Abstract
Purpose
Galectin-3 is a Mr 31,000 protein that belongs to a family of carbohydrate-binding proteins. Galectin-3 has already been associated with protection against apoptosis through cell to cell or cell to matrix adhesion processes. It seems that galectin-3 plays an important role in tumor progression, cell growth, invasion and metastasis. Galectin-3 is the only member of the chimeric galectins that has an N-terminal glycine and proline domain and a C-terminal carbohydrate recognition domain that allows galectin-3 to accommodate larger structures such us polylactosaminoglycans and intervene to DNA damage repair process. In this systematic review, our primary goal is to identify the effect of galectin-3 expression in association with drug resistance and apoptosis inhibition in breast cancer.
Materials and methods
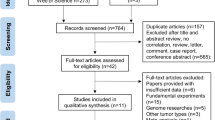
Scopus and PubMed databases were searched on 26 November 2018 using the following combination of keywords: (galectin-3 OR gal-3 OR LGALS3) AND (breast cancer) AND (chemoresistance OR (drug resistance) OR chemosensitivity). All the articles in English, regardless the time of publication, text availability and species included were initially accepted.
Results
In the majority of the included studies, the expression of galectin-3 had a protective role in cell survival via different pathways such as the response to DNA damage and repair or the inhibition of apoptosis after treatment with a chemotherapeutic agent.
Conclusion
Galectin-3 expression in breast tumors might be an important factor in the selection of the most suitable treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu FT, Rabinovich GA (2005) Galectins as modulators of tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 5(1):29–41
Barondes SH, Castronovo V, Cooper DN, Cummings RD, Drickamer K, Feizi T et al (1994) Galectins: a family of animal beta-galactoside-binding lectins. Cell 76(4):597–598
Takenaka Y, Fukumori T, Raz A (2002) Galectin-3 and metastasis. Glycoconj J 19(7–9):543–549
Yang RY, Liu FT (2003) Galectins in cell growth and apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 60(2):267–276
Kim HR, Lin HM, Biliran H, Raz A (1999) Cell cycle arrest and inhibition of anoikis by galectin-3 in human breast epithelial cells. Cancer Res 59(16):4148–4154
Akahani S, Nangia-Makker P, Inohara H, Kim HR, Raz A (1997) Galectin-3: a novel antiapoptotic molecule with a functional BH1 (NWGR) domain of Bcl-2 family. Cancer Res 57(23):5272–5276
Hughes RC (2001) Galectins as modulators of cell adhesion. Biochimie 83(7):667–676
Lord CJ, Ashworth A (2012) The DNA damage response and cancer therapy. Nature 481(7381):287–294
Knibbs RN, Agrwal N, Wang JL, Goldstein IJ (1993) Carbohydrate-binding protein 35. II. Analysis of the interaction of the recombinant polypeptide with saccharides. J Biol Chem 268(20):14940–14947
Dumic J, Dabelic S, Flogel M (2006) Galectin-3: an open-ended story. Biochim Biophys Acta 1760(4):616–635
Gillenwater A, Xu XC, el-Naggar AK, Clayman GL, Lotan R (1996) Expression of galectins in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 18(5):422–432
Tsuboi K, Shimura T, Masuda N, Ide M, Tsutsumi S, Yamaguchi S et al (2007) Galectin-3 expression in colorectal cancer: relation to invasion and metastasis. Anticancer Res 27(4B):2289–2296
Turkoz HK, Oksuz H, Yurdakul Z, Ozcan D (2008) Galectin-3 expression in tumor progression and metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocr Pathol 19(2):92–96
Kim SJ, Shin JY, Cheong TC, Choi IJ, Lee YS, Park SH et al (2011) Galectin-3 germline variant at position 191 enhances nuclear accumulation and activation of beta-catenin in gastric cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 28(8):743–750
Chen YR, Juan HF, Huang HC, Huang HH, Lee YJ, Liao MY et al (2006) Quantitative proteomic and genomic profiling reveals metastasis-related protein expression patterns in gastric cancer cells. J Proteome Res 5(10):2727–2742
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424
Honjo Y, Nangia-Makker P, Inohara H, Raz A (2001) Down-regulation of galectin-3 suppresses tumorigenicity of human breast carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 7(3):661–668
Song YK, Billiar TR, Lee YJ (2002) Role of galectin-3 in breast cancer metastasis: involvement of nitric oxide. Am J Pathol 160(3):1069–1075
Cory S, Adams JM (2002) The Bcl2 family: regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer 2(9):647–656
Boya P, Morales MC, Gonzalez-Polo RA, Andreau K, Gourdier I, Perfettini JL et al (2003) The chemopreventive agent N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide induces apoptosis through a mitochondrial pathway regulated by proteins from the Bcl-2 family. Oncogene 22(40):6220–6230
Moon BK, Lee YJ, Battle P, Jessup JM, Raz A, Kim HR (2001) Galectin-3 protects human breast carcinoma cells against nitric oxide-induced apoptosis: implication of galectin-3 function during metastasis. Am J Pathol 159(3):1055–1060
Koo JS, Jung W (2011) Clinicopathlogic and immunohistochemical characteristics of triple negative invasive lobular carcinoma. Yonsei Med J 52(1):89–97
Cheong TC, Shin JY, Chun KH (2010) Silencing of galectin-3 changes the gene expression and augments the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Sci 101(1):94–102
Mazurek N, Byrd JC, Sun Y, Ueno S, Bresalier RS (2011) A galectin-3 sequence polymorphism confers TRAIL sensitivity to human breast cancer cells. Cancer 117(19):4375–4380
Zhang H, Luo M, Liang X, Wang D, Gu X, Duan C et al (2014) Galectin-3 as a marker and potential therapeutic target in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 9(9):e103482
Carvalho RS, Fernandes VC, Nepomuceno TC, Rodrigues DC, Woods NT, Suarez-Kurtz G et al (2014) Characterization of LGALS3 (galectin-3) as a player in DNA damage response. Cancer Biol Ther 15(7):840–850
Choi JH, Chun KH, Raz A, Lotan R (2004) Inhibition of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells by galectin-3. Cancer Biol Ther 3(5):447–452
Wang Y, Nangia-Makker P, Balan V, Hogan V, Raz A (2010) Calpain activation through galectin-3 inhibition sensitizes prostate cancer cells to cisplatin treatment. Cell Death Dis 1:e101
Oishi T, Itamochi H, Kigawa J, Kanamori Y, Shimada M, Takahashi M et al (2007) Galectin-3 may contribute to Cisplatin resistance in clear cell carcinoma of the ovary. Int J Gynecol Cancer 17(5):1040–1046
Mazurek N, Sun YJ, Liu KF, Gilcrease MZ, Schober W, Nangia-Makker P et al (2007) Phosphorylated galectin-3 mediates tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand signaling by regulating phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 in human breast carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 282(29):21337–21348
Balan V, Nangia-Makker P, Schwartz AG, Jung YS, Tait L, Hogan V et al (2008) Racial disparity in breast cancer and functional germ line mutation in galectin-3 (rs4644): a pilot study. Cancer Res 68(24):10045–10050
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM (1998) Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281(5381):1305–1308
Cretney E, Takeda K, Smyth MJ (2007) Cancer: novel therapeutic strategies that exploit the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)/TRAIL receptor pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39(2):280–286
Baj G, Arnulfo A, Deaglio S, Mallone R, Vigone A, De Cesaris MG et al (2002) Arsenic trioxide and breast cancer: analysis of the apoptotic, differentiative and immunomodulatory effects. Breast Cancer Res Treat 73(1):61–73
Lo-Coco F, Avvisati G, Vignetti M, Thiede C, Orlando SM, Iacobelli S et al (2013) Retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide for acute promyelocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 369(2):111–121
Dilda PJ, Hogg PJ (2007) Arsenical-based cancer drugs. Cancer Treat Rev 33(6):542–564
Chen Z, Chen GQ, Shen ZX, Sun GL, Tong JH, Wang ZY et al (2002) Expanding the use of arsenic trioxide: leukemias and beyond. Semin Hematol 39(2 Suppl 1):22–26
Berenson JR, Yeh HS (2006) Arsenic compounds in the treatment of multiple myeloma: a new role for a historical remedy. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma 7(3):192–198
Poehlmann A, Roessner A (2010) Importance of DNA damage checkpoints in the pathogenesis of human cancers. Pathol Res Pract 206(9):591–601
Yarden RI, Pardo-Reoyo S, Sgagias M, Cowan KH, Brody LC (2002) BRCA1 regulates the G2/M checkpoint by activating Chk1 kinase upon DNA damage. Nat Genet 30(3):285–289
Tembe V, Henderson BR (2007) BARD1 translocation to mitochondria correlates with Bax oligomerization, loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 282(28):20513–20522
Yu F, Finley RL Jr, Raz A, Kim HR (2002) Galectin-3 translocates to the perinuclear membranes and inhibits cytochrome c release from the mitochondria. A role for synexin in galectin-3 translocation. J Biol Chem 277(18):15819–15827
Oridate N, Lotan D, Xu XC, Hong WK, Lotan R (1996) Differential induction of apoptosis by all-trans-retinoic acid and N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 2(5):855–863
Zou CP, Kurie JM, Lotan D, Zou CC, Hong WK, Lotan R (1998) Higher potency of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide than all-trans-retinoic acid in induction of apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 4(5):1345–1355
Zou C, Liebert M, Zou C, Grossman HB, Lotan R (2001) Identification of effective retinoids for inhibiting growth and inducing apoptosis in bladder cancer cells. J Urol 165(3):986–992
Maurer BJ, Metelitsa LS, Seeger RC, Cabot MC, Reynolds CP (1999) Increase of ceramide and induction of mixed apoptosis/necrosis by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)—retinamide in neuroblastoma cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst 91(13):1138–1146
Sun SY, Yue P, Lotan R (1999) Induction of apoptosis by N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide and its association with reactive oxygen species, nuclear retinoic acid receptors, and apoptosis-related genes in human prostate carcinoma cells. Mol Pharmacol 55(3):403–410
Delia D, Aiello A, Lombardi L, Pelicci PG, Grignani F, Grignani F et al (1993) N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide induces apoptosis of malignant hemopoietic cell lines including those unresponsive to retinoic acid. Cancer Res 53(24):6036–6041
De Palo G, Mariani L, Camerini T, Marubini E, Formelli F, Pasini B et al (2002) Effect of fenretinide on ovarian carcinoma occurrence. Gynecol Oncol 86(1):24–27
Wang TT, Phang JM (1996) Effect of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide on apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett 107(1):65–71
Matarrese P, Tinari N, Semeraro ML, Natoli C, Iacobelli S, Malorni W (2000) Galectin-3 overexpression protects from cell damage and death by influencing mitochondrial homeostasis. FEBS Lett 473(3):311–315
Zhou LJ, Zhu XZ (2000) Reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells and protective effect of bilobalide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293(3):982–988
Lu HF, Hsueh SC, Ho YT, Kao MC, Yang JS, Chiu TH et al (2007) ROS mediates baicalin-induced apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells through the expression of the Gadd153 and mitochondrial-dependent pathway. Anticancer Res 27(1A):117–125
Hail N Jr, Lotan R (2001) Mitochondrial respiration is uniquely associated with the prooxidant and apoptotic effects of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide. J Biol Chem 276(49):45614–45621
Funding
No funding has been given for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IB: data collection and manuscript writing; AP: data collection and manuscript writing; WB: data management; AL: data management; AH: data review and manuscript editing; SK: data review and manuscript editing; and MS: project development and manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boutas, I., Potiris, A., Brenner, W. et al. The expression of galectin-3 in breast cancer and its association with chemoresistance: a systematic review of the literature. Arch Gynecol Obstet 300, 1113–1120 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-019-05292-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-019-05292-9