L, Dini FM, Sennaroglu G, Gursel B, Ozkan S (1999) Transtympanic dexamethasone application in Ménière’s disease: an alternative treatment for intractable vertigo. J Larngol Otol 113:217–221
Swan EE, Mescher MJ, Sewell WF, Tao SL, Borenstein JT (2008) Inner ear drug delivery for auditory applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60:1583–1599
Xenellis J, Papadimitriou N, Nikolopoulos T et al (2006) Intratympanic steroid treatment in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a control study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 134:940–945
Ho HG, Lin HC, Shu MT, Yang CC, Tsai HT (2004) Effectiveness of intratympanic dexamethasone injection in sudden-deafness patients as salvage treatment. Laryngoscope 114:1184–1189
Gouveris H, Schuler-Schmidt W, Mewes T, Mann W (2011) Intratympanic dexamethasone/hyaluronic acid mix as an adjunct to intravenous steroid and vasoactive treatment in patients with severe idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 32:756–760
Stachler RJ, Chandrasekhar SS, Archer SM, Rosenfeld RM, Schwartz SR, Barrs DM, Brown SR, Fife TD, Ford P, Ganiats TG, Hollingsworth DB, Lewandowski CA, Montano JJ, Saunders JE, Tucci DL, Valente M, Warren BE, Yaremchuk KL, Robertson PJ (2012) Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146:1–35
Dallan I, Bruschini L, Nacci A et al (2006) Transtympanic steroids as a salvage therapy in sudden hearing loss: preliminary results. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 68:247–252
Hong SM, Park CH, Lee JH (2009) Hearing outcomes of daily intratympanic dexamethasone alone as a primary treatment modality for ISSHL. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 141:579–583
Rauch SD, Halpin CF, Antonelli PJ, Babu S, Carey JP, Gantz BJ, Goebel JA, Hammerschlag PE, Harris JP, Isaacson B, Lee D, Linstrom CJ, Parnes LS, Shi H, Slattery WH, Telian SA, Vrabec JT, Reda DJ (2011) Oral vs intratympanic corticosteroid therapy for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomized trial. JAMA 305:2071–2079
Han CS, Park JR, Boo SH, Jo JM, Park KW, Lee WY, Ahn JG, Kang MK, Park BG, Lee H (2009) Clinical efficacy of initial intratympanic steroid treatment on sudden sensorineural hearing loss with diabetes. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 141:572–578
Kara E, Cetik F, Tarkan O, Sürmelioğlu O (2010) Modified intratympanic treatment for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 267:701–707
Filipo R, Covelli E, Balsamo G, Attanasio G (2010) Intratympanic prednisolone therapy for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a new protocol. Acta Otolaryngol 130:1209–1213
Kakehata S, Sasaki A, Oji K et al (2006) Comparison of intratympanic and intravenous dexamethasone treatment on sudden sensorineural hearing loss with diabetes. Otol Neurotol 27:604–608
Battista RA (2005) Intratympanic dexamethasone for profound idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:902–905
Battaglia A, Burchette R, Cueva R (2008) Combination therapy (intratympanic dexamethasone + high-dose prednisone taper) for the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 29:453–460
She W, Dai Y, Du X, Yu C, Chen F, Wang J, Qin X (2010) Hearing evaluation of intratympanic methylprednisolone perfusion for refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 142:266–271
Cureoglu S, Schachern PA, Rinaldo A, Tsuprun V, Ferlito A, Paparella MM (2005) Round window membrane and labyrinthine pathological changes: an overview. Acta Otolaryngol 125:9–15
Haynes DS, O’Malley M, Cohen S, Watford K, Labadie RF (2007) Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy. Laryngoscope 117:3–15
Arslan N, Oğuz H, Demirci M, Şafak MA, İslam A, Kaytez SK, Samim E (2011) Combined intratympanic and systemic use of steroids for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otol Neurotol 32:393–397
Wu HP, Chou YF, Yu SH, Wang CP, Hsu CJ, Chen PR (2011) Intratympanic steroid injections as a salvage treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Otol Neurotol 32:774–779
Hamid M, Trune D (2008) Issues, indications, and controversies regarding intratympanic steroid perfusion. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 16:434–440
Spear SA, Schwartz SR (2011) Intratympanic steroids for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 145:534–543
Yeo SW, Lee DH, Jun BC, Park SY, Park YS (2007) Hearing outcome of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: long-term follow-up. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136:221–224
Labus J, Breil J, Stutzer H, Michel O (2010) Meta-analysis for the effect of medical therapy vs. placebo on recovery of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. Laryngoscope 120:1863–1871
Stokroos RJ, Albers FW, Tenvergert EM (1998) Antiviral treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a prospective, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Acta Otolaryngol 118:488–495
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ermutlu, G., Süslü, N., Yılmaz, T. et al. Sudden hearing loss: an effectivity comparison of intratympanic and systemic steroid treatments. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 3585–3591 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4691-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4691-8